Intro
Discover the 2015 Army pay grades and learn how they affect your military compensation. Understand the Armys pay scale, including enlisted and officer ranks, and how factors like time in service and family size impact your take-home pay. Get the inside scoop on Basic Pay, BAH, and BAS, and maximize your military salary.
Understanding the 2015 Army pay grades is essential for both active-duty soldiers and veterans. The Army's pay grade system determines the monthly basic pay for soldiers, and it's based on their rank and time in service. In this article, we'll break down the 2015 Army pay grades, explaining the different ranks, their corresponding pay grades, and the factors that influence a soldier's basic pay.
Army Rank Structure
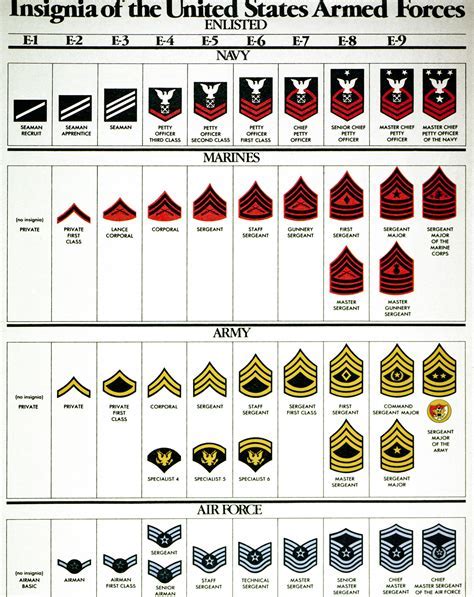

The Army has a hierarchical rank structure, divided into three main categories: Enlisted, Warrant Officers, and Officers. Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, and soldiers can advance through the ranks with experience and promotions.
Enlisted Ranks
The Enlisted ranks are the backbone of the Army, making up about 80% of the total force. These ranks range from Private (E-1) to Command Sergeant Major (E-9).
- Private (E-1): The lowest Enlisted rank, typically held by new recruits.
- Private Second Class (E-2): A higher rank than Private, with more responsibilities.
- Private First Class (E-3): A junior non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank.
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): A senior Enlisted rank, with more leadership responsibilities.
- Sergeant (E-5): A higher NCO rank, with increased responsibilities and leadership roles.
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): A senior NCO rank, with specialized skills and leadership roles.
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): A high-ranking NCO, with significant leadership and mentorship responsibilities.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): A senior NCO rank, with high-level leadership and advisory roles.
- Sergeant Major (E-9): The highest Enlisted rank, with significant leadership and advisory responsibilities.
Warrant Officer Ranks
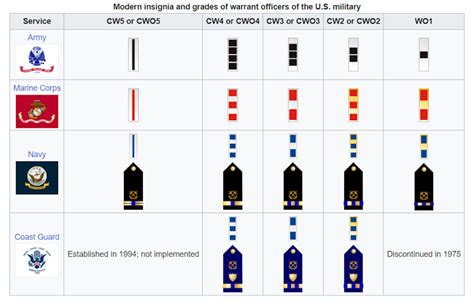
Warrant Officers are technical experts in specific fields, with a unique rank structure.
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): The lowest Warrant Officer rank, with technical expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): A higher Warrant Officer rank, with increased technical responsibilities.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): A senior Warrant Officer rank, with high-level technical expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): A high-ranking Warrant Officer, with significant technical and leadership responsibilities.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): The highest Warrant Officer rank, with exceptional technical expertise and leadership.
Officer Ranks
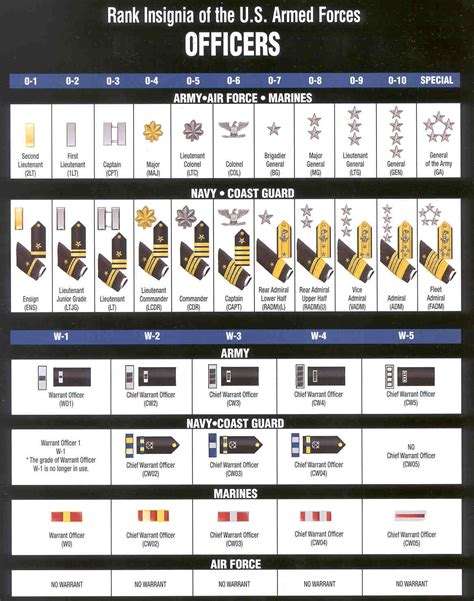
Officer ranks range from Second Lieutenant (O-1) to General (O-10).
- Second Lieutenant (O-1): The lowest Officer rank, typically held by new officers.
- First Lieutenant (O-2): A higher Officer rank, with increased responsibilities.
- Captain (O-3): A company-level Officer rank, with significant leadership responsibilities.
- Major (O-4): A field-grade Officer rank, with high-level leadership and staff responsibilities.
- Lieutenant Colonel (O-5): A senior Officer rank, with significant leadership and command responsibilities.
- Colonel (O-6): A high-ranking Officer, with high-level leadership and command responsibilities.
- Brigadier General (O-7): A one-star General rank, with significant leadership and command responsibilities.
- Major General (O-8): A two-star General rank, with high-level leadership and command responsibilities.
- Lieutenant General (O-9): A three-star General rank, with significant leadership and command responsibilities.
- General (O-10): The highest Officer rank, with exceptional leadership and command responsibilities.
Factors Affecting Basic Pay

Several factors influence a soldier's basic pay, including:
- Rank: Higher ranks receive higher basic pay.
- Time in service: Soldiers with more time in service receive higher basic pay.
- Time in grade: Soldiers with more time in their current grade receive higher basic pay.
- Family size: Soldiers with dependents receive a family allowance, which increases basic pay.
- Location: Soldiers stationed in high-cost areas receive a cost-of-living allowance, which increases basic pay.
2015 Army Pay Grades
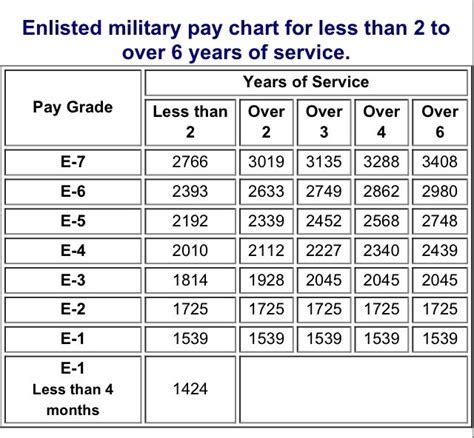
Here is a sample pay grade chart for the 2015 Army pay grades:
| Rank | Pay Grade | Monthly Basic Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | E-1 | $1,733.10 |
| Private Second Class (E-2) | E-2 | $1,942.50 |
| Private First Class (E-3) | E-3 | $2,043.90 |
| Specialist/Corporal (E-4) | E-4 | $2,244.40 |
| Sergeant (E-5) | E-5 | $2,555.80 |
| Staff Sergeant (E-6) | E-6 | $3,015.60 |
| Sergeant First Class (E-7) | E-7 | $3,455.40 |
| Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8) | E-8 | $4,035.40 |
| Sergeant Major (E-9) | E-9 | $4,622.80 |
| Second Lieutenant (O-1) | O-1 | $3,287.10 |
| First Lieutenant (O-2) | O-2 | $3,755.30 |
| Captain (O-3) | O-3 | $4,362.30 |
| Major (O-4) | O-4 | $5,238.40 |
| Lieutenant Colonel (O-5) | O-5 | $6,313.50 |
| Colonel (O-6) | O-6 | $7,521.60 |
Note: These pay grades are for the 2015 calendar year and do not include allowances, bonuses, or other forms of compensation.
Gallery of Army Rank Insignia
Army Rank Insignia









We hope this article has provided a comprehensive understanding of the 2015 Army pay grades. Remember to check the official Army website for the most up-to-date information on pay grades and other benefits.
What do you think about the 2015 Army pay grades? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
