Intro
Master Amoxicillin administration with our comprehensive medication template for nurses. Learn about dosage, side effects, and patient education for this widely-used antibiotic. Get expert guidance on contraindications, interactions, and monitoring parameters to ensure safe and effective patient care.
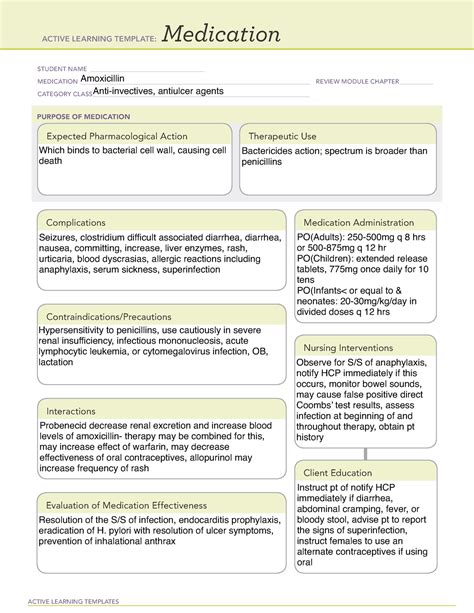
As a nurse, it's essential to have a thorough understanding of amoxicillin medication, including its uses, dosages, side effects, and potential interactions. Amoxicillin is a widely prescribed antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin class, and it's commonly used to treat various bacterial infections. In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive guide for nurses on amoxicillin medication, covering its mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, and more.
What is Amoxicillin?
Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. It's a semi-synthetic derivative of ampicillin and is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid suspensions.
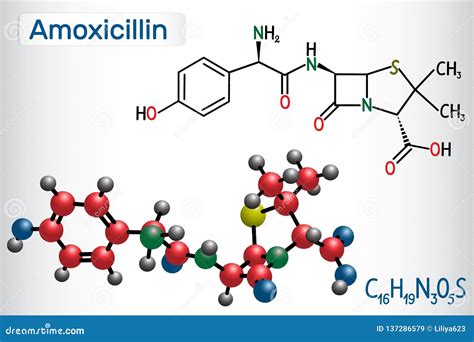
Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin exerts its antibacterial effect by binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) on the bacterial cell wall. This binding inhibits the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a critical component of the bacterial cell wall. As a result, the bacterial cell wall is weakened, leading to cell lysis and death.
Indications
Amoxicillin is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections, including:
- Upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), such as pharyngitis and tonsillitis
- Lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs), such as bronchitis and pneumonia
- Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), such as cellulitis and abscesses
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs), such as cystitis and pyelonephritis
- Gastrointestinal infections, such as gastritis and enteritis
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of amoxicillin varies depending on the age, weight, and condition of the patient. Here are some general guidelines:
- Adults: 250-500 mg every 8-12 hours
- Children: 25-50 mg/kg/day divided into 2-3 doses
- Neonates: 10-20 mg/kg/day divided into 2-3 doses
Amoxicillin can be administered orally or intravenously. The oral form is usually preferred, but the intravenous form may be used in severe cases or when the patient is unable to take oral medication.
Contraindications
Amoxicillin is contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to amoxicillin or other penicillins
- Severe renal impairment
- Hepatic dysfunction
- Mononucleosis
- Viral infections, such as the common cold or flu
Side Effects
Common side effects of amoxicillin include:
- Gastrointestinal upset, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, and urticaria
- Central nervous system effects, such as headache, dizziness, and seizures
Serious side effects of amoxicillin include:
- Anaphylaxis
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Interactions
Amoxicillin can interact with other medications, including:
- Antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide
- Warfarin
- Methotrexate
- Probenecid
Pregnancy and Lactation
Amoxicillin is classified as a category B medication, meaning that it is generally safe to use during pregnancy. However, it should be used with caution and only when the benefits outweigh the risks.
Amoxicillin is excreted in breast milk, and its use during lactation should be avoided. If amoxicillin is necessary, the patient should be advised to stop breastfeeding.
Pediatric and Geriatric Considerations
Amoxicillin is generally safe to use in children and the elderly. However, the dosage may need to be adjusted based on the patient's age, weight, and renal function.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Patients receiving amoxicillin should be monitored for:
- Clinical response to treatment
- Adverse reactions, such as allergic reactions and gastrointestinal upset
- Renal function, especially in patients with pre-existing renal impairment
- Hepatic function, especially in patients with pre-existing hepatic dysfunction
Gallery of Amoxicillin-Related Images
Amoxicillin Medication Image Gallery






Conclusion
Amoxicillin is a widely used antibiotic that is effective against a range of bacterial infections. As a nurse, it's essential to have a thorough understanding of amoxicillin's uses, dosages, side effects, and potential interactions. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, nurses can ensure safe and effective use of amoxicillin in their patients.
Call to Action
We encourage readers to share their experiences with amoxicillin medication in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about amoxicillin or any other medication, please don't hesitate to reach out to us.
