Intro
Unlock the US Air Force Enlisted Rank Structure: Understand the hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities of each rank, from Airman Basic to Command Chief Master Sergeant. Learn about the promotion process, insignia, and requirements for advancement. Discover how the Air Forces rank structure shapes its leadership and operations.
The United States Air Force (USAF) has a hierarchical rank structure for its enlisted personnel, which is designed to recognize and reward their growing levels of expertise, responsibility, and leadership. Understanding the USAF enlisted rank structure is crucial for both aspiring airmen and current service members, as it can significantly impact their careers and opportunities for advancement.
The Importance of Rank Structure in the USAF
The rank structure serves as a framework for evaluating an airman's skills, performance, and potential for future growth. As airmen progress through the ranks, they take on more complex tasks, lead teams, and assume greater responsibility for the success of their units. The rank structure also provides a clear path for career advancement, helping airmen set goals and work towards promotions.
Overview of the USAF Enlisted Rank Structure
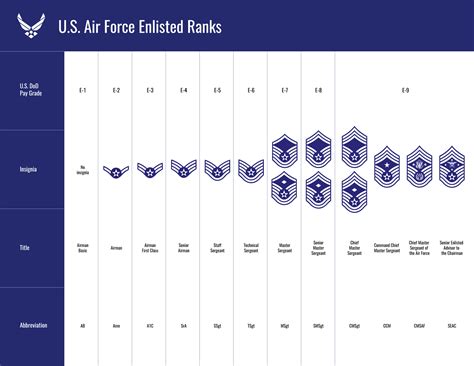
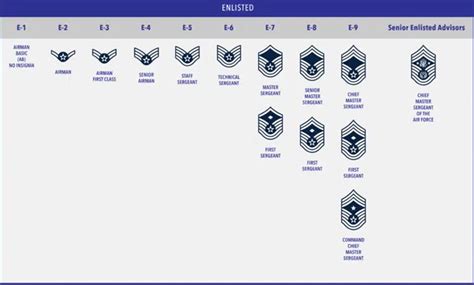
The USAF enlisted rank structure consists of nine pay grades, divided into three tiers: Junior Enlisted (E-1 to E-3), Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) (E-4 to E-6), and Senior NCO (E-7 to E-9). Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and privileges.
Junior Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-3)
-
Airman Basic (AB, E-1)
+ The entry-level rank for new airmen, with a focus on basic training and orientation. -
Airman (AMN, E-2)
+ Airmen at this rank are still in the early stages of their careers, learning their job skills and adapting to the military lifestyle. -
Airman First Class (A1C, E-3)
+ Airmen at this rank have completed their initial training and are taking on more responsibilities, such as leading small teams or mentoring junior airmen.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks (E-4 to E-6)
-
Senior Airman (SrA, E-4)
+ NCOs at this rank serve as team leaders, mentoring and guiding junior airmen, and taking on more complex tasks. -
Staff Sergeant (SSgt, E-5)
+ Staff Sergeants are experienced NCOs who lead larger teams, develop training programs, and advise senior leaders. -
Technical Sergeant (TSgt, E-6)
+ Technical Sergeants are highly skilled and experienced NCOs who serve as subject matter experts, instructors, and advisors.
Senior Non-Commissioned Officer (SNCO) Ranks (E-7 to E-9)
-
Master Sergeant (MSgt, E-7)
+ SNCOs at this rank serve as section chiefs, leading large teams, developing policies, and advising senior leaders. -
Senior Master Sergeant (SMSgt, E-8)
+ Senior Master Sergeants are highly experienced SNCOs who serve as unit superintendents, group superintendents, or squadron superintendents. -
Chief Master Sergeant (CMSgt, E-9)
+ Chief Master Sergeants are the most senior enlisted leaders, serving as wing command chiefs, group command chiefs, or as advisors to senior officers.
Factors Influencing Rank Advancement

Rank advancement in the USAF is based on a combination of factors, including:
- Performance evaluations: Airmen are evaluated on their job performance, leadership skills, and adherence to Air Force standards.
- Time-in-grade: Airmen must serve a minimum amount of time in their current rank before becoming eligible for promotion.
- Time-in-service: Airmen must have a minimum amount of total service time to be eligible for promotion.
- Education and training: Airmen must complete required education and training courses to be eligible for promotion.
- Leadership and mentorship: Airmen are evaluated on their leadership skills, ability to mentor junior airmen, and potential for future growth.
Conclusion
The USAF enlisted rank structure is a critical component of the Air Force's personnel system, providing a clear path for career advancement and recognizing the growing expertise and leadership abilities of airmen. By understanding the rank structure and the factors that influence rank advancement, airmen can set goals, work towards promotions, and achieve success in their careers.
Gallery of USAF Enlisted Rank Structure
USAF Enlisted Rank Structure Gallery