Managing accounts receivable is a crucial aspect of any business's financial health. It involves tracking the amounts owed to your company by customers, clients, or patients. One of the key metrics used to assess the effectiveness of accounts receivable management is the aging of accounts receivable. In this article, we will delve into the world of aging accounts receivable, exploring its importance, calculation methods, and practical examples.
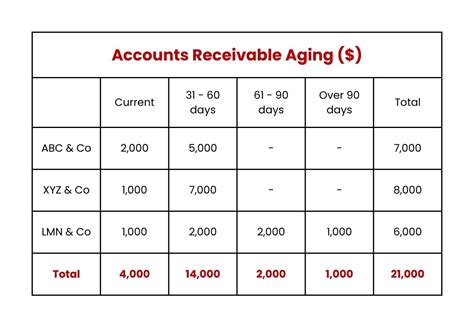
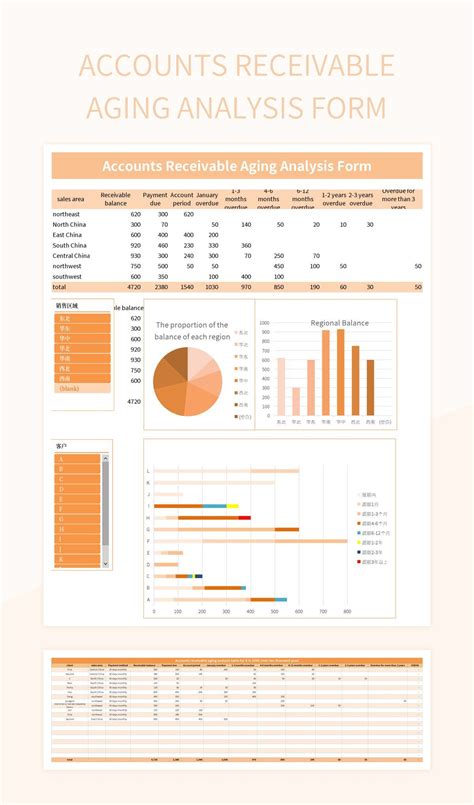
Understanding the concept of aging accounts receivable is vital for businesses to identify potential cash flow problems, make informed decisions about credit terms, and develop strategies to minimize bad debt. Aging accounts receivable refers to the process of categorizing outstanding invoices based on the number of days they have been outstanding. This categorization helps businesses to identify invoices that are approaching or have exceeded the credit terms, allowing them to take prompt action to collect the debt.
Calculating Aging Accounts Receivable
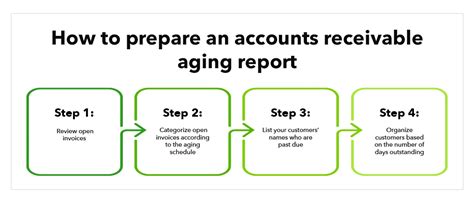
Calculating aging accounts receivable involves a straightforward process that can be performed manually or using accounting software. Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating aging accounts receivable:
- Identify the outstanding invoices: Start by compiling a list of all outstanding invoices, including the invoice date, customer name, and outstanding balance.
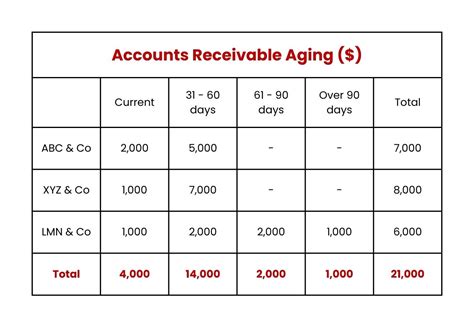
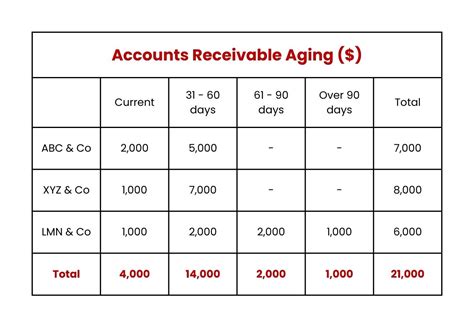
- Determine the aging categories: Establish aging categories, typically 0-30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, and over 90 days.
- Calculate the aging of each invoice: Calculate the number of days each invoice has been outstanding by subtracting the invoice date from the current date.
- Assign each invoice to an aging category: Based on the calculated aging, assign each invoice to the corresponding aging category.
- Calculate the total outstanding balance for each aging category: Add up the outstanding balances for each aging category.

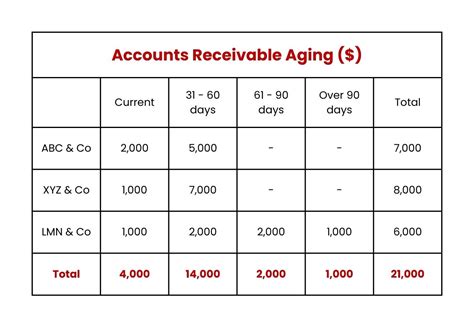
Aging Accounts Receivable Example
Let's consider an example to illustrate the calculation of aging accounts receivable. Suppose we have the following outstanding invoices:
| Invoice Date | Customer Name | Outstanding Balance |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 | John Smith | $1,000 |
| 2022-02-01 | Jane Doe | $500 |
| 2022-03-01 | Bob Johnson | $2,000 |
Using the steps outlined above, we can calculate the aging of each invoice as follows:
| Invoice Date | Customer Name | Outstanding Balance | Aging (Days) | Aging Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 | John Smith | $1,000 | 90 | 61-90 days |
| 2022-02-01 | Jane Doe | $500 | 60 | 31-60 days |
| 2022-03-01 | Bob Johnson | $2,000 | 30 | 0-30 days |
Based on the aging categories, we can calculate the total outstanding balance for each category as follows:
| Aging Category | Total Outstanding Balance |
|---|---|
| 0-30 days | $2,000 |
| 31-60 days | $500 |
| 61-90 days | $1,000 |
| Over 90 days | $0 |
Benefits of Aging Accounts Receivable
Aging accounts receivable offers several benefits to businesses, including:
- Improved cash flow management: By identifying outstanding invoices that are approaching or have exceeded the credit terms, businesses can take prompt action to collect the debt, reducing the risk of bad debt and improving cash flow.
- Enhanced credit risk management: Aging accounts receivable helps businesses to identify customers who are struggling to pay their debts, allowing them to adjust their credit terms or take alternative measures to minimize bad debt.
- Better decision-making: By analyzing the aging of accounts receivable, businesses can make informed decisions about credit terms, pricing, and customer relationships.

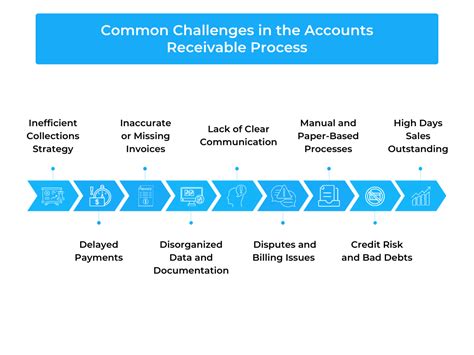
Common Challenges in Aging Accounts Receivable
While aging accounts receivable is a valuable tool for businesses, there are several common challenges that can arise, including:
- Inaccurate or incomplete data: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to incorrect aging calculations, making it difficult to make informed decisions.
- Lack of standardization: Without a standardized aging process, businesses may struggle to compare and analyze aging data across different departments or locations.
- Insufficient resources: Small businesses or those with limited resources may struggle to dedicate the necessary time and resources to aging accounts receivable.
Best Practices for Aging Accounts Receivable
To overcome the challenges associated with aging accounts receivable, businesses can follow best practices, including:
- Implement a standardized aging process: Establish a standardized aging process that includes clear aging categories and calculation methods.
- Use accounting software: Utilize accounting software that automates the aging process, reducing the risk of errors and increasing efficiency.
- Regularly review and analyze aging data: Regularly review and analyze aging data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.

Conclusion
Aging accounts receivable is a crucial aspect of accounts receivable management that offers numerous benefits to businesses. By calculating and analyzing aging accounts receivable, businesses can identify potential cash flow problems, make informed decisions about credit terms, and develop strategies to minimize bad debt. While common challenges can arise, following best practices and implementing a standardized aging process can help businesses to overcome these challenges and achieve improved cash flow management.
Aging Accounts Receivable Image Gallery




We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of aging accounts receivable. By implementing a standardized aging process and following best practices, businesses can improve cash flow management, enhance credit risk management, and make informed decisions about credit terms. Share your thoughts and experiences with aging accounts receivable in the comments below.
