Intro
Unlock your military potential with the Army General Classification Test (AGCT). Discover how this standardized assessment evaluates aptitude and classifies personnel for suitable roles. Learn how to prepare, understand scoring, and explore careers aligned with your strengths, from combat to administration, in the US Armys multifaceted ranks and Military Occupational Specialties (MOS).
The Army General Classification Test, also known as the AGCT, is a crucial evaluation tool used by the United States military to assess an individual's aptitude and potential for various roles within the armed forces. The test was originally designed in 1942 to help the Army categorize new recruits and assign them to suitable positions based on their skills and abilities.
Since its introduction, the AGCT has undergone several revisions to better reflect the changing needs of the military. Today, it remains a vital component of the enlistment process, providing recruiters and commanders with valuable insights into a candidate's strengths and weaknesses. In this article, we will delve into the world of the Army General Classification Test, exploring its history, structure, and significance in the military recruitment process.
History of the Army General Classification Test
The AGCT was first developed during World War II, as the military sought to optimize its recruitment and placement processes. The test was designed to measure a candidate's verbal, spatial, and arithmetic abilities, providing a comprehensive assessment of their cognitive skills. The AGCT was administered to millions of soldiers during the war, helping the military to identify talent and allocate personnel effectively.
Over the years, the AGCT has undergone several revisions, with updates aimed at refining its assessment tools and improving its validity. In the 1960s, the test was revised to include new sections and scoring systems, while the 1980s saw the introduction of computerized testing methods. Today, the AGCT remains an essential part of the military enlistment process, used in conjunction with other evaluation tools to identify suitable candidates for various roles.
Structure of the Army General Classification Test
The AGCT is a multiple-choice test, comprising several sections designed to assess different aspects of cognitive ability. The test typically includes the following sections:
- Verbal Ability: This section evaluates a candidate's language skills, including reading comprehension, vocabulary, and grammar.
- Spatial Ability: This section assesses a candidate's visual-spatial skills, including their ability to understand and manipulate spatial relationships.
- Arithmetic Reasoning: This section tests a candidate's mathematical abilities, including basic arithmetic operations and problem-solving skills.
Each section of the test contains a series of questions, with candidates required to choose the correct answer from a range of options. The test is scored based on the number of correct answers, with candidates receiving a separate score for each section.

Significance of the Army General Classification Test
The AGCT plays a critical role in the military recruitment process, providing commanders and recruiters with valuable insights into a candidate's aptitude and potential. The test helps to identify suitable candidates for various roles, ensuring that individuals are matched with positions that align with their skills and abilities.
The AGCT also helps to:
- Streamline the recruitment process: By providing a comprehensive assessment of a candidate's cognitive abilities, the AGCT helps recruiters to identify potential candidates more efficiently.
- Improve job placement: The AGCT helps commanders to allocate personnel more effectively, ensuring that individuals are placed in roles that match their skills and abilities.
- Enhance military effectiveness: By identifying and allocating talent more effectively, the AGCT helps to enhance military effectiveness, ensuring that the armed forces are equipped with the best possible personnel.
Preparation and Tips for the Army General Classification Test
While the AGCT is a challenging test, there are several steps that candidates can take to prepare and improve their chances of success. Here are some tips and strategies to help you prepare for the test:
- Practice with sample questions: Familiarize yourself with the test format and question types by practicing with sample questions.
- Improve your verbal skills: Focus on developing your reading comprehension, vocabulary, and grammar skills to improve your performance in the verbal section.
- Develop your spatial skills: Practice visual-spatial exercises and puzzles to improve your spatial reasoning skills.
- Brush up on your math skills: Review basic arithmetic operations and practice problem-solving exercises to improve your performance in the arithmetic reasoning section.
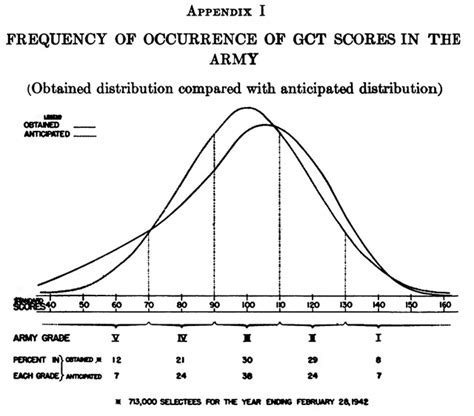
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Army General Classification Test:
- What is the Army General Classification Test? The AGCT is a cognitive ability test used by the United States military to assess an individual's aptitude and potential for various roles within the armed forces.
- How long does the test take to complete? The test typically takes around 2-3 hours to complete, depending on the individual's pace and performance.
- What is the passing score for the AGCT? The passing score for the AGCT varies depending on the specific role or position being applied for. However, a minimum score of 110 is typically required for most roles.
- Can I retake the test if I don't pass? Yes, candidates can retake the test after a minimum waiting period of 6 months.
Army General Classification Test Image Gallery
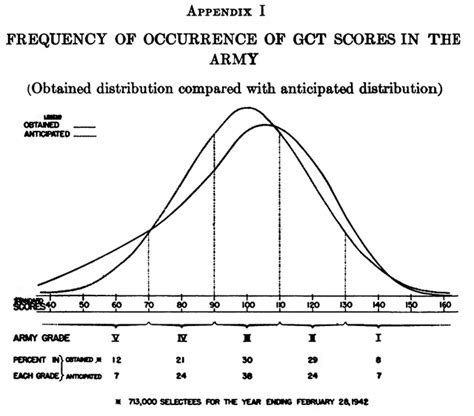
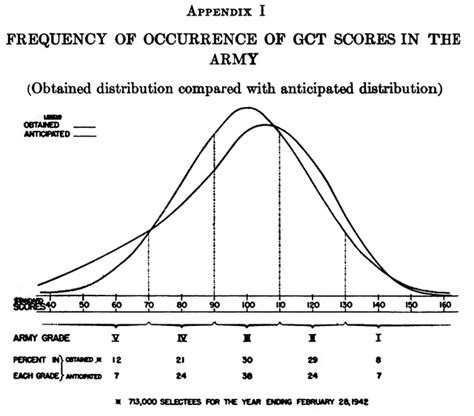
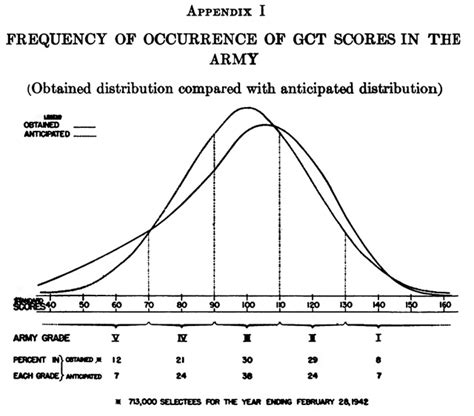
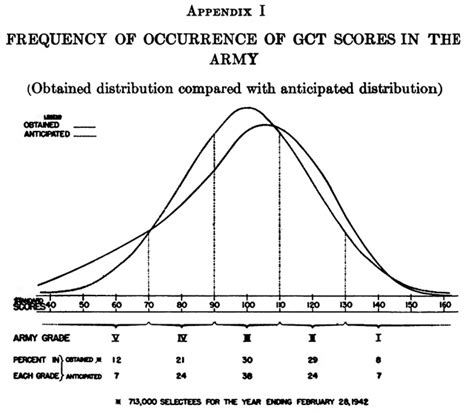

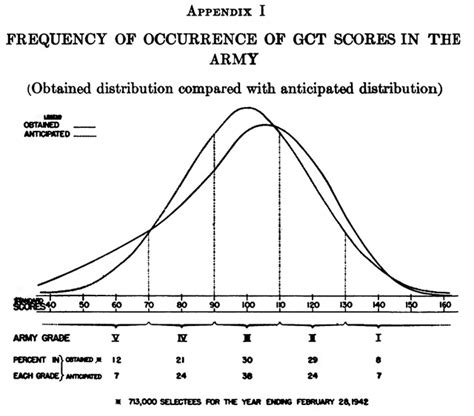
In conclusion, the Army General Classification Test is a critical component of the military recruitment process, providing commanders and recruiters with valuable insights into a candidate's aptitude and potential. By understanding the test's structure, significance, and preparation strategies, candidates can improve their chances of success and unlock their military potential.
