Intro
Discover 5 ways to tackle 105 Fahrenheit temperatures, from heat safety tips to cooling methods, beating the extreme heat with hydration and sun protection strategies.
The temperature of 105 degrees Fahrenheit is a significant milestone, often associated with extreme heat and potential health risks. Understanding the implications and management of such temperatures is crucial for both personal health and environmental awareness. As we delve into the world of temperatures, it's essential to recognize the importance of being informed about heat-related issues, especially during the peak summer months. The impact of high temperatures on human health, the environment, and daily activities cannot be overstated, making it a topic of considerable interest and concern. Whether you're looking to protect yourself from heat strokes, manage your home's cooling system efficiently, or simply understand the science behind temperature, this article aims to provide comprehensive insights and practical advice.
In many parts of the world, temperatures soaring to 105 degrees Fahrenheit are not uncommon, especially in regions with desert climates or during heatwaves. The human body's ability to regulate its temperature is remarkable, but extreme heat poses significant challenges, potentially leading to dehydration, heat exhaustion, and in severe cases, heat strokes. Moreover, high temperatures have profound effects on the environment, including increased evaporation from water bodies, altered ecosystems, and exacerbated climate change. Given these factors, it's crucial to approach the topic with a multifaceted perspective, considering both immediate personal safety and long-term environmental sustainability.
As we explore the world of 105 degrees Fahrenheit, it's also important to recognize the role of technology and innovation in managing and mitigating the effects of high temperatures. From advanced cooling systems and smart home technologies to sustainable urban planning and green architecture, there are numerous strategies and solutions available to help individuals and communities cope with extreme heat. Furthermore, understanding the psychological and social impacts of high temperatures, such as increased irritability and community stress, can provide valuable insights into developing holistic approaches to heat management. By combining scientific knowledge with practical applications and social awareness, we can work towards creating more resilient and adaptive societies in the face of climate challenges.
Understanding 105 Degrees Fahrenheit
To grasp the significance of 105 degrees Fahrenheit, it's essential to understand the basics of temperature measurement and its effects on the human body and environment. The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Gabriel Fahrenheit, is one of the earliest temperature scales and is still widely used in the United States. On this scale, 105 degrees represents a temperature that is significantly higher than the average human body temperature of 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit, indicating potential heat stress if proper precautions are not taken. Furthermore, temperatures at this level can accelerate chemical reactions, affect the viscosity of fluids, and alter the physical properties of materials, which has implications for various industrial processes and technological applications.
Human Health Implications
The human body's response to high temperatures is complex, involving various physiological mechanisms to maintain its internal temperature balance. At 105 degrees Fahrenheit, the risk of heat-related illnesses increases significantly, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Heat exhaustion, characterized by symptoms such as heavy sweating, pale skin, fast and weak pulse, nausea or vomiting, and dizziness or fainting, can progress to heat stroke if not addressed promptly. Heat stroke is a medical emergency, marked by a body temperature of 103 degrees Fahrenheit or higher, confusion, agitation, slurred speech, seizures, and loss of consciousness, requiring immediate medical attention.Environmental Impact

The environmental impact of temperatures reaching 105 degrees Fahrenheit is multifaceted, affecting ecosystems, biodiversity, and the climate as a whole. High temperatures can lead to increased evaporation from rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, contributing to drought conditions and water scarcity. This, in turn, affects plant life and agriculture, potentially leading to crop failures and food shortages. Moreover, extreme heat events can trigger wildfires, especially in dry and combustible areas, posing a significant threat to wildlife, human settlements, and the environment. The long-term effects of consistent high temperatures also contribute to climate change, as they can accelerate the melting of polar ice caps and raise sea levels, altering coastlines and threatening coastal ecosystems and communities.
Technological Innovations
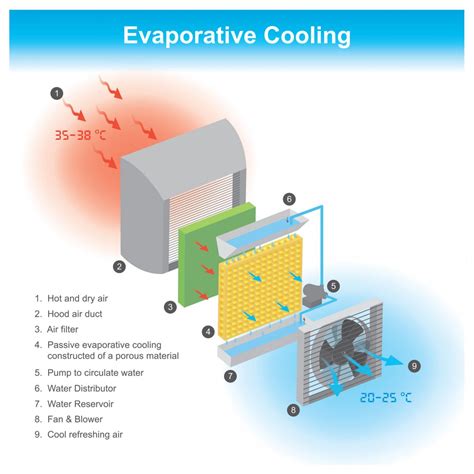
In response to the challenges posed by high temperatures, various technological innovations have been developed to mitigate their effects. Advanced cooling systems, including evaporative cooling, air conditioning, and heat pumps, play a crucial role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures. Smart home technologies and building automation systems can optimize energy consumption and cooling efficiency, reducing the strain on power grids during peak summer months. Furthermore, materials science has led to the development of cool roofs and walls, which can reflect sunlight and heat away from buildings, reducing the need for mechanical cooling. These technologies not only improve comfort and safety but also contribute to energy conservation and environmental sustainability.Practical Strategies for Heat Management

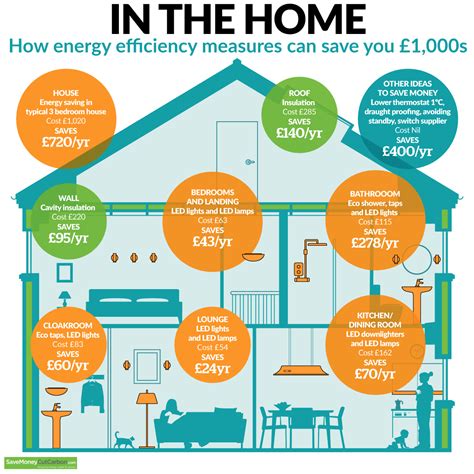
Managing heat effectively requires a combination of personal precautions, technological solutions, and community efforts. On a personal level, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water, wearing light and loose clothing, and avoiding strenuous activities during the hottest part of the day can help prevent heat-related illnesses. Utilizing cooling technologies and maintaining a cool home environment are also crucial. Community-wide initiatives, such as creating green spaces, implementing cool pavement programs, and organizing heat wave response plans, can provide broader protection and support. Additionally, educating the public about heat safety, recognizing the signs of heat-related illnesses, and promoting community resilience are vital components of an effective heat management strategy.
Social and Psychological Aspects
The impact of high temperatures extends beyond physical health and environmental concerns, affecting social dynamics and psychological well-being. Extreme heat can increase irritability, stress, and anxiety, potentially leading to social conflicts and decreased productivity. Furthermore, the economic burden of heat-related illnesses, damage to infrastructure, and loss of productivity can be significant, affecting both individuals and communities. Understanding these social and psychological aspects is essential for developing comprehensive strategies that address not only the physical but also the emotional and social challenges posed by high temperatures.Future Perspectives and Challenges

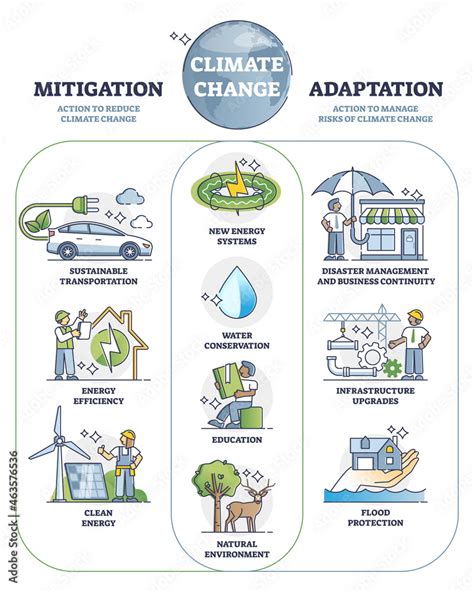
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and extreme weather events, managing high temperatures like 105 degrees Fahrenheit will become increasingly important. Future perspectives involve not only advancing cooling technologies and sustainable practices but also adopting a more holistic approach to heat management, incorporating social, psychological, and environmental considerations. The challenges ahead include balancing energy consumption with the need for cooling, protecting vulnerable populations, and ensuring that solutions are equitable and accessible to all. By combining scientific research, technological innovation, and community engagement, we can work towards creating more resilient and sustainable societies capable of thriving in a warmer world.
Global Cooperation and Climate Action
The issue of high temperatures and climate change is inherently global, requiring international cooperation and collective action. Global agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius and pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Implementing these agreements involves transitioning to renewable energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and protecting natural carbon sinks like forests and oceans. Moreover, sharing knowledge, technologies, and best practices across borders can accelerate the development and deployment of climate solutions, ensuring that no country is left behind in the fight against climate change.Heat Management Image Gallery




In conclusion, the topic of 105 degrees Fahrenheit encompasses a wide range of issues, from personal health and environmental sustainability to technological innovations and global cooperation. As we move forward in addressing the challenges posed by high temperatures, it's essential to adopt a comprehensive approach that considers the interconnectedness of these factors. By sharing knowledge, promoting awareness, and encouraging action, we can work together towards a future where the impacts of extreme heat are mitigated, and the well-being of both people and the planet is protected. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and strategies for managing heat in the comments below, and to spread the word about the importance of heat management and climate action. Together, we can make a difference and create a more sustainable and resilient world for all.
