Intro
Unlock Air Force career opportunities with the right ASVAB scores. Discover the required scores for various Air Force careers, including enlisted and officer positions. Learn how to interpret your scores, the importance of line scores, and how to prepare for the ASVAB test to pursue your desired career in the United States Air Force.
Pursuing a career in the United States Air Force (USAF) requires meeting specific eligibility requirements, including achieving a qualifying score on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test. The ASVAB is a standardized test that measures a candidate's aptitude in various subjects, such as mathematics, reading comprehension, and mechanical comprehension.
In this article, we will explore the different ASVAB scores required for various Air Force careers, also known as Air Force Specialty Codes (AFSCs). We will also discuss how the ASVAB scoring system works and provide tips for preparing for the test.
How ASVAB Scoring Works
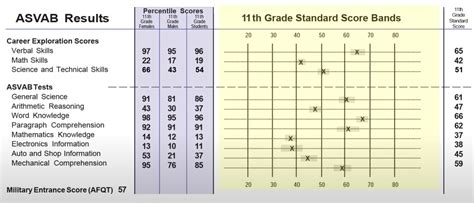
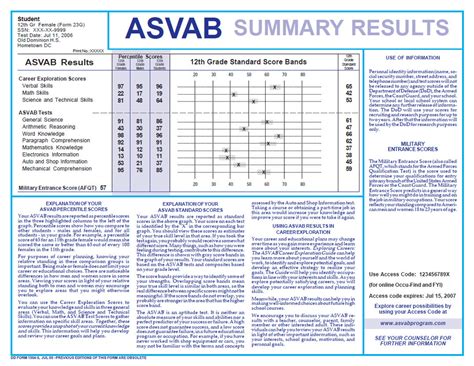
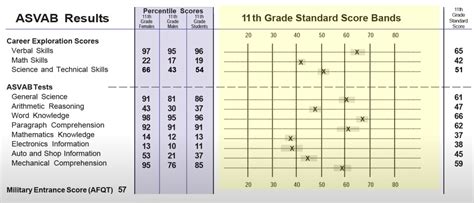
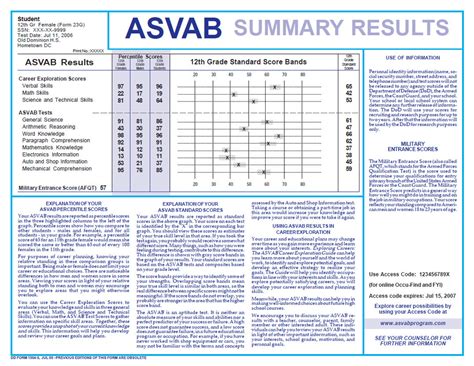
The ASVAB test consists of nine individual tests, each measuring a specific area of knowledge. The tests are:
- General Science (GS)
- Arithmetic Reasoning (AR)
- Word Knowledge (WK)
- Paragraph Comprehension (PC)
- Mathematics Knowledge (MK)
- Electronics Information (EI)
- Auto and Shop Information (AS)
- Mechanical Comprehension (MC)
- Assembling Objects (AO)
The scores from these individual tests are then combined to produce a series of composite scores, known as line scores. These line scores are used to determine an individual's qualifications for specific military careers.
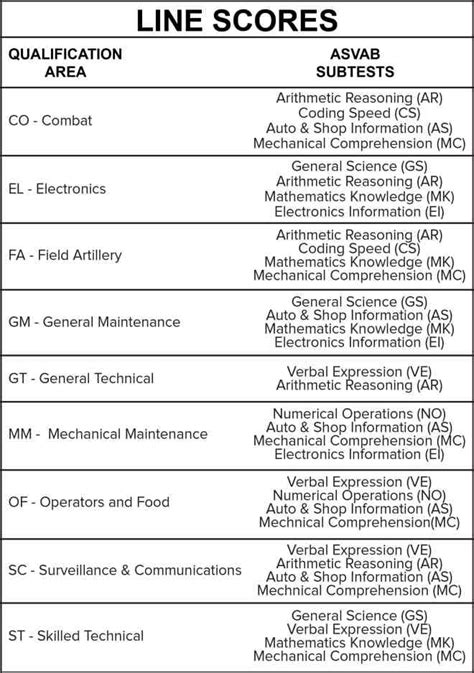
Line Scores and AFSCs
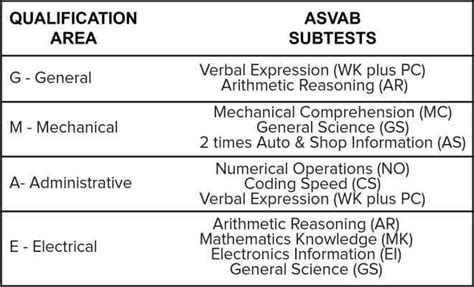
There are four main line scores used by the Air Force:
- General (G): Measures verbal and quantitative abilities
- Mechanical (M): Measures mechanical aptitude and technical skills
- Administrative (A): Measures administrative and clerical skills
- Electronics (E): Measures electronic and technical skills
Each AFSC requires a specific combination of line scores, which are used to determine an individual's eligibility for that career.
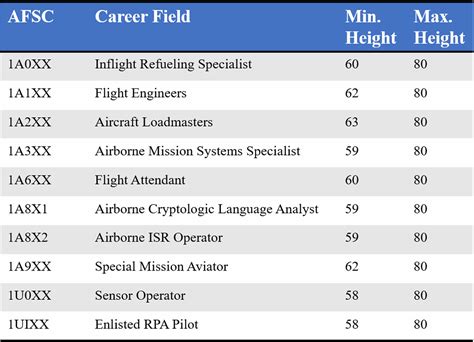
ASVAB Scores Required for Air Force Careers

Here are some examples of ASVAB scores required for various Air Force careers:
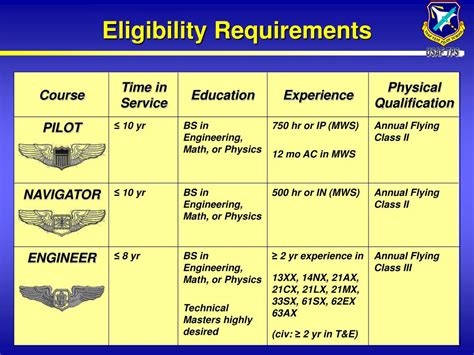
- Pilot (AFSC 11X): G - 60, M - 50, A - 45
- Navigator (AFSC 12X): G - 60, M - 55, A - 50
- Air Traffic Control (AFSC 1C1X1): G - 55, M - 45, A - 50
- Cyber Systems Operations (AFSC 1B4X1): G - 55, M - 50, A - 60
- Intelligence Analyst (AFSC 1N0X1): G - 60, M - 45, A - 55
- Communications Systems Operator (AFSC 3C0X1): G - 55, M - 50, A - 60
- Security Forces (AFSC 3P0X1): G - 50, M - 45, A - 50
- Maintenance Operations Coordinator (AFSC 2M0X1): G - 55, M - 50, A - 60
Note that these scores are subject to change, and individual requirements may vary depending on the specific AFSC and the needs of the Air Force.
Preparing for the ASVAB Test

To prepare for the ASVAB test, candidates can use a variety of study materials and resources, including:
- Official ASVAB study guides
- Online practice tests and tutorials
- Mobile apps and games
- Classroom instruction and tutoring
It is also essential to understand the format and content of the test, as well as to develop strategies for managing test anxiety and time management.
Tips for Improving Your ASVAB Scores
- Take practice tests to identify areas for improvement
- Focus on building your math and reading comprehension skills
- Use flashcards and other memory aids to learn key terms and concepts
- Practice under timed conditions to simulate the actual test-taking experience
By understanding the ASVAB scoring system and preparing effectively for the test, candidates can improve their chances of qualifying for their desired Air Force career.
ASVAB Score Image Gallery


We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the ASVAB scoring system and the requirements for various Air Force careers. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
