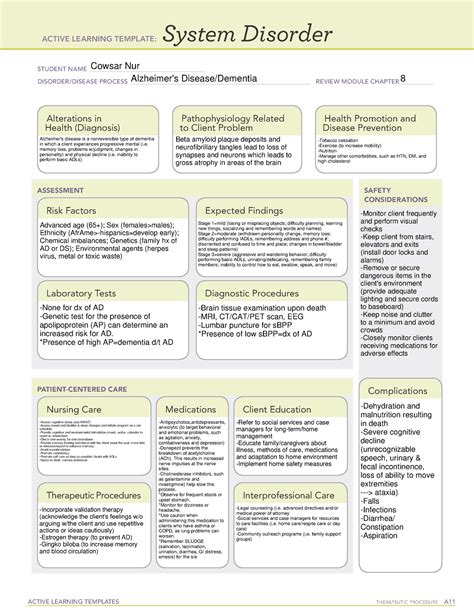
Intro
Unlock the complexities of Alzheimers disease with a comprehensive 5-system disorder template. Learn how this multifaceted condition affects cognition, emotions, behavior, physical health, and social interactions. Discover the interconnected systems and subtle nuances of Alzheimers, empowering you to better understand and support those affected by this neurodegenerative disorder.
Alzheimer's disease is a complex and multifaceted disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a progressive neurological disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, leading to problems with communication, problem-solving, and daily activities. While the exact causes of Alzheimer's are still not fully understood, research has shed light on the various systems involved in the development and progression of the disease. In this article, we will explore the 5-system disorder template of Alzheimer's, highlighting the key factors that contribute to its development.
The 5-system disorder template of Alzheimer's consists of the following systems:
System 1: The Amyloid System
The amyloid system is a key player in the development of Alzheimer's disease. Amyloid is a type of protein that is normally produced by the body, but in people with Alzheimer's, it is produced in excess and accumulates in the brain, forming sticky clumps called plaques. These plaques are toxic to brain cells and can lead to cell death and tissue damage.
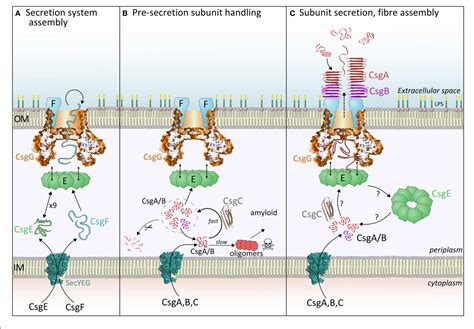
Key Features of the Amyloid System
- Excess production of amyloid protein
- Accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain
- Toxicity to brain cells and tissue damage
System 2: The Tau System
The tau system is another critical component of the 5-system disorder template of Alzheimer's. Tau is a protein that helps to stabilize microtubules, which are essential for maintaining the structure and function of brain cells. In people with Alzheimer's, tau protein becomes abnormally phosphorylated, leading to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles.

Key Features of the Tau System
- Abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein
- Formation of neurofibrillary tangles
- Disruption of microtubule structure and function
System 3: The Inflammatory System
The inflammatory system plays a significant role in the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, but in people with Alzheimer's, it becomes chronic and leads to tissue damage and cell death.
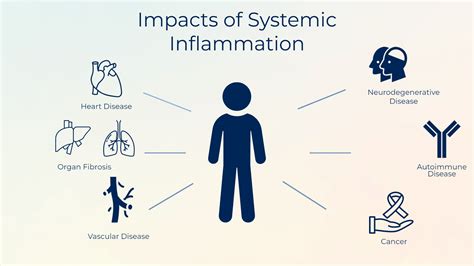
Key Features of the Inflammatory System
- Chronic inflammation in the brain
- Activation of immune cells and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines
- Tissue damage and cell death
System 4: The Oxidative Stress System
The oxidative stress system is another key factor in the development of Alzheimer's disease. Oxidative stress occurs when the body's antioxidant defenses are overwhelmed by free radicals, leading to cell damage and tissue damage.
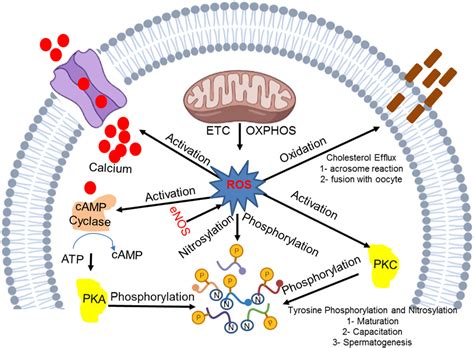
Key Features of the Oxidative Stress System
- Overproduction of free radicals
- Imbalance in antioxidant defenses
- Cell damage and tissue damage
System 5: The Hormonal System
The hormonal system is the final component of the 5-system disorder template of Alzheimer's. Hormones play a critical role in maintaining brain health, and disruptions to hormone levels and function can contribute to the development of Alzheimer's.
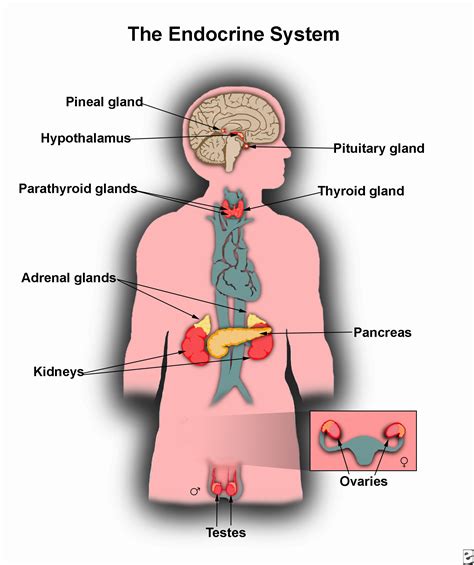
Key Features of the Hormonal System
- Disruptions to hormone levels and function
- Impact on brain health and function
- Contribution to Alzheimer's development and progression
Alzheimer's Disease Image Gallery


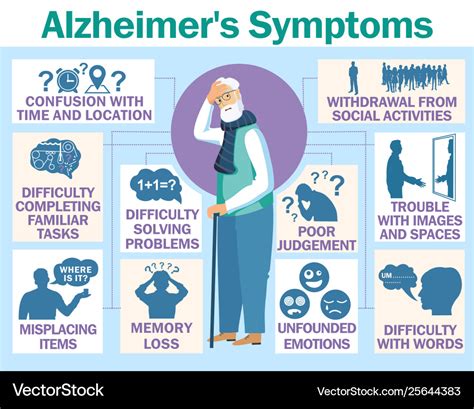



In conclusion, the 5-system disorder template of Alzheimer's provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the complex factors that contribute to the development and progression of the disease. By recognizing the key features of each system, researchers and clinicians can develop targeted interventions and therapies to prevent, diagnose, and treat Alzheimer's. As our understanding of the disease continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed and up-to-date on the latest research and breakthroughs.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Alzheimer's disease in the comments section below. What do you think are the most critical factors in understanding and addressing the disease? How can we work together to support those affected by Alzheimer's and advance our knowledge of the disease?
