Intro
Discover the underlying causes and symptoms of Amenorrhea, a hormonal disorder affecting menstrual cycles. Learn about primary and secondary Amenorrhea, its impact on fertility, and related conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders. Understand the diagnosis and treatment options available to restore regular periods and overall reproductive health.
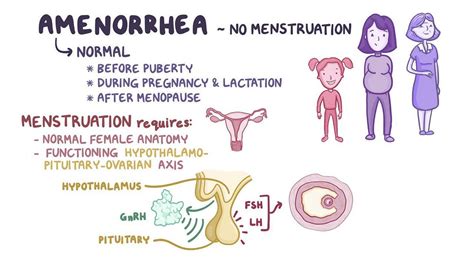
Amenorrhea, which is the absence of menstruation, is a symptom that affects many women worldwide. It can be a source of concern, anxiety, and stress for those who experience it. Understanding the causes and symptoms of amenorrhea can help individuals seek proper medical attention and find relief from this condition.
What is Amenorrhea?
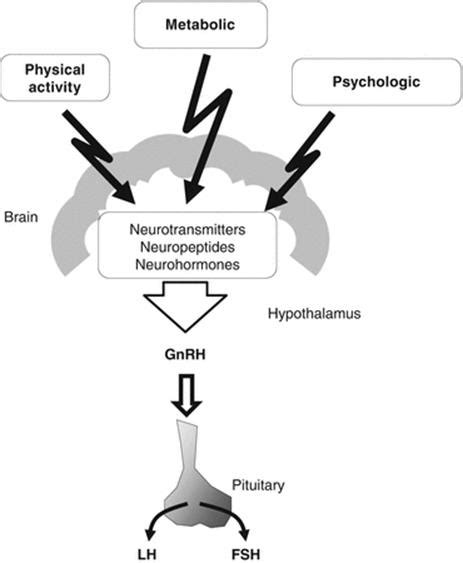
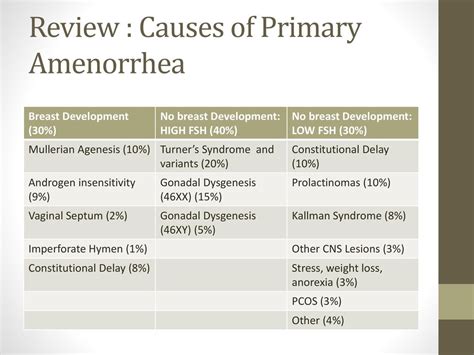
Amenorrhea is a menstrual disorder characterized by the absence of menstruation. There are two types of amenorrhea: primary and secondary. Primary amenorrhea occurs when a woman has never experienced menstruation by the age of 16, while secondary amenorrhea occurs when a woman has previously menstruated but experiences an absence of menstruation for three months or more.
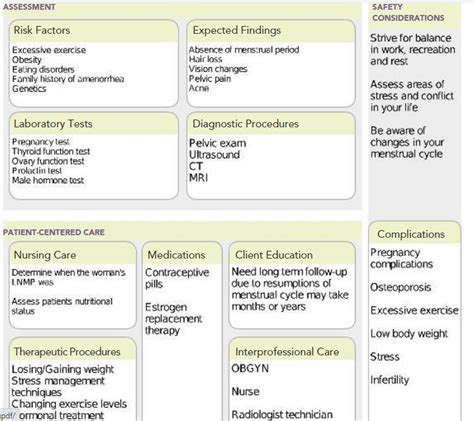
Causes of Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance is one of the primary causes of amenorrhea. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone play a crucial role in regulating menstruation. An imbalance of these hormones can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to amenorrhea.
Genetic Disorders
Certain genetic disorders, such as Turner syndrome, can cause amenorrhea. Turner syndrome is a condition that affects women and is characterized by the absence of one X chromosome.
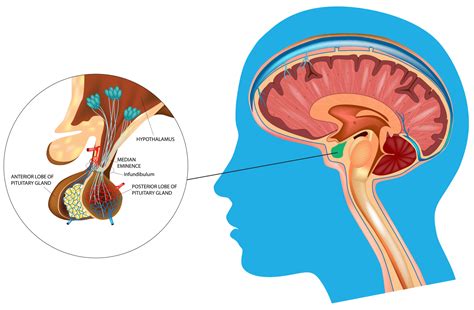
Pituitary Gland Problems
The pituitary gland regulates hormone production in the body. Any problems with the pituitary gland, such as a tumor or hypoplasia, can lead to hormonal imbalance and amenorrhea.
Thyroid Problems
Thyroid problems, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can cause amenorrhea. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, and any imbalance can disrupt the menstrual cycle.
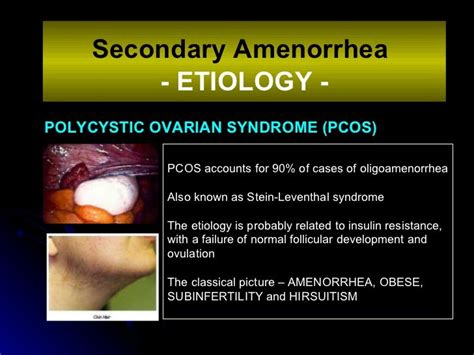
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by cysts on the ovaries, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalance, which can lead to amenorrhea.
Other Causes
Other causes of amenorrhea include:
- Stress: Stress can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to amenorrhea.
- Weight loss or gain: Significant weight loss or gain can disrupt hormone production and lead to amenorrhea.
- Exercise: Excessive exercise can disrupt hormone production and lead to amenorrhea.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants and blood thinners, can cause amenorrhea.
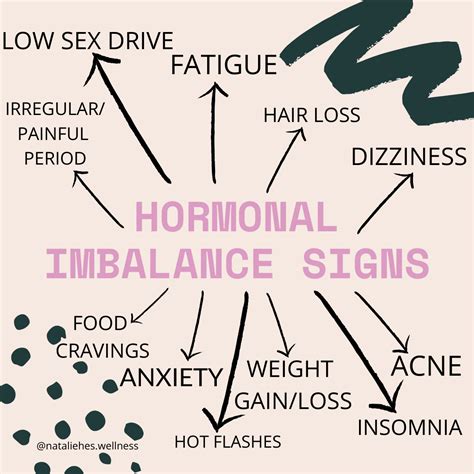
Symptoms of Amenorrhea
The symptoms of amenorrhea can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
Absence of Menstruation
The most obvious symptom of amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation. This can be a source of concern and anxiety for women who experience it.
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance can cause a range of symptoms, including mood swings, hot flashes, and changes in libido.
Weight Gain or Loss
Weight gain or loss can be a symptom of amenorrhea, particularly if it is caused by hormonal imbalance or thyroid problems.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of amenorrhea, particularly if it is caused by hormonal imbalance or thyroid problems.
Mood Changes
Mood changes, such as depression and anxiety, can be a symptom of amenorrhea.
Diagnosing Amenorrhea
Diagnosing amenorrhea involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The doctor may perform the following tests:
Pelvic Exam
A pelvic exam is performed to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are performed to check for hormonal imbalance and thyroid problems.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound and MRI, may be performed to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing may be performed to check for genetic disorders, such as Turner syndrome.
Treating Amenorrhea
Treating amenorrhea depends on the underlying cause. The following treatments may be recommended:
Hormonal Replacement Therapy
Hormonal replacement therapy may be recommended to regulate hormone production and stimulate menstruation.
Medications
Medications, such as antidepressants and blood thinners, may be prescribed to treat underlying conditions.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and managing stress, may be recommended to regulate hormone production and stimulate menstruation.
Surgery
Surgery may be recommended to treat underlying conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome.
Gallery of Amenorrhea Symptoms and Causes
Amenorrhea Symptoms and Causes Image Gallery




Conclusion
Amenorrhea is a complex condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the causes and symptoms of amenorrhea can help individuals seek proper medical attention and find relief from this condition. If you are experiencing symptoms of amenorrhea, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.
We encourage you to share your experiences with amenorrhea in the comments below. Have you experienced symptoms of amenorrhea? What were your symptoms, and how did you manage them? Share your story to help others understand this condition better.
Remember, amenorrhea is a treatable condition. With proper medical attention and lifestyle changes, it is possible to regulate hormone production and stimulate menstruation. Don't hesitate to seek help if you are experiencing symptoms of amenorrhea.
