Discover the nuances of homophones with Air and Are Words: Understanding Homophones. Learn to master words that sound alike but have different meanings, including to, too, and two, their, there, and theyre. Improve your language skills and clarity with this in-depth guide on homophones, homographs, and homonyms.
The English language is full of quirks and nuances that can make it challenging to navigate, even for native speakers. One such aspect is homophones, which are words that are pronounced the same but have different meanings and often different spellings. Two commonly confused homophones are "air" and "are". In this article, we will delve into the world of homophones, explore the differences between "air" and "are", and provide tips on how to use them correctly.
What are Homophones?
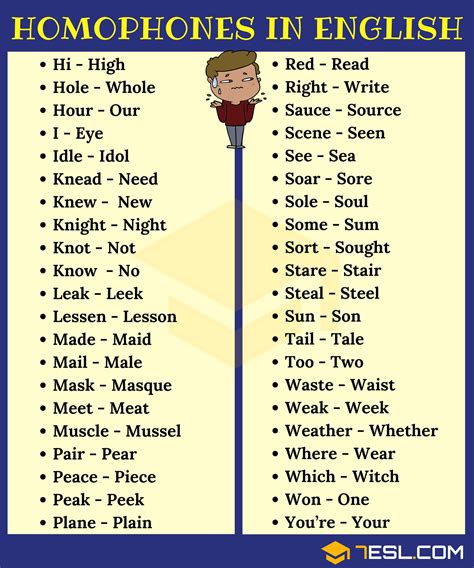
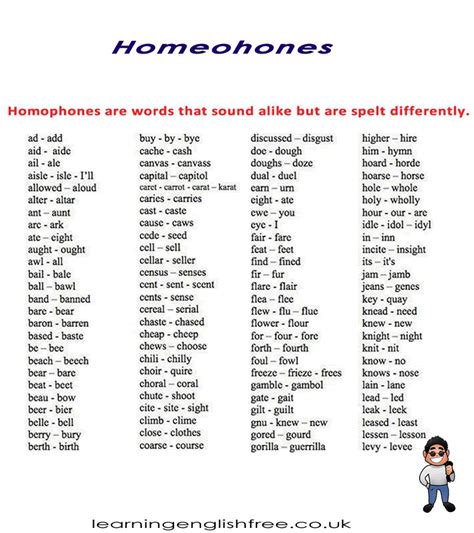
Homophones are words that are pronounced the same but have different meanings and often different spellings. They can be confusing, especially when listening to spoken language, as the words are pronounced the same but have different meanings. Homophones can be classified into two categories: homographs and heteronyms. Homographs are words that are spelled the same but have different meanings, while heteronyms are words that are spelled differently but pronounced the same.
Examples of Homophones
- To/Too/Two
- Their/There/They're
- Bare/Bear
- Fair/Fare
- Four/For
Understanding the Difference between "Air" and "Are"
"Air" and "are" are two commonly confused homophones. "Air" is a noun that refers to the invisible gaseous substance surrounding the earth, while "are" is a verb that is the second person plural of "to be".
- "Air" can be used in sentences such as:
- The air is fresh and clean.
- She took a deep breath of air.
- "Are" can be used in sentences such as:
- You are going to love this new restaurant.
- They are coming over tonight.
When to Use "Air" and When to Use "Are"
- Use "air" when referring to the invisible gaseous substance surrounding the earth.
- Use "are" when referring to the second person plural of "to be".
Common Mistakes to Avoid
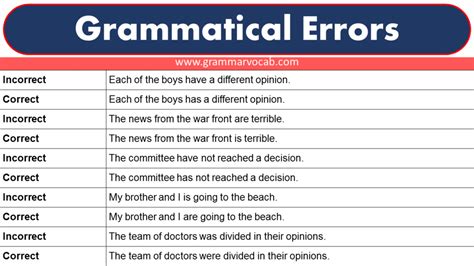
One common mistake to avoid is using "air" instead of "are" in sentences. For example:
- Incorrect: "You air going to love this new restaurant."
- Correct: "You are going to love this new restaurant."
Tips for Mastering Homophones
- Read widely and often to improve your vocabulary and grammar skills.
- Practice using homophones in sentences to reinforce their meanings.
- Use flashcards or create a cheat sheet to help you remember the differences between homophones.
Mastering Homophones in Writing

Mastering homophones is crucial in writing, as using the wrong word can change the meaning of a sentence entirely. Here are some tips for mastering homophones in writing:
- Use a dictionary or thesaurus to check the meanings of words.
- Read your writing aloud to catch any errors.
- Use grammar and spell check tools to help you identify mistakes.
Homophones in Literature and Poetry
Homophones have been used in literature and poetry to create clever wordplay and add depth to language. For example:
- In Shakespeare's "A Midsummer Night's Dream", the character Puck uses homophones to confuse and mislead the other characters.
- In Emily Dickinson's poetry, she often uses homophones to create clever wordplay and add depth to her language.
Conclusion

In conclusion, mastering homophones is an essential part of language learning and writing. By understanding the differences between "air" and "are", you can improve your vocabulary and grammar skills, and avoid common mistakes in writing. Remember to read widely, practice using homophones in sentences, and use tools such as dictionaries and grammar checkers to help you master homophones.
Final Thoughts
Homophones are a fascinating aspect of the English language, and mastering them can add depth and nuance to your language skills. By following the tips and advice in this article, you can improve your vocabulary and grammar skills, and become a more confident writer and communicator.
Air and Are Image Gallery








We hope this article has been helpful in understanding the differences between "air" and "are", and has provided you with tips and advice for mastering homophones. Share your thoughts and comments below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and family!
