Intro
Explore the key differences between the A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt, two iconic fighter aircraft. Discover their unique design features, combat capabilities, and historical roles in close air support and ground attack missions. Learn how these planes earned their legendary status and which one stands out in terms of durability, firepower, and tactical prowess.
The A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt are two of the most iconic fighter planes in history, known for their durability, firepower, and distinctive designs. While both aircraft have their own unique characteristics, they were designed for different eras and purposes. In this article, we'll delve into the key differences between these two legendary planes.

The A-10 Warthog, also known as the Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II, is a single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft designed for close air support (CAS) and ground attack missions. Its primary function is to provide air support for ground troops, destroying enemy tanks, armored vehicles, and fortifications. The A-10's design emphasizes survivability, with a robust airframe, redundant systems, and a titanium armor "bathtub" around the cockpit to protect the pilot.
On the other hand, the P-47 Thunderbolt was a single-seat, single-engine fighter plane used during World War II. Its primary role was to engage enemy aircraft in dogfights and escort bombers. The P-47 was known for its speed, agility, and impressive firepower, earning it the nickname "Jug" among pilots.
Design and Development
The A-10 Warthog was designed in the 1960s by Fairchild Republic, with the first flight taking place in 1972. The aircraft's design was influenced by the experiences of the Vietnam War, where the need for a dedicated close air support platform became apparent. The A-10's unique design features a straight wing, a robust fuselage, and a pair of General Electric TF34 high-bypass turbofan engines.
In contrast, the P-47 Thunderbolt was designed in the 1940s by Republic Aviation, with the first flight occurring in 1941. The P-47 was a response to the US Army Air Forces' (USAAF) need for a high-performance fighter plane. Its design featured a streamlined fuselage, a unique bubble canopy, and a massive Pratt & Whitney R-2800 radial engine.
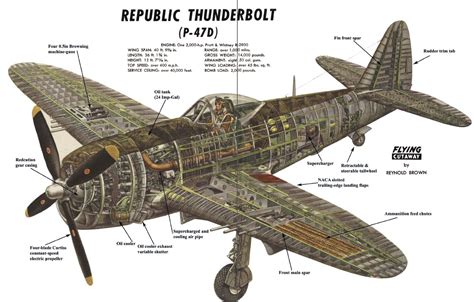
Key Design Differences
- The A-10 Warthog has a straight wing, while the P-47 Thunderbolt features a swept wing design.
- The A-10 has a pair of high-bypass turbofan engines, whereas the P-47 has a single radial engine.
- The A-10's airframe is made of titanium and steel, providing exceptional durability, whereas the P-47's airframe is primarily made of aluminum.
Operational History
The A-10 Warthog has been in service since 1976, with the US Air Force (USAF) operating over 700 aircraft. The A-10 has seen action in various conflicts, including the Gulf War, Kosovo War, and Operation Iraqi Freedom. Its impressive combat record has earned it a reputation as a reliable and effective close air support platform.
The P-47 Thunderbolt played a significant role in World War II, particularly in the European Theater of Operations. The P-47 served as an escort fighter for bomber formations and engaged enemy aircraft in dogfights. Its impressive performance and firepower made it a favorite among Allied pilots.

Operational Differences
- The A-10 Warthog is primarily used for close air support and ground attack missions, while the P-47 Thunderbolt was used for air-to-air combat and bomber escort.
- The A-10 has a longer range and loiter time compared to the P-47, thanks to its more efficient engines and larger fuel capacity.
- The A-10 is equipped with advanced avionics and targeting systems, whereas the P-47 relied on simpler navigation and communication systems.
Specifications
Here's a comparison of the A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt specifications:
- A-10 Warthog
- Length: 53 ft 4 in (16.3 m)
- Wingspan: 57 ft 6 in (17.5 m)
- Height: 14 ft 8 in (4.5 m)
- Empty weight: 24,000 lb (10,886 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 50,000 lb (22,680 kg)
- Engines: 2 x General Electric TF34 high-bypass turbofan engines
- Thrust: 9,065 lb (4,080 kgf)
- P-47 Thunderbolt
- Length: 36 ft 1 in (11 m)
- Wingspan: 40 ft 9 in (12.4 m)
- Height: 14 ft 2 in (4.3 m)
- Empty weight: 10,000 lb (4,536 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 17,000 lb (7,711 kg)
- Engine: 1 x Pratt & Whitney R-2800 radial engine
- Power: 2,600 hp (1,942 kW)

Performance Differences
- The A-10 Warthog has a slower top speed compared to the P-47 Thunderbolt, but its range and loiter time are significantly longer.
- The A-10 has a higher service ceiling and a more advanced avionics suite compared to the P-47.
- The P-47 has a higher rate of climb and a tighter turning radius, making it more agile in dogfighting scenarios.
Legacy
Both the A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt have left an indelible mark on aviation history. The A-10's reputation as a reliable and effective close air support platform has made it a favorite among ground troops, while the P-47's impressive performance and firepower made it a legendary fighter plane.

Lasting Impact
- The A-10 Warthog's design has influenced the development of modern close air support platforms, such as the A-29 Super Tucano and the Textron AirLand Scorpion.
- The P-47 Thunderbolt's performance and design features have influenced the development of post-war fighter planes, such as the F-86 Sabre and the F-100 Super Sabre.
Gallery of A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt Images
A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt Image Gallery










As we've explored the key differences between the A-10 Warthog and P-47 Thunderbolt, it's clear that both aircraft have their own unique strengths and weaknesses. The A-10's durability and firepower make it an ideal close air support platform, while the P-47's agility and performance made it a legendary fighter plane.
