Intro
Explore the USA military hierarchy with our comprehensive Army rank list in order. Learn about the enlisted, warrant officer, and officer ranks, from Private to General. Understand the rank structure, insignia, and responsibilities of each position, and discover how the militarys chain of command works.
The United States Armed Forces are a proud and prestigious institution, with a long history of defending the country and its interests. One of the most important aspects of the military is its rank structure, which is used to denote a soldier's level of responsibility, authority, and expertise. In this article, we will explore the army rank list in order, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of the different ranks and their responsibilities.
Why is Understanding the Army Rank List Important?
Understanding the army rank list is important for several reasons. First, it helps to clarify the chain of command and the level of authority and responsibility that each soldier has. Second, it provides a framework for career advancement and professional development. Finally, it helps to promote a sense of pride and esprit de corps among soldiers, who can identify with their rank and the responsibilities that come with it.
The Army Rank List in Order
Here is the army rank list in order, from the lowest to the highest:
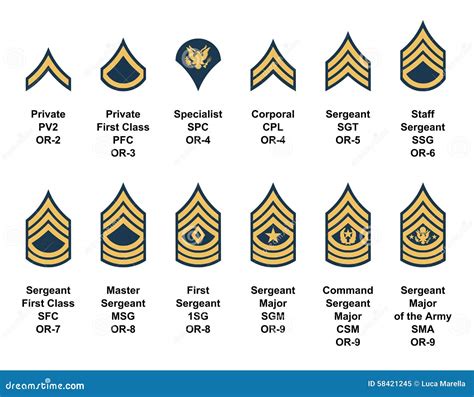
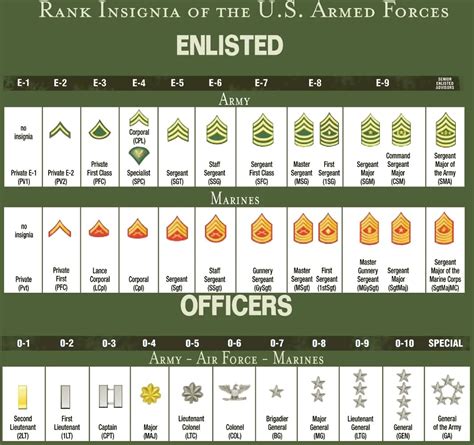
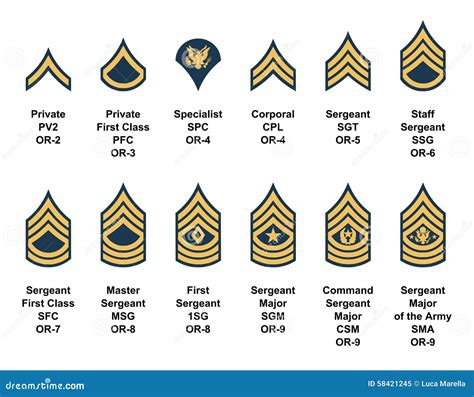
Enlisted Ranks

- Private (PVT): The lowest rank in the army, typically held by new recruits.
- Private Second Class (PV2): A higher rank than Private, typically held by soldiers who have completed basic training.
- Private First Class (PFC): A rank higher than Private Second Class, typically held by soldiers who have gained experience and demonstrated leadership potential.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): A rank higher than Private First Class, typically held by soldiers who have specialized skills or have demonstrated leadership ability.
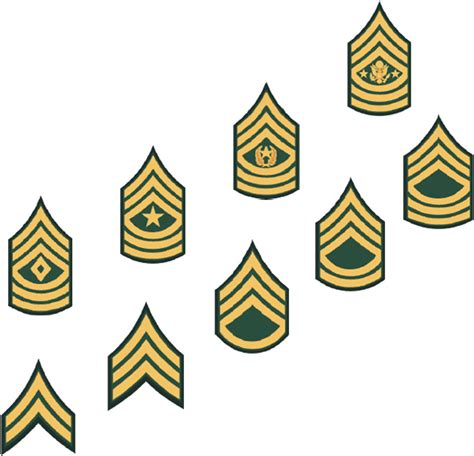
- Sergeant (SGT): A rank higher than Specialist/Corporal, typically held by soldiers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
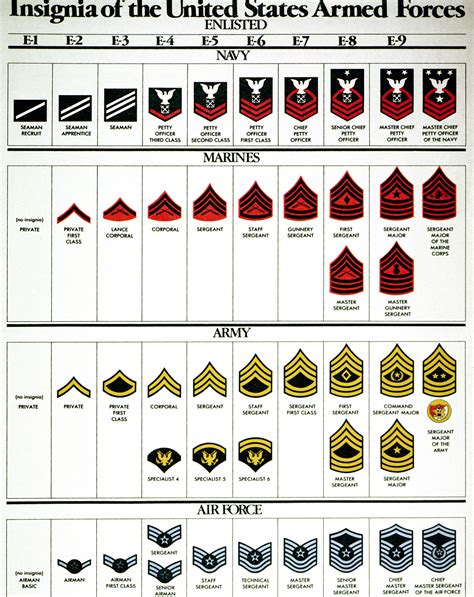
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): A rank higher than Sergeant, typically held by soldiers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): A rank higher than Staff Sergeant, typically held by soldiers who have advanced leadership skills and experience.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): A rank higher than Sergeant First Class, typically held by soldiers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
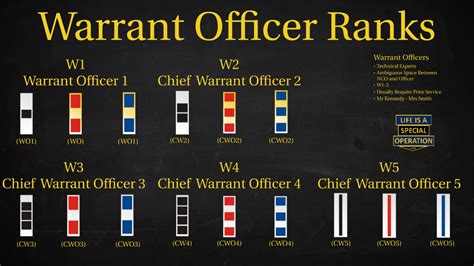
Warrant Officer Ranks
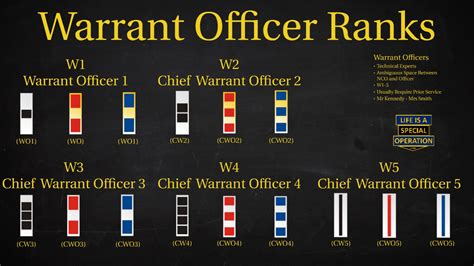
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The lowest rank in the warrant officer corps, typically held by soldiers who have specialized skills and expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A rank higher than Warrant Officer 1, typically held by soldiers who have advanced specialized skills and expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A rank higher than Chief Warrant Officer 2, typically held by soldiers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): A rank higher than Chief Warrant Officer 3, typically held by soldiers who have advanced leadership skills and experience.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest rank in the warrant officer corps, typically held by soldiers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
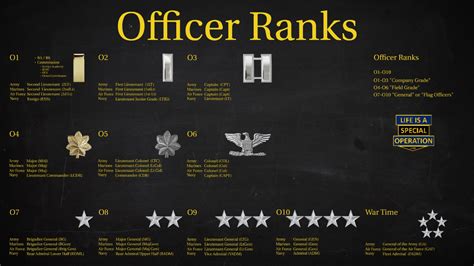
Officer Ranks
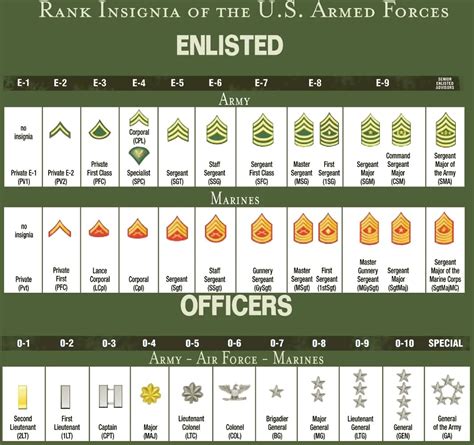
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The lowest rank in the officer corps, typically held by new officers.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A rank higher than Second Lieutenant, typically held by officers who have gained experience and demonstrated leadership potential.
- Captain (CPT): A rank higher than First Lieutenant, typically held by officers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
- Major (MAJ): A rank higher than Captain, typically held by officers who have advanced leadership skills and experience.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A rank higher than Major, typically held by officers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
- Colonel (COL): A rank higher than Lieutenant Colonel, typically held by officers who have advanced leadership skills and experience.
General Officer Ranks

- Brigadier General (BG): The lowest rank in the general officer corps, typically held by officers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
- Major General (MG): A rank higher than Brigadier General, typically held by officers who have advanced leadership skills and experience.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): A rank higher than Major General, typically held by officers who have significant experience and leadership ability.
- General (GEN): The highest rank in the army, typically held by officers who have advanced leadership skills and experience.
Army Rank List Gallery
Army Rank List Image Gallery




Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the army rank list is essential for any soldier or military enthusiast. By familiarizing yourself with the different ranks and their responsibilities, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the military hierarchy and the sacrifices that soldiers make to serve their country.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the army rank list in order. Whether you are a new recruit or a seasoned veteran, we encourage you to continue learning and growing in your military career.
If you have any questions or comments about the army rank list, please feel free to leave them in the comments section below. We would love to hear from you and help you in any way that we can.
Share this article with your friends and family to help them learn more about the army rank list.
