Intro
Mastering airway management is a crucial skill for healthcare professionals, particularly those working in emergency and critical care settings. Effective airway management can mean the difference between life and death, making it essential to stay up-to-date with the latest techniques and best practices. In this article, we'll explore the five steps to master airway management using the ATI template, a widely recognized and respected framework for airway management.
The Importance of Airway Management
Airway management is a high-stakes, high-reward skill that requires a deep understanding of human anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology. When done correctly, airway management can restore oxygenation and ventilation to a patient in distress, preventing complications and improving outcomes. However, when done incorrectly, airway management can lead to serious consequences, including brain damage, cardiac arrest, and even death.
Step 1: Preparation is Key
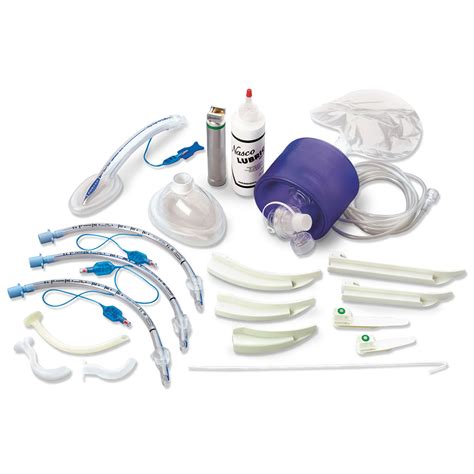
Preparation is the first step in mastering airway management with the ATI template. This involves having the right equipment, knowledge, and skills to manage any airway scenario. Healthcare professionals should familiarize themselves with the ATI template, which includes the following components:
- Airway assessment: Evaluating the patient's airway to determine the best course of action.
- Airway management: Using various techniques and devices to establish and maintain a patent airway.
- Airway protection: Protecting the airway from obstruction, aspiration, and other complications.
Step 2: Airway Assessment
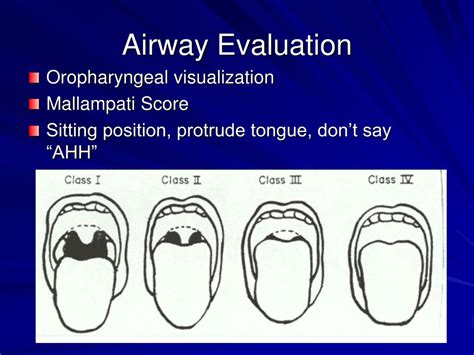
Airway assessment is a critical component of the ATI template, and it involves evaluating the patient's airway to determine the best course of action. This includes assessing the patient's:
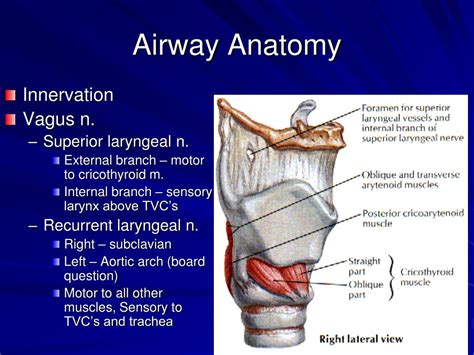
- Airway anatomy: Evaluating the patient's airway anatomy to identify potential difficulties or complications.
- Airway pathology: Identifying any underlying airway pathology, such as tumors or foreign bodies.
- Airway physiology: Understanding the patient's airway physiology, including their respiratory rate, tidal volume, and oxygen saturation.
Components of Airway Assessment
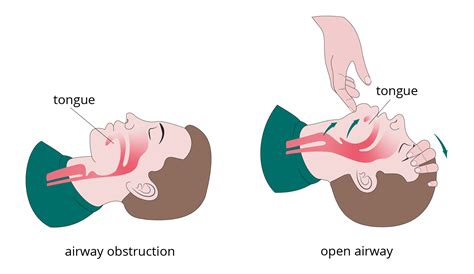
- Visual inspection: Visually inspecting the patient's airway to identify any obvious obstructions or complications.
- Palpation: Palpating the patient's airway to identify any abnormalities or tenderness.
- Auscultation: Auscultating the patient's airway to identify any abnormal sounds or breath sounds.
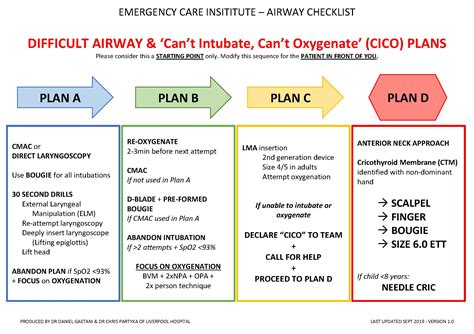
Step 3: Airway Management
Airway management is the third step in the ATI template, and it involves using various techniques and devices to establish and maintain a patent airway. This includes:
- Bag-valve-mask ventilation: Using a bag-valve-mask device to provide positive pressure ventilation.
- Endotracheal intubation: Inserting an endotracheal tube into the patient's airway to establish a secure airway.
- Supraglottic airway devices: Using supraglottic airway devices, such as laryngeal mask airways or esophageal-tracheal Combitubes.
Step 4: Airway Protection
Airway protection is the fourth step in the ATI template, and it involves protecting the airway from obstruction, aspiration, and other complications. This includes:
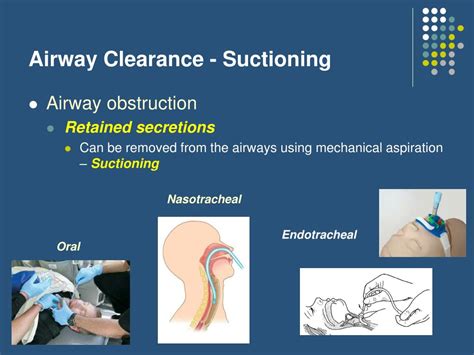
- Aspiration prevention: Using techniques and devices to prevent aspiration, such as suctioning and using aspiration precaution devices.
- Airway clearance: Using techniques and devices to clear the airway of secretions and debris.
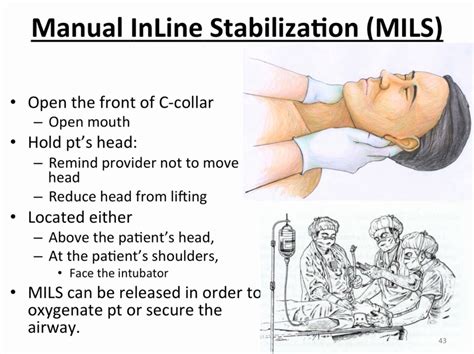
- Airway stabilization: Using techniques and devices to stabilize the airway, such as using airway stabilization devices or securing the endotracheal tube.
Step 5: Ongoing Evaluation and Adjustment
The final step in the ATI template is ongoing evaluation and adjustment. This involves continuously evaluating the patient's airway and adjusting the airway management plan as needed. This includes:
- Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the patient's airway and vital signs to identify any changes or complications.
- Adjusting: Adjusting the airway management plan as needed to ensure the patient's airway remains patent and protected.
Gallery of Airway Management Images
Airway Management Image Gallery


By following the five steps outlined in the ATI template, healthcare professionals can master airway management and provide high-quality care to their patients. Remember, airway management is a high-stakes, high-reward skill that requires continuous practice, education, and evaluation. Stay up-to-date with the latest techniques and best practices, and always prioritize patient safety and well-being.
