Intro
Discover how warts spread through skin-to-skin contact, contaminated surfaces, and weakened immune systems, exploring viral transmission and prevention methods to reduce risk of infection and outbreak.
Warts are a common skin condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. They are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and can appear on various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, face, and genital area. One of the most concerning aspects of warts is their ability to spread from person to person, as well as from one part of the body to another. Understanding how warts spread is crucial in preventing their transmission and reducing the risk of infection.
Warts can be highly contagious, and their spread can occur through direct or indirect contact with an infected person. The virus that causes warts can survive on surfaces for extended periods, making it possible to contract the infection through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces. Additionally, certain factors such as skin-to-skin contact, sharing personal items, and walking barefoot in public areas can increase the risk of wart transmission. It is essential to take preventive measures to avoid contracting warts and to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
The spread of warts can have significant physical and emotional implications, particularly if left untreated. Warts can cause discomfort, pain, and embarrassment, affecting a person's quality of life and self-esteem. Furthermore, certain types of warts, such as genital warts, can increase the risk of cervical cancer and other health complications. Therefore, it is vital to understand the ways in which warts spread and to take proactive steps in preventing their transmission. By adopting good hygiene practices, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting warts and promote overall skin health.
Understanding Wart Transmission
Direct Contact
Direct contact with an infected person is a common way in which warts spread. This can occur through skin-to-skin contact, such as shaking hands or touching an infected area. Additionally, direct contact can occur through sexual activity, particularly if one partner has genital warts. It is essential to practice safe sex and to avoid close contact with individuals who have warts, especially if they are not taking steps to prevent transmission.Ways Warts Spread
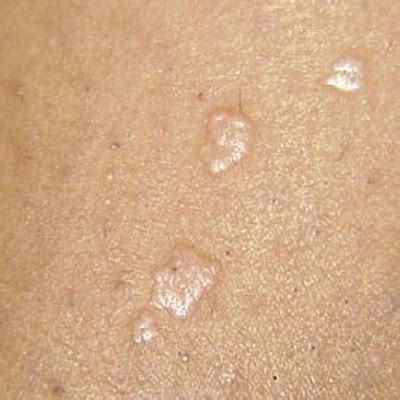
Indirect Contact
Indirect contact with contaminated surfaces or objects is another way in which warts can spread. The HPV virus can survive on surfaces for extended periods, making it possible to contract the infection through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces. This can occur in public areas, such as swimming pools or locker rooms, where the virus can survive on surfaces such as floors, benches, or equipment.Preventing Wart Transmission
Treatment Options
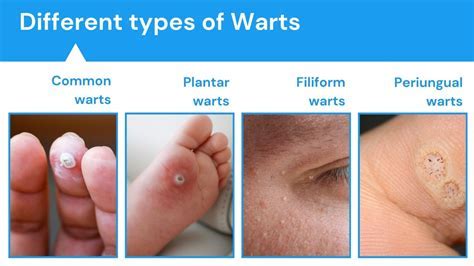
If symptoms persist or worsen over time, it is essential to seek medical attention. There are several treatment options available for warts, including over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, and surgical removal. A healthcare professional can determine the best course of treatment based on the type and severity of the warts, as well as the individual's overall health.Common Types of Warts
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of contracting warts, including: * Children and adolescents, who are more likely to contract common warts * Individuals with weakened immune systems, who are more susceptible to infection * Individuals who engage in high-risk behaviors, such as sharing personal items or having multiple sexual partnersComplications of Warts
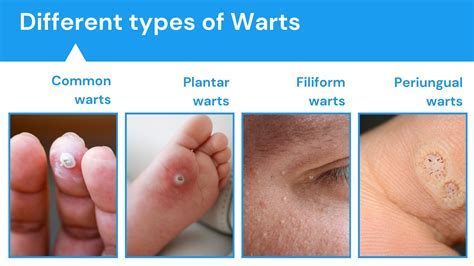
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing wart transmission and seeking medical attention when necessary are crucial in reducing the risk of complications. By adopting good hygiene practices, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and seeking medical attention when symptoms persist or worsen, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting warts and promote overall skin health.Wart Image Gallery
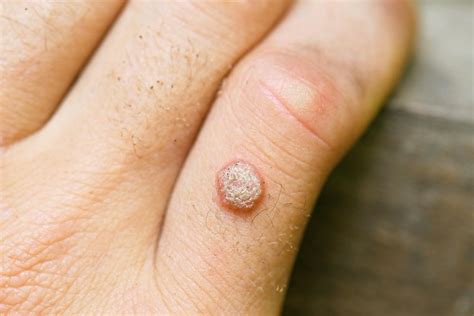
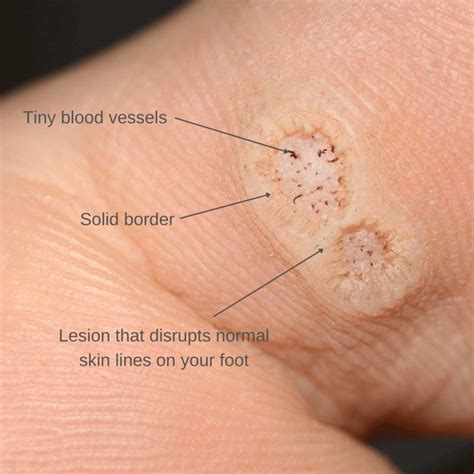
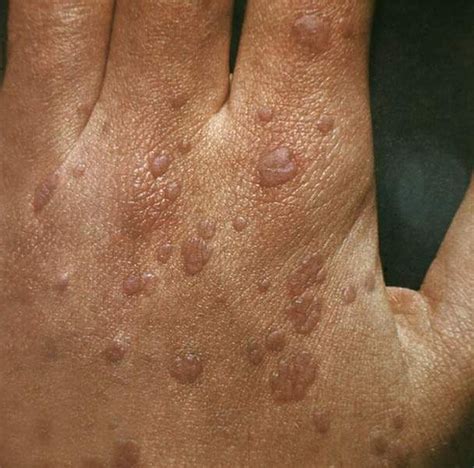
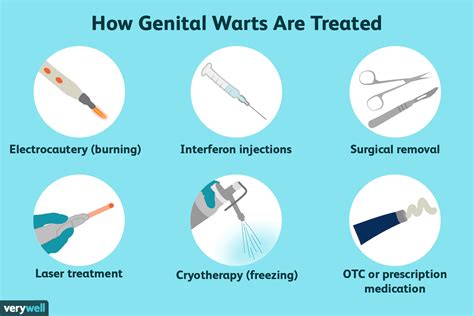


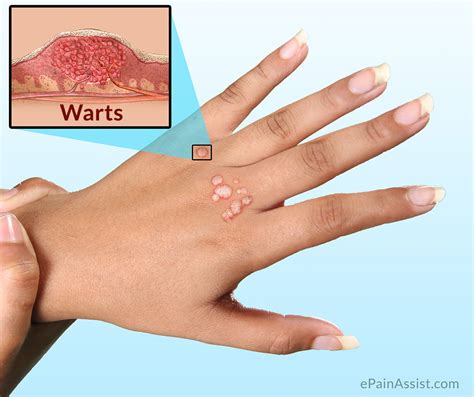
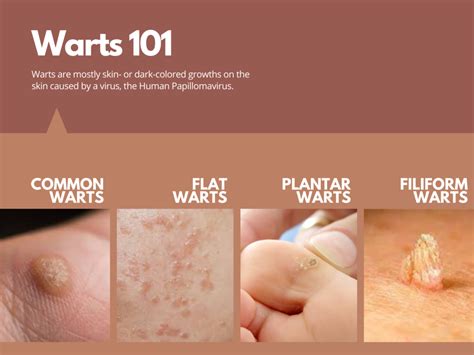
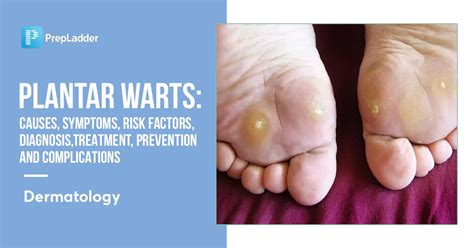
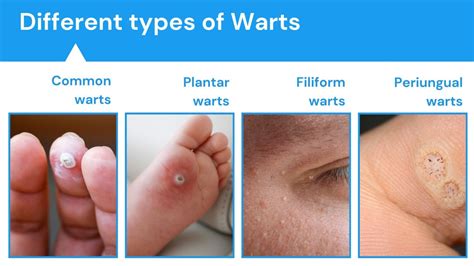
In conclusion, warts are a common skin condition that can spread through direct or indirect contact with an infected person. Understanding the ways in which warts spread and taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of infection and promote overall skin health. If symptoms persist or worsen over time, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the best course of treatment. By adopting good hygiene practices, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting warts and prevent significant physical and emotional complications. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with warts in the comments section below and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this common skin condition.
