Master the art of air-to-air refueling with expert techniques and cutting-edge technology. Discover the importance of precision and timing in aerial refueling, and explore the latest advancements in tanker and receiver aircraft systems. Learn how to optimize refueling operations for safe and efficient mission execution.
Air-to-air refueling, also known as aerial refueling, is a complex and highly specialized process that requires great skill and precision. This technique allows military aircraft to extend their range and endurance, making it a crucial aspect of modern airpower. In this article, we will delve into the world of air-to-air refueling, exploring the techniques and technology that make it possible.
Introduction to Air-to-Air Refueling

Air-to-air refueling has been in use since the 1920s, but it wasn't until the 1950s that it became a standard practice in military aviation. The technique involves transferring fuel from a tanker aircraft to a receiver aircraft while both are in flight. This process requires a high degree of coordination and communication between the two aircraft, as well as a great deal of skill and training on the part of the pilots and aircrew.
The Basics of Air-to-Air Refueling

There are two main types of air-to-air refueling: probe-and-drogue and boom-and-receptacle. The probe-and-drogue system involves a tanker aircraft trailing a hose with a cone-shaped drogue on the end. The receiver aircraft then extends a probe to connect with the drogue, allowing fuel to flow. The boom-and-receptacle system, on the other hand, uses a rigid boom that extends from the tanker aircraft to a receptacle on the receiver aircraft.
Probe-and-Drogue Refueling
The probe-and-drogue system is the most common method of air-to-air refueling. It is used by a wide range of military aircraft, including fighter jets, bombers, and transport planes. The system is relatively simple and requires minimal equipment, making it a cost-effective option for many air forces.
Boom-and-Receptacle Refueling
The boom-and-receptacle system is used by some military aircraft, including the US Air Force's KC-135 Stratotanker and the Royal Air Force's Voyager tanker. This system is more complex and requires a higher degree of precision than the probe-and-drogue system, but it offers higher fuel transfer rates and greater flexibility.
The Technology Behind Air-to-Air Refueling

Air-to-air refueling relies on a range of advanced technologies, including precision navigation, communication systems, and fuel transfer equipment. The tanker aircraft is equipped with a range of sensors and computers that allow it to track the receiver aircraft and guide the fuel transfer process.
Navigation and Communication Systems
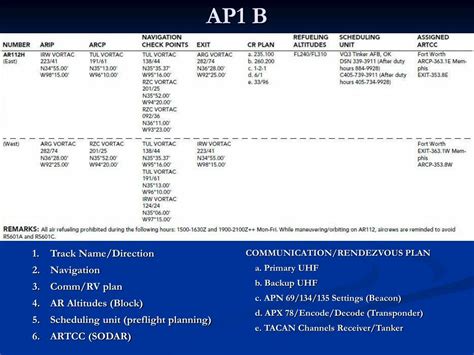
The navigation and communication systems used in air-to-air refueling are highly advanced and require a high degree of precision. The tanker aircraft uses a range of sensors, including GPS and radar, to track the receiver aircraft and guide the fuel transfer process. The communication systems used in air-to-air refueling include radio and data links, which allow the tanker and receiver aircraft to communicate and coordinate the refueling process.
Fuel Transfer Equipment
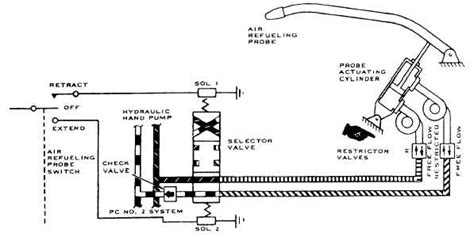
The fuel transfer equipment used in air-to-air refueling is highly specialized and requires a great deal of maintenance and upkeep. The equipment includes the hose and drogue or boom, as well as the pumps and valves that control the fuel flow.
Techniques for Successful Air-to-Air Refueling

Successful air-to-air refueling requires a great deal of skill and training on the part of the pilots and aircrew. The techniques used in air-to-air refueling include formation flying, precision navigation, and communication.
Formation Flying
Formation flying is a critical aspect of air-to-air refueling. The receiver aircraft must fly in close formation with the tanker aircraft, following precise instructions from the tanker's crew. The receiver aircraft must also be able to adjust its speed and altitude to match the tanker's.
Precision Navigation
Precision navigation is also essential for successful air-to-air refueling. The tanker aircraft must be able to track the receiver aircraft and guide it into position for refueling. The receiver aircraft must also be able to navigate to the correct position and altitude.
Communication
Communication is critical in air-to-air refueling. The tanker and receiver aircraft must be able to communicate clearly and precisely, using standardized protocols and procedures.
Challenges and Risks of Air-to-Air Refueling

Air-to-air refueling is a complex and challenging process that carries a range of risks. The risks include collision, fuel spills, and equipment failure.
Collision Risks
One of the most significant risks of air-to-air refueling is collision. The receiver aircraft must fly in close formation with the tanker aircraft, which increases the risk of collision.
Fuel Spills
Fuel spills are another risk of air-to-air refueling. If the fuel transfer process is not managed correctly, fuel can spill from the hose or drogue, posing a risk to the environment and the aircraft.
Equipment Failure
Equipment failure is also a risk of air-to-air refueling. The fuel transfer equipment is highly complex and requires a great deal of maintenance and upkeep. If the equipment fails, it can pose a significant risk to the aircraft and the crew.
Gallery of Air-to-Air Refueling Images
Air-to-Air Refueling Image Gallery







Conclusion
Air-to-air refueling is a complex and challenging process that requires great skill and precision. The techniques and technology used in air-to-air refueling are highly advanced and require a great deal of training and practice. By understanding the basics of air-to-air refueling, the technology behind it, and the challenges and risks involved, we can appreciate the importance of this critical aspect of modern airpower.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of air-to-air refueling. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share your thoughts and experiences with us, and let's keep the conversation going!
