Intro
Discover the Muscle Vs Fat Difference, exploring body composition, weight loss, and muscle gain, to understand how lean muscle mass impacts metabolism, fat burning, and overall health, and learn to achieve a healthy balance between muscle and body fat.
The human body is composed of various types of tissues, with muscle and fat being two of the most significant components. Understanding the difference between muscle and fat is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, as it can impact our overall well-being, physical appearance, and athletic performance. In this article, we will delve into the world of muscle and fat, exploring their distinct characteristics, functions, and importance in our bodies.
Muscle and fat are two types of tissues that serve different purposes in the body. Muscle tissue is responsible for movement, supporting our skeletal system, and maintaining posture. It is composed of contractile units called muscle fibers, which work together to generate force and facilitate movement. On the other hand, fat tissue, also known as adipose tissue, plays a vital role in energy storage, insulation, and hormone regulation. Fat cells, or adipocytes, store energy in the form of lipids, which can be broken down and utilized by the body when needed.
The difference between muscle and fat is not just limited to their functions; their compositions and characteristics are also distinct. Muscle tissue is denser and more compact than fat tissue, with a higher water content and a more extensive network of blood vessels. This allows for efficient oxygen and nutrient delivery to the muscles, enabling them to function optimally. In contrast, fat tissue is less dense and has a lower water content, with a more limited blood supply. This makes it more challenging for the body to break down and utilize fat for energy.
Muscle Composition and Function
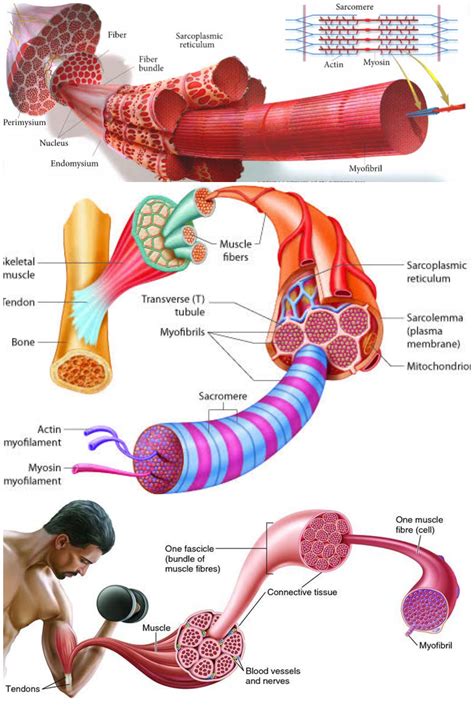
Muscle function is dependent on a variety of factors, including muscle fiber type, size, and distribution. There are two primary types of muscle fibers: fast-twitch and slow-twitch. Fast-twitch fibers are designed for high-intensity, short-duration activities, such as sprinting or weightlifting. Slow-twitch fibers, on the other hand, are better suited for low-intensity, long-duration activities, like distance running or cycling. Understanding the differences between muscle fiber types can help individuals optimize their training programs and improve overall performance.
Fat Composition and Function
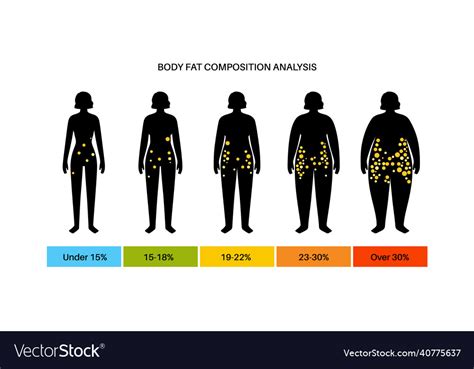
Fat function is not limited to energy storage; it also plays a critical role in hormone regulation and inflammation. Adipose tissue produces various hormones, such as leptin and adiponectin, which help regulate energy balance, glucose metabolism, and inflammation. An imbalance of these hormones can contribute to various metabolic disorders, including obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes.
Benefits of Muscle Mass
The benefits of muscle mass are numerous and well-documented. Having a healthy amount of muscle tissue can: * Improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism * Enhance athletic performance and reduce injury risk * Support bone health and reduce osteoporosis risk * Boost metabolism and aid in weight management * Improve mental health and reduce stressIn contrast, having excessive fat tissue can lead to various health problems, including:
- Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease and stroke
- Certain types of cancer, such as breast and colon cancer
- Osteoarthritis and joint pain
- Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety
Muscle vs Fat: Which is More Important?

Rather than focusing on which tissue is more important, it's essential to prioritize overall health and wellness. This can be achieved through a combination of regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can help build and maintain muscle mass, while aerobic exercise, like cardio or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), can improve cardiovascular health and reduce fat tissue.
Practical Tips for Building Muscle and Reducing Fat
Here are some practical tips for building muscle and reducing fat: * Engage in regular resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises * Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your workout routine * Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates * Get enough sleep and prioritize stress management * Stay hydrated and limit processed foods and sugary drinksThe Role of Nutrition in Muscle and Fat Balance
Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide energy for the body and support healthy digestion. It's also essential to limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats, which can contribute to fat gain and metabolic disorders.
Supplements and Muscle Growth
Supplements can be a useful addition to a muscle-building program, but it's essential to choose the right ones. Some popular supplements for muscle growth include: * Protein powder: helps increase protein intake and support muscle growth * Creatine: enhances muscle strength and endurance * Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): reduces muscle soreness and improves recovery * HMB (beta-Hydroxy beta-Methylbutyrate): helps reduce muscle damage and improve recoveryHowever, it's crucial to remember that supplements should not replace a healthy diet and regular exercise. Always consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplements to your routine.
Muscle and Fat: The Importance of Balance

Aiming for a body fat percentage that is within a healthy range (8-24% for men and 16-30% for women) and maintaining a healthy amount of muscle mass can help support overall health and wellness. Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management are all crucial components of achieving and maintaining this balance.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, muscle and fat are two distinct tissues that play critical roles in our overall health and well-being. Understanding the differences between these tissues and prioritizing a healthy balance of both is essential for maintaining optimal physical function, metabolic health, and mental well-being. By incorporating regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management into our daily routines, we can support muscle growth, reduce fat tissue, and achieve a healthy balance that promotes overall health and wellness.Muscle and Fat Image Gallery









We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the difference between muscle and fat, as well as the importance of maintaining a healthy balance of both tissues. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to share them with us. We'd love to hear your thoughts and help you achieve your health and wellness goals. Share this article with your friends and family, and let's work together to promote a culture of health and wellness.
