Intro
Elevated Alk Phos levels diagnosed with ICD 10 codes, indicating liver or bone disorders, requiring medical attention and treatment to prevent complications like osteomalacia or liver disease.
Elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels in the blood can be an indicator of various health issues, ranging from bone disorders to liver diseases. The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), provides a standardized system for coding and classifying these conditions. Understanding the different ways ALP can be elevated and their corresponding ICD-10 codes is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and billing purposes.
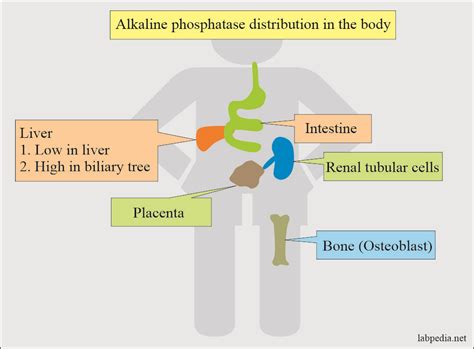
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme found in several tissues throughout the body, including the liver, bones, kidneys, and digestive system. High levels of ALP in the blood can signify conditions such as bone growth, liver damage, or certain types of cancer. The interpretation of ALP levels must be done in conjunction with other clinical findings and laboratory tests to determine the underlying cause.
The diagnosis and coding of conditions related to elevated ALP levels involve a comprehensive approach, considering the patient's symptoms, medical history, and the results of diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers must be aware of the various ICD-10 codes that correspond to different conditions associated with elevated ALP levels to ensure accurate documentation and billing. This article will delve into five ways ALP can be elevated, their causes, symptoms, and the corresponding ICD-10 codes, providing a comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to understand these conditions better.
Introduction to Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase

Elevated alkaline phosphatase levels can be due to a variety of reasons, including but not limited to, bone disorders, liver diseases, and certain types of cancer. The enzyme is produced in higher amounts during periods of bone growth or when the body is repairing bone tissue. Therefore, children and adolescents, who are still growing, naturally have higher levels of ALP than adults.
Causes of Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase
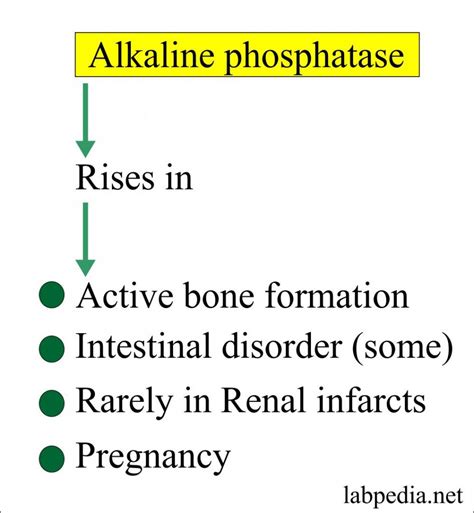
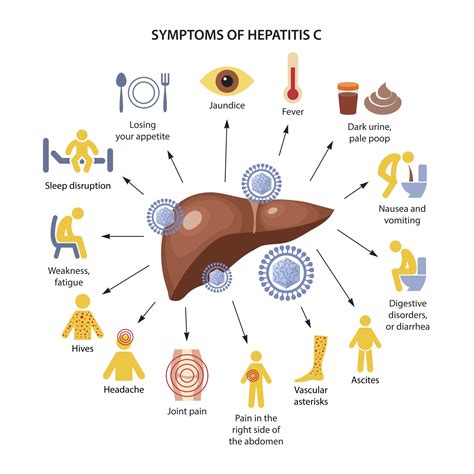
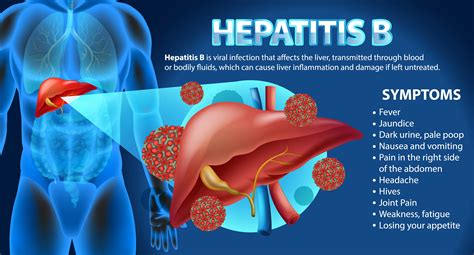
The causes of elevated ALP can be broadly categorized into bone-related and non-bone related conditions. Bone-related conditions include diseases that affect bone growth or density, such as Paget's disease, osteomalacia, and rickets. Non-bone related conditions primarily involve liver diseases, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and bile duct obstruction, which can lead to an increase in ALP levels.
Bone-Related Conditions
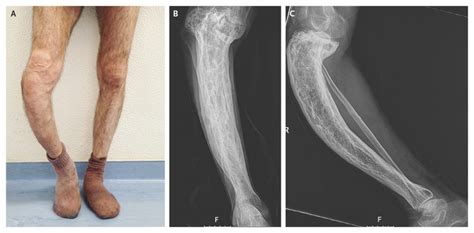
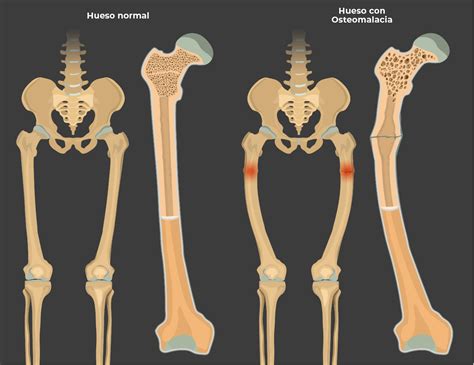
Bone-related conditions that lead to elevated ALP levels often involve diseases or disorders that affect bone metabolism or density. These can include: - Paget's disease of bone, a chronic condition that can result in enlarged and misshapen bones due to abnormal bone destruction and regrowth. - Osteomalacia, which is characterized by the softening of bones due to a deficiency of vitamin D or a problem with the body's ability to break down and use this vitamin. - Rickets, a condition found in children where the bones become soft and weak, often due to severe deficiency in vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate.Non-Bone Related Conditions
Non-bone related conditions that cause elevated ALP levels are predominantly associated with liver and biliary diseases. These conditions can lead to an increase in the liver's production of ALP, which then enters the bloodstream. Examples include:
- Hepatitis, which is inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections, although other factors like alcohol use, toxins, and certain medications can also be responsible.
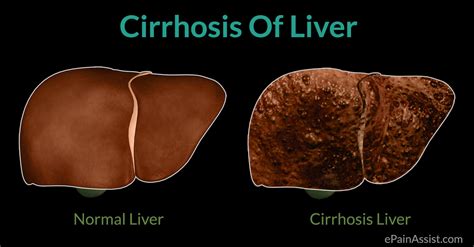
- Cirrhosis, a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism.
- Bile duct obstruction, which can be due to gallstones, tumors, or other conditions that block the bile ducts, leading to a buildup of bile and causing liver damage.
Liver Diseases and Elevated ALP
Liver diseases are a significant cause of elevated ALP levels. The liver produces ALP, and any condition that affects liver function or causes liver damage can lead to increased levels of this enzyme in the blood. The diagnosis of liver diseases involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests (including liver function tests), and sometimes imaging studies or liver biopsy.ICD-10 Codes for Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase Conditions

The ICD-10 coding system provides specific codes for various conditions associated with elevated ALP levels. For instance:
- Paget's disease of bone is coded as M88.
- Osteomalacia is coded as M83.
- Hepatitis is coded under the category K70-K77, depending on the type and cause.
- Cirrhosis of the liver is coded as K74, with more specific codes for different types of cirrhosis.
- Bile duct obstruction can be coded under the category K80-K87, depending on the cause and specifics of the obstruction.
Importance of Accurate ICD-10 Coding
Accurate ICD-10 coding is crucial for the proper documentation of patient conditions, insurance billing, and statistical analysis of diseases. Healthcare providers must ensure that they use the most specific and appropriate codes for the conditions they diagnose and treat. This not only aids in the management of patient care but also contributes to public health surveillance and research by providing detailed data on the prevalence and treatment outcomes of various conditions.Treatment and Management of Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase
The treatment and management of conditions associated with elevated ALP levels depend on the underlying cause. For bone-related conditions, treatment may involve addressing the underlying deficiency (such as vitamin D and calcium supplements for osteomalacia) or managing the symptoms and progression of the disease (as in the case of Paget's disease). For liver diseases, treatment can range from medications to manage symptoms and slow disease progression, to more invasive procedures like liver transplantation in severe cases.
Role of Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in the management of conditions associated with elevated ALP levels. For example, individuals with liver diseases may benefit from avoiding alcohol, losing weight if obese, and following a healthy diet. Similarly, ensuring adequate intake of vitamin D and calcium through diet or supplements can help manage bone health and prevent conditions like osteomalacia.Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase Image Gallery
In conclusion, elevated alkaline phosphatase levels can be indicative of a range of health conditions, from bone disorders to liver diseases. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and corresponding ICD-10 codes for these conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and management. By recognizing the importance of elevated ALP and taking appropriate steps for diagnosis and treatment, individuals can better manage their health and prevent complications associated with these conditions. We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about elevated alkaline phosphatase and its related conditions, and to explore the resources provided for further information and support.
