Intro
Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic procedure that involves withdrawing a sample of amniotic fluid from the uterus to detect any genetic abnormalities or disorders in the fetus. This procedure is usually performed between the 15th and 20th week of pregnancy. Here are the 5 steps of the amniocentesis diagnostic procedure:
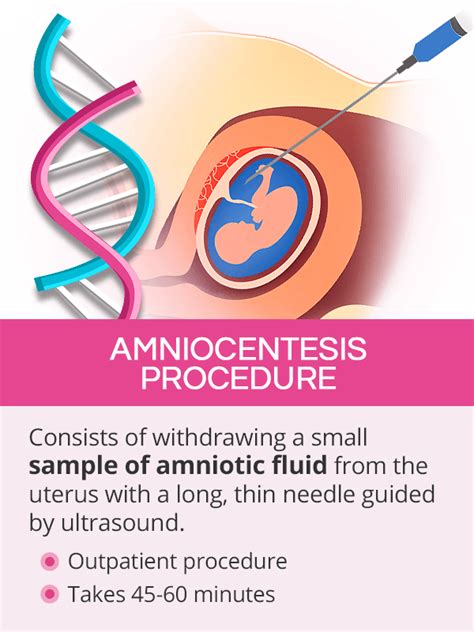
Step 1: Preparation and Counseling
Before the procedure, the patient will undergo a thorough counseling session with a genetic counselor or a medical professional. The purpose of this session is to inform the patient about the risks and benefits of the procedure, as well as to discuss the possible outcomes. The patient will also be asked to provide a medical history and undergo a physical examination to ensure that they are suitable for the procedure.
Step 2: Ultrasound Examination
Before the amniocentesis procedure, an ultrasound examination will be performed to confirm the gestational age of the fetus and to check for any multiple pregnancies. The ultrasound will also help the medical professional to locate the position of the fetus and the placenta.
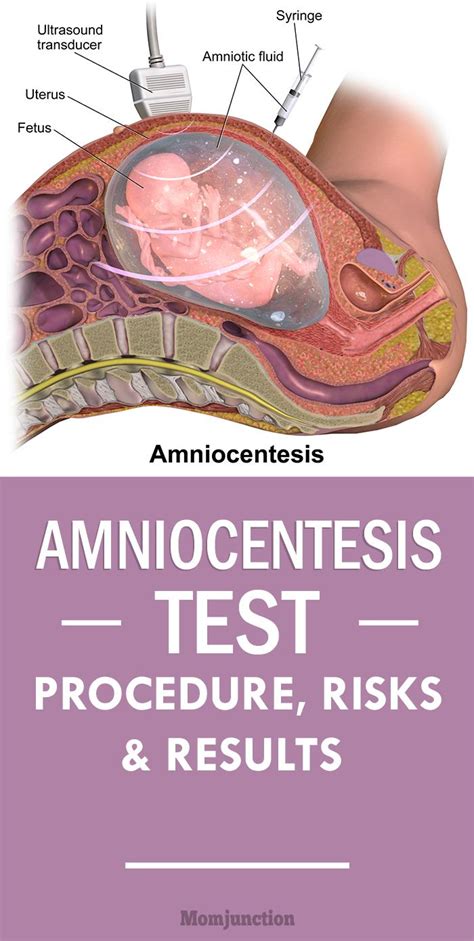
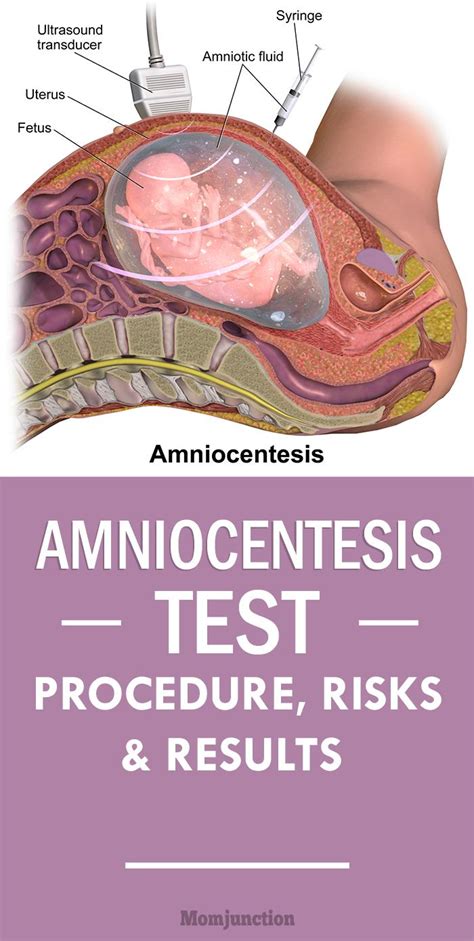
Ultrasound-Guided Amniocentesis
During the procedure, the medical professional will use the ultrasound images to guide the insertion of the needle into the uterus. This ensures that the needle is inserted into the correct position and that the amniotic fluid is withdrawn safely.
Step 3: Insertion of the Needle
The medical professional will insert a thin needle through the abdomen and into the uterus, guided by the ultrasound images. The needle is inserted through the skin and into the amniotic sac, which contains the amniotic fluid.

Step 4: Withdrawal of Amniotic Fluid
Once the needle is in place, a sample of amniotic fluid will be withdrawn into a syringe. The fluid will then be sent to a laboratory for analysis. The sample will be tested for chromosomal abnormalities, genetic disorders, and infections.
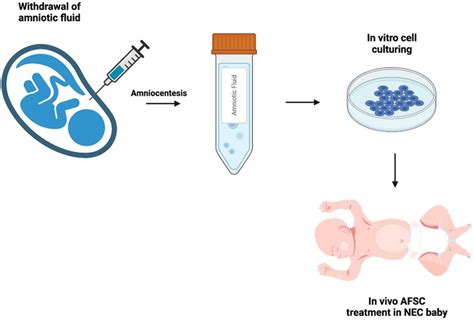
Step 5: Follow-Up and Results
After the procedure, the patient will be monitored for any complications, such as bleeding or cramping. The results of the amniocentesis will be available within 1-2 weeks and will be discussed with the patient by a genetic counselor or a medical professional. If any abnormalities are detected, the patient will be counseled on the options available.
Risks and Complications
As with any medical procedure, there are risks and complications associated with amniocentesis. These include:
- Miscarriage: The risk of miscarriage is estimated to be around 0.1-0.3%.
- Infection: There is a small risk of infection, which can be treated with antibiotics.
- Bleeding: There is a small risk of bleeding, which can be treated with rest and medication.
- Fetal injury: There is a small risk of fetal injury, which can be treated with rest and medication.
Benefits of Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about the health of the fetus. The benefits of amniocentesis include:
- Detection of chromosomal abnormalities: Amniocentesis can detect chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
- Detection of genetic disorders: Amniocentesis can detect genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia.
- Detection of infections: Amniocentesis can detect infections, such as rubella.
- Reassurance: Amniocentesis can provide reassurance to parents that their baby is healthy.
Amniocentesis Image Gallery







We hope this article has provided valuable information about the 5 steps of the amniocentesis diagnostic procedure. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below.
