Intro
Discover the differences between Air Guard and National Guard in this comprehensive guide. Learn about the unique roles, responsibilities, and requirements of each branch, including deployment, training, and benefits. Understand the distinctions between federal and state missions, and make informed decisions about your military career. Get the facts on Air Guard vs National Guard.
The United States military is composed of several branches, each with its own unique role and responsibilities. Two of these branches are the Air National Guard and the Army National Guard, which are often confused with one another. While both are part of the National Guard, they have distinct differences in their mission, organization, and requirements.

The Air National Guard (ANG) is a reserve component of the United States Air Force, while the Army National Guard (ARNG) is a reserve component of the United States Army. Both branches are composed of citizen-soldiers who serve part-time, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while also maintaining a civilian career.
Mission and Responsibilities
The primary mission of the Air National Guard is to provide air power and support to the federal government during times of war or national emergency. This includes flying combat missions, providing airlift and tanker support, and conducting space operations. The ANG also participates in humanitarian and disaster relief efforts, both domestically and internationally.
In contrast, the Army National Guard's primary mission is to provide ground troops and support to the federal government during times of war or national emergency. This includes conducting combat operations, peacekeeping, and humanitarian missions. The ARNG also plays a critical role in homeland defense and domestic emergency response.
Organization and Structure
The Air National Guard is organized into wings, groups, and squadrons, similar to the active-duty Air Force. ANG units are typically stationed at airports and air bases, and are equipped with a variety of aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters.
The Army National Guard, on the other hand, is organized into brigades, battalions, and companies, similar to the active-duty Army. ARNG units are typically stationed at armories and training centers, and are equipped with a variety of vehicles, including tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, and trucks.

Requirements and Training
To join the Air National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 39, and meeting physical and medical standards. ANG members must also complete basic training, also known as Basic Military Training (BMT), and technical training in their specific career field.
Similarly, to join the Army National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting physical and medical standards. ARNG members must also complete basic training, also known as Basic Combat Training (BCT), and advanced individual training (AIT) in their specific military occupational specialty (MOS).
Benefits and Pay
Both the Air National Guard and the Army National Guard offer a range of benefits, including education assistance, medical and dental care, and access to military facilities and services. ANG and ARNG members also receive pay and allowances for their service, including drill pay, annual training pay, and deployment pay.

Deployment and Service
ANG and ARNG members can be deployed in support of federal missions, including combat operations, peacekeeping, and humanitarian missions. They can also be called upon to serve in state and local emergencies, such as natural disasters and civil unrest.
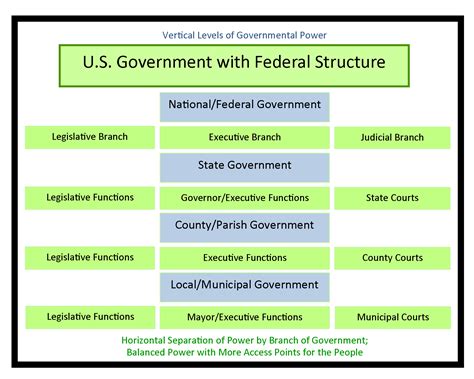
State and Federal Roles
The Air National Guard and the Army National Guard have both state and federal roles. In their state role, ANG and ARNG units can be called upon to support state and local authorities during emergencies and disasters. In their federal role, ANG and ARNG units can be deployed in support of federal missions, including combat operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the Air National Guard and the Army National Guard share some similarities, they have distinct differences in their mission, organization, and requirements. Both branches offer a range of benefits and opportunities for service, and play critical roles in supporting national defense and homeland security.
Air Guard Vs National Guard Image Gallery










We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the differences between the Air National Guard and the Army National Guard. Both branches offer unique opportunities for service and can be a rewarding way to serve one's country while also pursuing a civilian career.
