Intro
Explore the birthplace of America with our Blank 13 Colonies Map Printable, perfect for educational use. Discover the original 13 colonies, including Virginia, Massachusetts, and New York, and learn about their historical significance in the American Revolution. Ideal for students, teachers, and history enthusiasts, this printable map is a valuable resource for geography and history education.
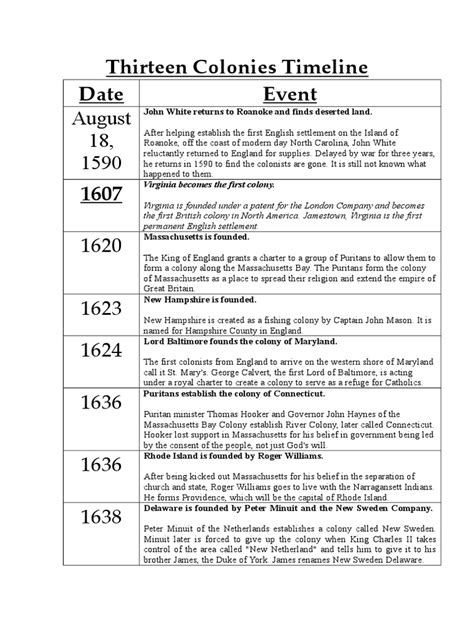
The 13 Colonies played a pivotal role in shaping the history of the United States. These British colonies, established on the eastern coast of North America in the 17th and 18th centuries, were the precursors to the United States of America. Understanding the geography, culture, and history of these colonies is essential for grasping the complexities of American history.
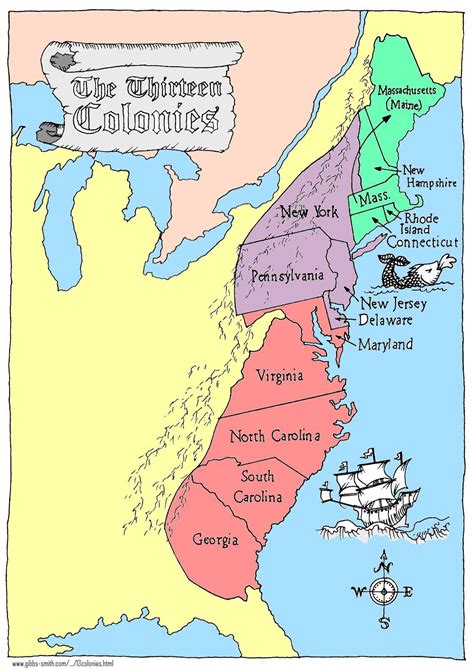
The 13 Colonies were divided into three regions: the New England Colonies, the Middle Colonies, and the Southern Colonies. Each region had its unique characteristics, shaped by factors such as climate, economy, and cultural background.
Geography and Climate of the 13 Colonies
The geography and climate of the 13 Colonies varied greatly, influencing the way people lived, worked, and interacted with one another. The New England Colonies, consisting of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Connecticut, were characterized by rocky soil, dense forests, and a harsh climate. This region was ideal for fishing, shipbuilding, and trade.
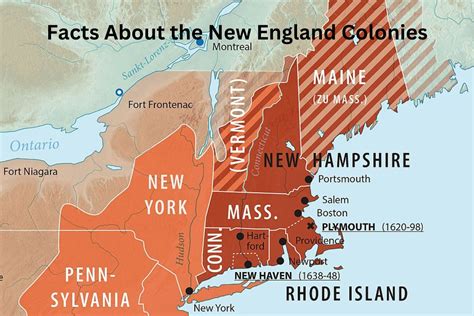
The Middle Colonies, comprising New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, were marked by fertile soil, moderate climate, and abundant natural resources. This region was suitable for farming, and it became a hub for trade and commerce.
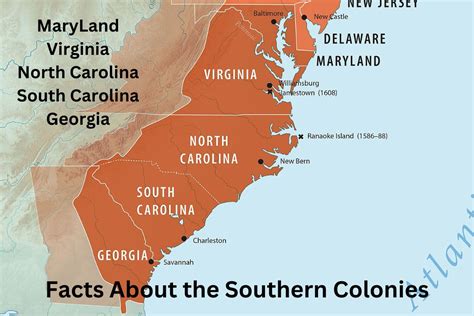
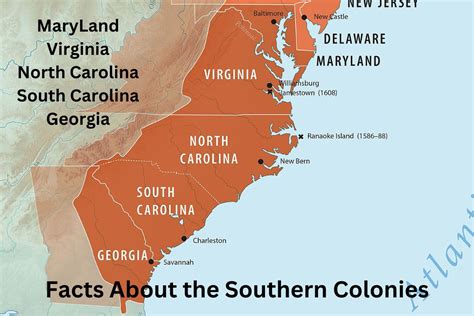
The Southern Colonies
The Southern Colonies, including Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, were characterized by warm climate, long growing season, and rich soil. This region was ideal for plantations, and it became a major producer of tobacco, rice, and indigo.
Economy and Trade in the 13 Colonies
The economy of the 13 Colonies was diverse, with each region specializing in different industries. The New England Colonies excelled in shipbuilding, fishing, and trade, while the Middle Colonies focused on farming, and the Southern Colonies became a major producer of cash crops.
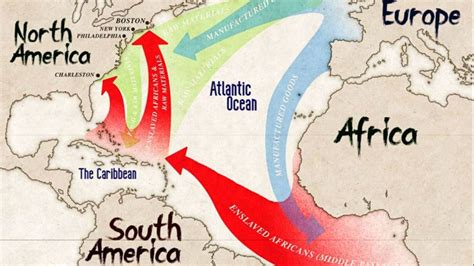
Triangular Trade
The Triangular Trade was a system of trade that connected the 13 Colonies, Africa, and the Caribbean. The colonies exported goods such as tobacco, sugar, and cotton to Africa and the Caribbean, while importing slaves, sugar, and other goods.
Culture and Society in the 13 Colonies
The culture and society of the 13 Colonies were shaped by the diverse backgrounds of the colonists. The New England Colonies were predominantly English, while the Middle Colonies were inhabited by people of Dutch, German, and Scottish descent. The Southern Colonies were characterized by a mix of English, African, and Native American cultures.
Education and Religion
Education and religion played a significant role in the 13 Colonies. The New England Colonies were known for their emphasis on education, with the establishment of Harvard University in 1636. The Middle Colonies were home to a diverse range of religions, including Quakerism, Lutheranism, and Anglicanism. The Southern Colonies were predominantly Anglican.

Printable Blank Maps for Educational Use
Blank maps are an excellent tool for teaching students about the geography and history of the 13 Colonies. Here are some printable blank maps that you can use for educational purposes:
- Blank Map of the 13 Colonies
- Blank Map of the New England Colonies
- Blank Map of the Middle Colonies
- Blank Map of the Southern Colonies
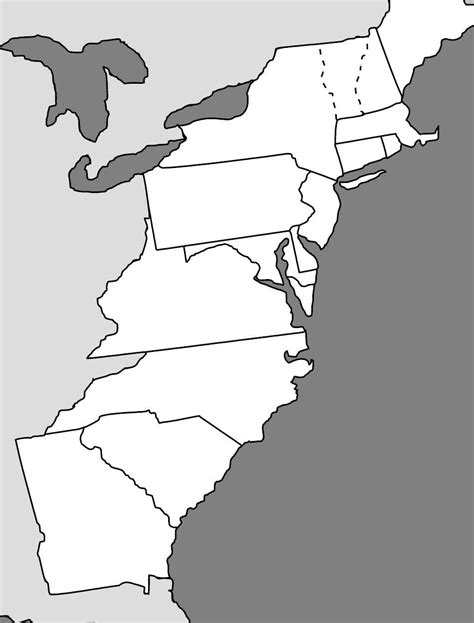
13 Colonies Image Gallery
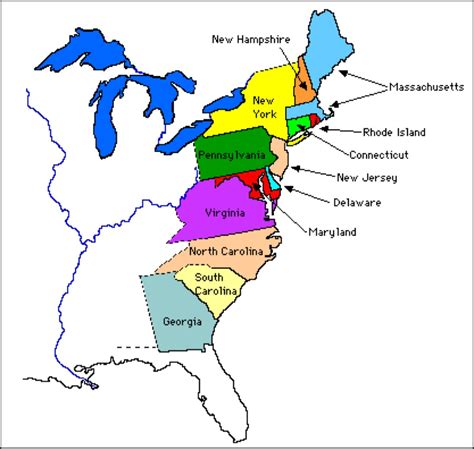
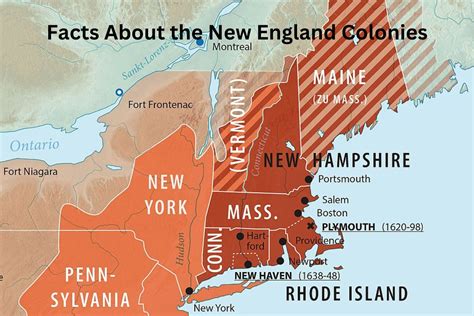
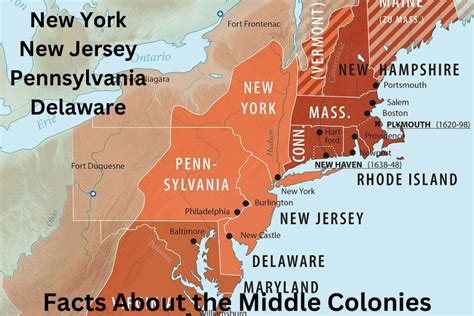




We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the 13 Colonies. Whether you're a student, teacher, or history enthusiast, we encourage you to explore the maps, images, and resources provided to deepen your understanding of this pivotal period in American history. Share your thoughts, ask questions, and engage with us in the comments below!
