Intro
Unlock the mysteries of Anemia System Disorder, a condition affecting millions worldwide. Discover its underlying causes, recognize the telltale symptoms, and explore effective treatment options. Learn how to manage iron deficiency, vitamin deficiencies, and chronic diseases that contribute to anemia, and take the first step towards a healthier you.
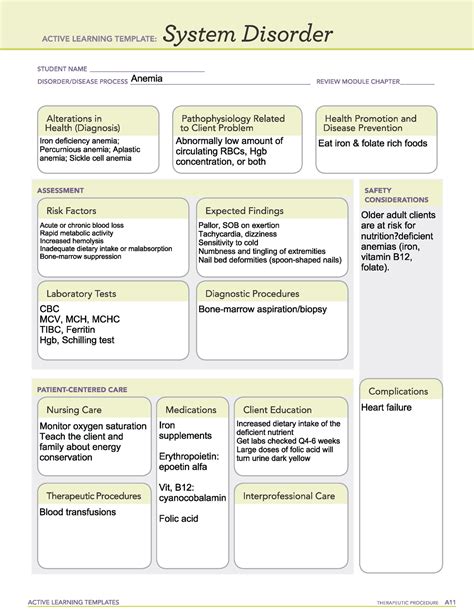
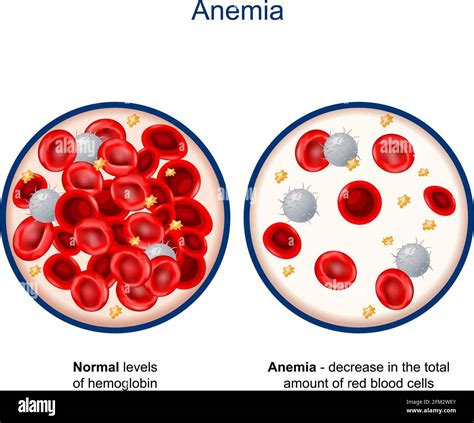
Anemia is a common health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When there is not enough hemoglobin or red blood cells, the body's tissues and organs may not receive enough oxygen, leading to various health problems.
Anemia can be acute or chronic, and it can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, nutrition, chronic diseases, and certain medications. Women, especially those of childbearing age, are at higher risk of developing anemia due to menstrual blood loss. Additionally, individuals with chronic diseases such as kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer are also at higher risk of developing anemia.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of anemia is crucial for early detection and treatment. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anemia, as well as provide tips on how to manage the condition.
Causes of Anemia
Anemia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
-
Genetics
Anemia can be inherited from one's parents. Certain genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia and thalassemia, can affect the production of hemoglobin and red blood cells.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies
A diet that lacks essential nutrients, such as iron, vitamin B12, and folate, can lead to anemia. Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia worldwide.
-
Chronic Diseases
Certain chronic diseases, such as kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer, can lead to anemia.
-
Medications
Certain medications, such as anticoagulants and anti-inflammatory medications, can increase the risk of anemia.
-
Menstrual Blood Loss
Women, especially those of childbearing age, are at higher risk of developing anemia due to menstrual blood loss.
Symptoms of Anemia
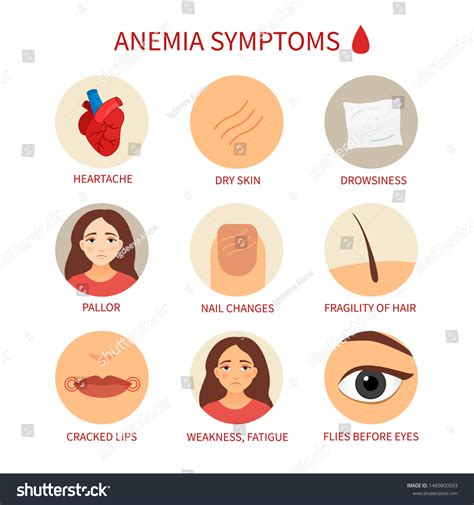
The symptoms of anemia can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of anemia include:
-
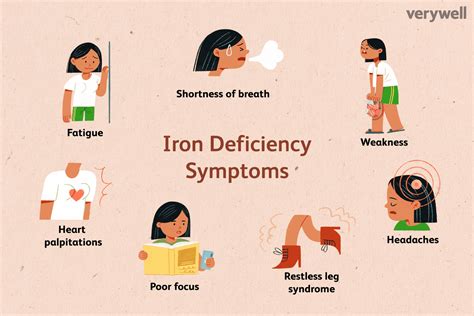
Fatigue and Weakness
Anemia can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
-
Pale Skin
Anemia can cause pale skin, lips, and nails due to a lack of hemoglobin.
-
Dizziness and Lightheadedness
Anemia can cause dizziness and lightheadedness, especially when standing up or changing positions.
Anemia can cause headaches and migraines due to a lack of oxygen in the brain.
-
Cold Hands and Feet
Anemia can cause cold hands and feet due to poor circulation.
Diagnosis of Anemia
Anemia can be diagnosed using a variety of tests, including:
-
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A CBC measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood.
-
Iron Studies
Iron studies measure the level of iron in the blood and bone marrow.
-
Vitamin B12 and Folate Levels
Vitamin B12 and folate levels can be measured to diagnose deficiencies.
-
Reticulocyte Count
A reticulocyte count measures the number of immature red blood cells in the blood.
Treatment Options for Anemia
The treatment of anemia depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
-
Iron Supplements
Iron supplements can help to increase iron levels in the blood.
-
Vitamin B12 and Folate Supplements
Vitamin B12 and folate supplements can help to increase levels of these essential nutrients in the blood.
-
Red Blood Cell Transfusions
Red blood cell transfusions may be necessary in severe cases of anemia.
-
Medications
Medications, such as erythropoietin, can stimulate the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Managing Anemia
Managing anemia requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatment. Here are some tips on how to manage anemia:
-
Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet that includes essential nutrients, such as iron, vitamin B12, and folate, can help to manage anemia.
-
Avoid Certain Foods
Certain foods, such as those high in caffeine and tannins, can inhibit iron absorption and worsen anemia.
-
Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated can help to improve circulation and reduce fatigue.
-
Exercise Regularly
Exercise can help to improve circulation and reduce fatigue.
-
Manage Stress
Managing stress can help to reduce fatigue and improve overall health.
Anemia Image Gallery




In conclusion, anemia is a common health disorder that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, nutrition, chronic diseases, and certain medications. Understanding the causes and symptoms of anemia is crucial for early detection and treatment. Treatment options may include iron supplements, vitamin B12 and folate supplements, red blood cell transfusions, and medications. Managing anemia requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatment. By following these tips and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can manage anemia and improve their overall health.
