Uncover the pivotal moments that shaped Americas history. From independence to innovation, explore the 10 key events that transformed the nation. Discover the impact of the American Revolution, Civil Rights Movement, Industrialization, and more on the countrys development. A comprehensive guide to the most significant events in American history.
The history of America is a rich tapestry of events that have shaped the country into what it is today. From its early days as a colonial power to its current status as a global superpower, the United States has been witness to numerous events that have left an indelible mark on its history. Here are 10 key events in the annals of America that have helped shape the country's narrative.
The American Revolution (1775-1783)

The American Revolution was a pivotal event in American history that saw the colonies declaring independence from British rule. The revolution was sparked by a series of taxes imposed by the British government, which led to widespread protests and eventually, the outbreak of war. The Continental Army, led by George Washington, fought against the British Army, ultimately securing independence for the colonies.
Causes of the American Revolution
- The Proclamation of 1763, which restricted westward settlement
- The Stamp Act, which imposed a tax on printed materials
- The Boston Massacre, which heightened tensions between the colonies and Britain
The Louisiana Purchase (1803)
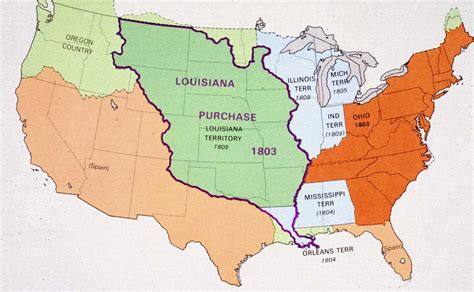
The Louisiana Purchase was a landmark event in American history that saw the United States purchasing a vast tract of land from France. The purchase, which was negotiated by Robert Livingston, James Monroe, and François Barbé-Marbois, doubled the size of the United States and set the stage for the country's westward expansion.
Key Figures
- Robert Livingston, James Monroe, and François Barbé-Marbois, who negotiated the purchase
- Thomas Jefferson, who supported the purchase as President of the United States
The Civil War (1861-1865)

The Civil War was a devastating conflict that pitted the Union (the northern states) against the Confederacy (the southern states) over issues of slavery and states' rights. The war, which was fought from 1861 to 1865, resulted in the deaths of an estimated 620,000 to 750,000 soldiers and civilians and led to the abolition of slavery in the United States.
Key Events
- The Battle of Fort Sumter, which marked the start of the war
- The Emancipation Proclamation, which declared freedom for all slaves in Confederate territory
- The Battle of Gettysburg, which turned the tide of the war in favor of the Union
The Industrial Revolution ( Late 19th-Early 20th Centuries)

The Industrial Revolution was a period of rapid industrialization that transformed the United States from an agrarian society to an industrial powerhouse. New technologies, such as the steam engine and the telegraph, enabled mass production and improved communication, leading to the growth of cities and the rise of a new industrial elite.
Key Innovations
- The steam engine, which revolutionized transportation and industry
- The telegraph, which enabled rapid communication over long distances
- The Bessemer process, which enabled the mass production of steel
World War I (1917-1918)

The United States entered World War I in 1917, after Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare and sank several American ships. The war marked a significant turning point in American history, as the country emerged as a global power and took on a more prominent role in international affairs.
Key Events
- The sinking of the Lusitania, which led to the United States' entry into the war
- The Battle of Belleau Wood, which marked a turning point in the war on the Western Front
- The Armistice of November 11, 1918, which ended the war
The Great Depression and the New Deal (1929-1941)

The Great Depression was a period of economic downturn that lasted from 1929 to the late 1930s. In response to the crisis, President Franklin D. Roosevelt launched the New Deal, a series of programs and policies aimed at stimulating economic recovery and providing relief to those affected by the Depression.
Key Programs
- The Works Progress Administration (WPA), which provided jobs for millions of Americans
- The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), which employed young men in conservation and infrastructure projects
- The Social Security Act, which established a system of old-age pensions
World War II (1941-1945)

The United States entered World War II after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941. The war marked a significant turning point in American history, as the country emerged as one of the world's two superpowers and took on a more prominent role in international affairs.
Key Events
- The attack on Pearl Harbor, which led to the United States' entry into the war
- The Battle of Midway, which turned the tide of the war in the Pacific
- The D-Day invasion of Normandy, which marked a turning point in the war in Europe
The Civil Rights Movement (1950s-1960s)

The Civil Rights Movement was a social movement aimed at ending racial segregation and discrimination in the United States. The movement, which was led by figures such as Martin Luther King Jr. and Rosa Parks, used nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience to achieve its goals.
Key Events
- The Montgomery Bus Boycott, which was sparked by Rosa Parks' refusal to give up her seat on a bus
- The March on Washington, which was a major civil rights rally where Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his famous "I Have a Dream" speech
- The passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which outlawed segregation and protected voting rights
The September 11 Attacks (2001)
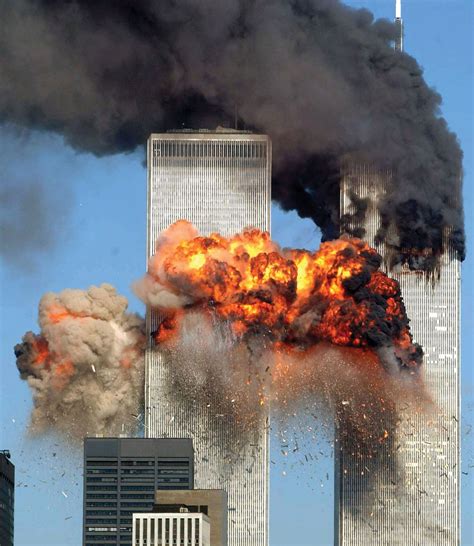

The September 11 attacks were a series of terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda on September 11, 2001. The attacks, which targeted the World Trade Center in New York City and the Pentagon in Washington, D.C., resulted in the deaths of nearly 3,000 people and had a profound impact on American society and foreign policy.
Key Events
- The attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon
- The collapse of the Twin Towers
- The passage of the USA PATRIOT Act, which expanded surveillance powers of law enforcement agencies
Gallery of Key Events in American History
America's History in Images










These 10 key events in American history have shaped the country into what it is today. From the American Revolution to the September 11 attacks, each event has played a significant role in shaping the United States' politics, society, and culture.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of these pivotal events in American history. Share your thoughts on these events and how they have impacted the country in the comments section below.
