Intro
Discover 5 ways to reach 250f Celsius, exploring heat treatment, kiln firing, and high-temperature processing techniques for ceramics, glass, and metalworking applications.
The concept of 250 degrees Celsius is quite significant in various fields, including science, technology, and everyday life. Understanding the implications and applications of such a high temperature can be fascinating. In this article, we will delve into the importance of 250 degrees Celsius and explore its relevance in different contexts.
Temperature is a fundamental physical quantity that plays a crucial role in shaping our environment and influencing the behavior of materials. The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a common temperature scale used in most parts of the world. The freezing point of water is defined as 0 degrees Celsius, while the boiling point is 100 degrees Celsius. Therefore, 250 degrees Celsius is significantly higher than the boiling point of water, indicating a very high temperature.
The significance of 250 degrees Celsius can be understood by considering its applications in various fields. For instance, in the context of materials science, temperatures above 200 degrees Celsius can cause significant changes in the properties of materials, such as melting, decomposition, or phase transitions. In the field of chemistry, high temperatures like 250 degrees Celsius are often required for certain chemical reactions to occur, such as combustion, synthesis, or decomposition reactions.
Introduction to High-Temperature Applications

High-temperature applications are crucial in various industries, including manufacturing, energy production, and transportation. For example, in the production of steel, high temperatures are required to melt and shape the metal. Similarly, in the field of aerospace engineering, high-temperature materials are used to withstand the extreme conditions encountered during space exploration.
Benefits of High-Temperature Technology
The benefits of high-temperature technology are numerous and significant. Some of the advantages include: * Increased efficiency: High-temperature processes can be more efficient and cost-effective than traditional methods. * Improved performance: High-temperature materials and technologies can enhance the performance of various systems and applications. * Enhanced safety: High-temperature materials can provide improved safety features, such as fire resistance and thermal insulation.Applications of 250 Degrees Celsius

The applications of 250 degrees Celsius are diverse and widespread. Some examples include:
- Heat treatment: 250 degrees Celsius is often used for heat treatment processes, such as annealing, hardening, or tempering of metals.
- Chemical reactions: High temperatures like 250 degrees Celsius are required for certain chemical reactions, such as combustion, synthesis, or decomposition reactions.
- Materials processing: 250 degrees Celsius can be used for processing materials, such as melting, casting, or molding.
Chemical Reactions at 250 Degrees Celsius
Chemical reactions at 250 degrees Celsius can be complex and fascinating. Some examples include: * Combustion reactions: 250 degrees Celsius can be used to initiate combustion reactions, such as burning fossil fuels or biomass. * Synthesis reactions: High temperatures like 250 degrees Celsius can be used to synthesize new compounds or materials. * Decomposition reactions: 250 degrees Celsius can be used to decompose materials, such as plastics or organic waste.Materials Science and 250 Degrees Celsius
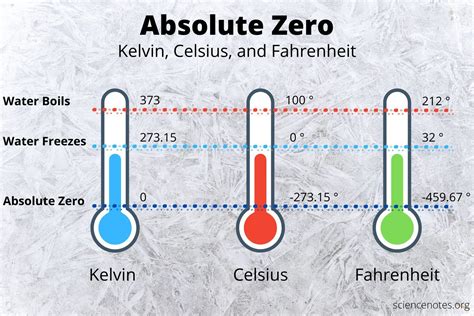
Materials science is a crucial field that deals with the properties and applications of various materials. The behavior of materials at 250 degrees Celsius can be significant, and some examples include:
- Melting points: 250 degrees Celsius can be above the melting point of certain materials, such as metals or plastics.
- Phase transitions: High temperatures like 250 degrees Celsius can cause phase transitions, such as solid-to-liquid or liquid-to-gas transitions.
- Thermal expansion: 250 degrees Celsius can cause significant thermal expansion in materials, which can be important in various applications.
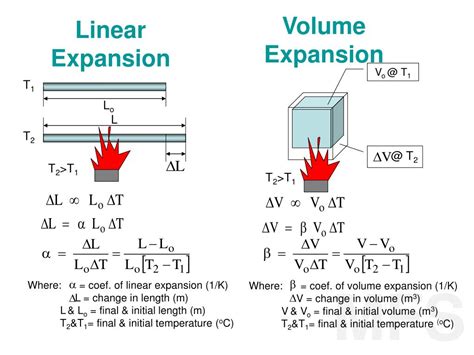
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Thermal expansion and contraction are critical phenomena that occur in materials due to temperature changes. Some key points to consider include: * Coefficient of thermal expansion: The coefficient of thermal expansion is a measure of how much a material expands or contracts with temperature changes. * Thermal stress: Thermal stress can occur due to thermal expansion or contraction, which can be significant in certain applications. * Material selection: The selection of materials for high-temperature applications requires careful consideration of thermal expansion and contraction properties.Energy Production and 250 Degrees Celsius
Energy production is a vital field that requires high temperatures, including 250 degrees Celsius. Some examples include:
- Fossil fuel combustion: 250 degrees Celsius can be used to combust fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, or gas.
- Nuclear power: High temperatures like 250 degrees Celsius can be used in nuclear power plants to generate steam and produce electricity.
- Solar energy: Concentrated solar power systems can reach temperatures above 250 degrees Celsius, which can be used to generate electricity or produce fuels.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly important, and some examples include: * Solar energy: Solar energy can be harnessed using photovoltaic panels or concentrated solar power systems. * Wind energy: Wind energy can be harnessed using wind turbines, which can generate electricity. * Geothermal energy: Geothermal energy can be harnessed using heat exchangers, which can produce electricity or provide heating and cooling.Transportation and 250 Degrees Celsius

Transportation is a critical field that requires high temperatures, including 250 degrees Celsius. Some examples include:
- Internal combustion engines: 250 degrees Celsius can be reached in internal combustion engines, which can be used to power vehicles.
- Jet engines: High temperatures like 250 degrees Celsius can be used in jet engines to generate thrust and propel aircraft.
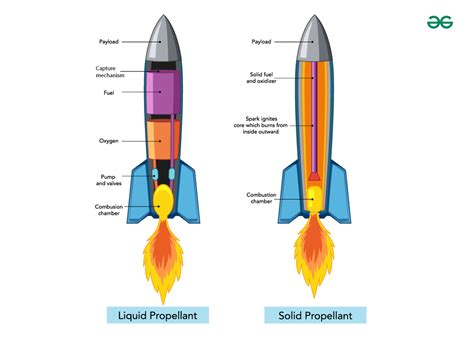
- Rocket propulsion: 250 degrees Celsius can be used in rocket propulsion systems to generate thrust and propel spacecraft.
Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering is a vital field that deals with the design and development of aircraft, spacecraft, and missiles. Some key points to consider include: * Materials selection: The selection of materials for aerospace applications requires careful consideration of high-temperature properties. * Thermal protection: Thermal protection systems are crucial in aerospace applications to protect against extreme temperatures. * Propulsion systems: Propulsion systems, such as jet engines or rocket engines, require high temperatures to generate thrust and propel vehicles.High-Temperature Image Gallery







In conclusion, the concept of 250 degrees Celsius is significant in various fields, including science, technology, and everyday life. Understanding the implications and applications of such a high temperature can be fascinating, and this article has explored its relevance in different contexts. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences related to high-temperature applications and to explore further the many fascinating aspects of this topic. Please feel free to comment, share this article, or take specific actions to learn more about the importance of 250 degrees Celsius in shaping our world.
