Intro
Take to the skies with a rewarding career as an Air Traffic Controller. Learn the 5 simple steps to become an ATC, from meeting basic qualifications to acing the FAA exam. Discover the skills and training required to navigate the complex world of air traffic control, ensuring safe takeoffs and landings. Start your journey now!
Are you fascinated by the world of aviation and interested in a career that requires strong communication skills, quick thinking, and attention to detail? Then becoming an air traffic controller (ATC) might be the perfect profession for you. As an ATC, you will be responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the National Airspace System. Here's how you can become an air traffic controller in 5 simple steps.

Step 1: Meet the Basic Requirements
To be eligible to apply for the Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) Air Traffic Control (ATC) program, you must meet certain basic requirements. These include:
- Being at least 18 years old
- Being a U.S. citizen
- Passing a physical exam
- Passing a psychological evaluation
- Having a high school diploma or equivalent
- Having three years of progressively responsible work experience, or four years of college
- Being willing to work varying shifts, including nights, weekends, and holidays
Step 2: Get the Right Education and Training
While a college degree is not required to become an ATC, having one can be beneficial. The FAA recommends that applicants have a degree in a field such as air traffic control, aviation, or a related field. Additionally, the FAA offers a training program at the Air Traffic Control Academy in Oklahoma City, OK. The program includes both classroom and simulation training and is designed to prepare students for the demands of the job.
Some of the topics covered in the training program include:
- Air traffic control procedures and regulations
- Aircraft performance and weather
- Communication techniques
- Decision-making and problem-solving

Step 3: Pass the FAA Pre-Employment Test
The FAA pre-employment test is a computer-based test that assesses an applicant's ability to perform the duties of an ATC. The test is designed to evaluate an applicant's:
- Ability to learn and apply air traffic control procedures and regulations
- Ability to communicate effectively
- Ability to make quick and accurate decisions
- Ability to work well under pressure
Applicants who pass the pre-employment test will be invited to take the Air Traffic Selection and Training (AT-SAT) exam.
Step 4: Pass the AT-SAT Exam
The AT-SAT exam is a multiple-choice test that assesses an applicant's knowledge of air traffic control procedures and regulations. The exam includes questions on topics such as:
- Air traffic control procedures and regulations
- Aircraft performance and weather
- Communication techniques
- Decision-making and problem-solving
Applicants who pass the AT-SAT exam will be invited to an interview with the FAA.

Step 5: Complete the FAA Training Program
Applicants who are selected for the FAA training program will attend the Air Traffic Control Academy in Oklahoma City, OK. The program includes both classroom and simulation training and is designed to prepare students for the demands of the job.
After completing the training program, students will be assigned to an air traffic control facility where they will work under the supervision of an experienced ATC. Once they have gained sufficient experience and have demonstrated their ability to perform the duties of an ATC, they will be certified as a developmental controller.
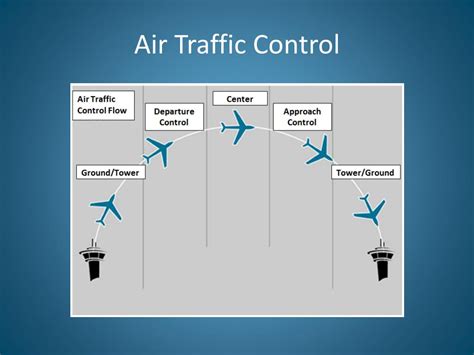
Types of Air Traffic Controllers
There are several types of air traffic controllers, each with different responsibilities and requirements. Some of the most common types of ATCs include:
- Tower Controllers: Tower controllers work in airport control towers and are responsible for clearing aircraft for takeoff and landing, as well as issuing instructions to pilots.
- Approach/Departure Controllers: Approach/departure controllers work in approach/departure control facilities and are responsible for guiding aircraft to and from airports.
- Center Controllers: Center controllers work in air route traffic control centers and are responsible for guiding aircraft through the National Airspace System.
Salary and Benefits
Air traffic controllers are among the highest-paid professionals in the aviation industry. According to the FAA, the median annual salary for air traffic controllers is around $62,900. However, salaries can range from around $40,000 to over $170,000 per year, depending on experience and location.
In addition to their salary, air traffic controllers also receive a range of benefits, including:
- Health Insurance: The FAA provides air traffic controllers with comprehensive health insurance, including medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Retirement Benefits: Air traffic controllers are eligible for retirement benefits through the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS).
- Paid Time Off: Air traffic controllers receive paid time off, including vacation days, sick leave, and holidays.

Challenges and Opportunities
While being an air traffic controller can be a rewarding and challenging career, it is not without its challenges. Some of the challenges that air traffic controllers face include:
- High Levels of Stress: Air traffic controllers work in a high-stress environment, where they must make quick and accurate decisions to ensure the safety of aircraft and passengers.
- Long Hours and Variable Schedules: Air traffic controllers often work long hours and variable schedules, including nights, weekends, and holidays.
- Continuous Training and Certification: Air traffic controllers must undergo continuous training and certification to stay up-to-date with the latest procedures and regulations.
Despite these challenges, being an air traffic controller can also provide a range of opportunities, including:
- Career Advancement: Air traffic controllers can advance to positions of increasing responsibility, including supervisory and management roles.
- Specialized Training: Air traffic controllers can receive specialized training in areas such as approach/departure control, tower control, and center control.
- Opportunities for Advancement: Air traffic controllers can also advance to positions in other areas of the FAA, such as aviation safety and security.
Air Traffic Controller Image Gallery









Conclusion
Becoming an air traffic controller is a challenging and rewarding career that requires strong communication skills, quick thinking, and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined above, you can begin your journey to becoming a certified air traffic controller. Remember to always follow your dreams and never give up on your goals. With hard work and determination, you can achieve anything you set your mind to.
