Intro
The world of genetics and molecular biology can be fascinating, yet complex. One of the fundamental concepts in this field is understanding the sequence of bases that make up our DNA. At the heart of this understanding lies the concept of a triplet of bases, also known as a codon. In this article, we will explore the three crucial steps to comprehend the particular triplet of bases and its significance in the grand scheme of genetics.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics of DNA Structure
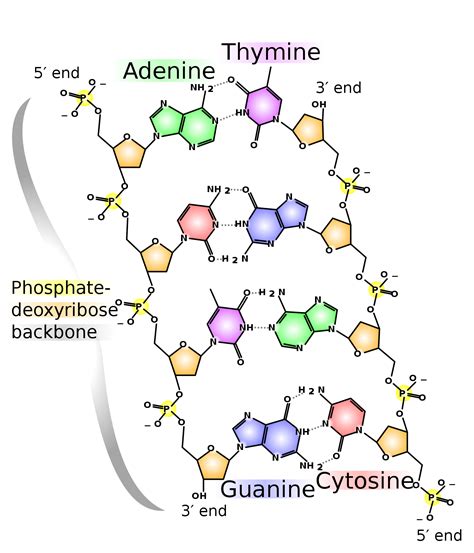
Before diving into the specifics of triplet bases, it's essential to grasp the fundamental structure of DNA. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a long, double-stranded helix made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide, in turn, consists of a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). The sequence of these nitrogenous bases determines the genetic information encoded in the DNA.
The Role of Nitrogenous Bases
The nitrogenous bases play a crucial role in the formation of the DNA double helix. Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T), while guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C). This base pairing is crucial for the stability and replication of DNA. Understanding the properties and pairing of these nitrogenous bases is essential for comprehending the triplet code.
Step 2: Deciphering the Triplet Code
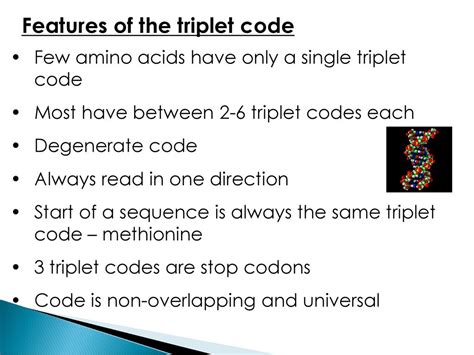
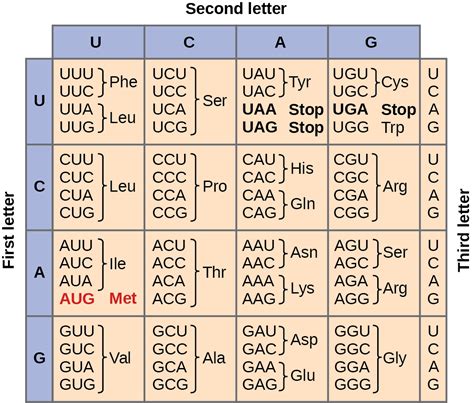
The sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA is read in groups of three, known as triplets or codons. Each triplet code corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal. The genetic code is almost universal, meaning that the same triplet code corresponds to the same amino acid in almost all living organisms. This universality allows us to understand the genetic information encoded in DNA.
How the Triplet Code Works
The triplet code is read in a sequence of three bases, with each base occupying one of the three positions. The sequence of these bases determines the amino acid that will be incorporated into a protein. For example, the triplet code "ATG" codes for the amino acid methionine, while the triplet code "TAA" codes for a stop signal. Understanding the triplet code is crucial for deciphering the genetic information encoded in DNA.
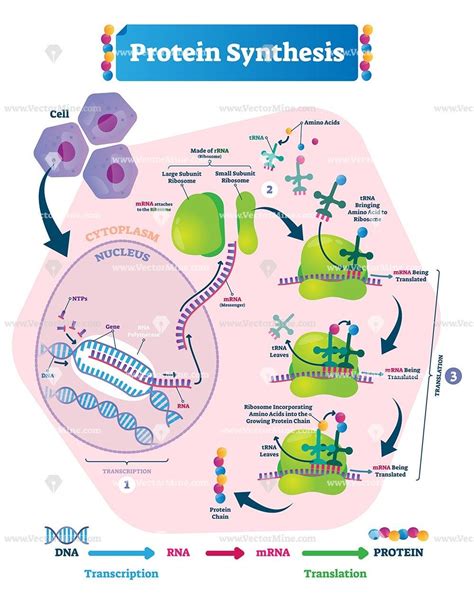
Step 3: Translating the Triplet Code into Proteins
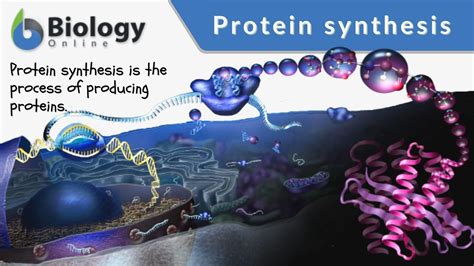
The final step in understanding the particular triplet of bases is to comprehend how the triplet code is translated into proteins. This process occurs through a complex series of steps, including transcription, translation, and protein synthesis. During transcription, the genetic information encoded in DNA is transcribed into a complementary RNA molecule. The RNA molecule is then translated into a sequence of amino acids, which are assembled into a protein.
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins is known as the central dogma of molecular biology. This concept describes the sequence of events that occurs during the translation of the triplet code into proteins. Understanding the central dogma is essential for comprehending the significance of the triplet code in the grand scheme of genetics.
Triplet Code Image Gallery
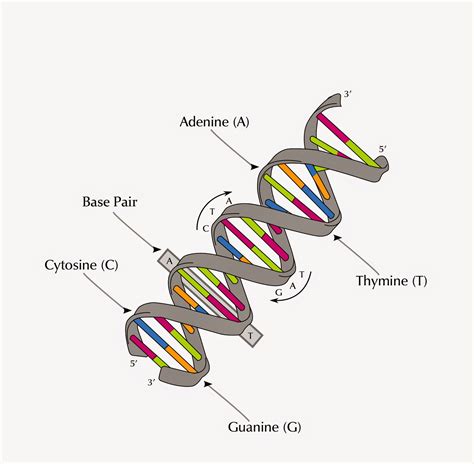


In conclusion, understanding the particular triplet of bases is crucial for deciphering the genetic information encoded in DNA. By comprehending the structure of DNA, deciphering the triplet code, and translating the code into proteins, we can unlock the secrets of genetics and molecular biology. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the triplet code and its significance in the grand scheme of genetics. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
