Intro
Compare the differences between the US Army and Air Force in our in-depth analysis. Discover which branch excels in combat, technology, and benefits, and learn about the unique roles and responsibilities of each. Explore the pros and cons of serving in the Army vs Air Force, including enlistment requirements, training, and career opportunities.
The age-old debate between the Army and Air Force has been a staple of military discussions for decades. Both branches have their own unique strengths, weaknesses, and missions, making it challenging to declare a clear winner. However, in this article, we'll delve into the differences between the two branches, exploring their histories, roles, and requirements to help you decide which branch reigns supreme.

A Brief History of the Army and Air Force
The United States Army and Air Force have distinct histories that have shaped their roles and responsibilities. The Army was founded on June 14, 1775, as the Continental Army, with the primary mission of defending the newly independent nation. Over the years, the Army has evolved to become a global force, with a presence in over 100 countries.
The Air Force, on the other hand, was established on September 18, 1947, as a separate branch of the military. Prior to this, aviation was a part of the Army, known as the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). The creation of the Air Force as a separate branch marked a significant shift in the country's military strategy, acknowledging the importance of air power in modern warfare.
Roles and Responsibilities
The Army and Air Force have different primary roles and responsibilities, which are reflected in their respective missions.
Army Mission
The Army's mission is to "protect the American people, the Nation, and our way of life." To achieve this, the Army focuses on:
- Defending the country against external threats
- Maintaining a strong presence in regions of strategic importance
- Providing humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
- Supporting civil authorities in times of crisis
Key Army Responsibilities
- Ground combat operations
- Peacekeeping and stability operations
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
- Homeland security

Air Force Mission
The Air Force's mission is to "fly, fight, and win in air, space, and cyberspace." The Air Force focuses on:
- Maintaining air superiority and global reach
- Providing strategic deterrence and nuclear operations
- Supporting joint military operations
- Developing and acquiring new technologies to stay ahead of emerging threats
Key Air Force Responsibilities
- Air combat operations
- Space operations
- Cyber operations
- Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR)

Enlistment Requirements
Both the Army and Air Force have similar enlistment requirements, but there are some differences:
Army Enlistment Requirements
- Age: 17-35 years old (with parental consent) or 17-42 years old (without parental consent)
- Citizenship: U.S. citizen or resident alien
- Education: High school diploma or equivalent
- Physical fitness: Pass the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT)
- Background: Pass a background check and obtain a security clearance
Air Force Enlistment Requirements
- Age: 17-39 years old (with parental consent) or 17-44 years old (without parental consent)
- Citizenship: U.S. citizen or resident alien
- Education: High school diploma or equivalent
- Physical fitness: Pass the Air Force Physical Fitness Test (PFT)
- Background: Pass a background check and obtain a security clearance

Training and Education
Both the Army and Air Force offer comprehensive training and education programs for their service members.
Army Training
- Basic Combat Training (BCT): 10 weeks
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): varies by Military Occupational Specialty (MOS)
- Officer Candidate School (OCS): 12 weeks
- West Point: 4-year degree program
Air Force Training
- Basic Military Training (BMT): 7 weeks
- Technical Training: varies by Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC)
- Officer Training School (OTS): 12 weeks
- Air Force Academy: 4-year degree program
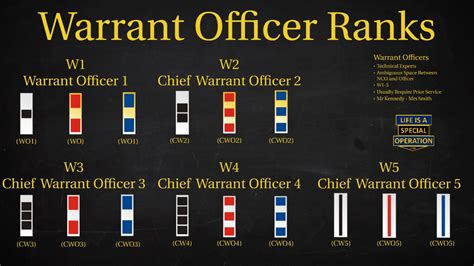
Career Opportunities
Both the Army and Air Force offer a wide range of career opportunities for their service members.
Army Careers
- Infantry and armor
- Artillery and engineering
- Aviation and transportation
- Medical and healthcare
- Administration and support
Air Force Careers
- Pilots and navigators
- Maintenance and logistics
- Intelligence and cyber
- Medical and healthcare
- Administration and support

Gallery of Military Branches
Military Branches Image Gallery










Final Thoughts
In conclusion, both the Army and Air Force are essential branches of the United States military, each with their own unique strengths and weaknesses. While the Army excels in ground combat operations and humanitarian assistance, the Air Force dominates the skies with its air superiority and global reach. Ultimately, the choice between the two branches depends on individual preferences and career goals.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the differences between the Army and Air Force. Share your thoughts and opinions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and family who may be interested in joining the military.
FAQs
Q: Which branch is better, the Army or Air Force? A: Both branches have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the better branch depends on individual preferences and career goals.
Q: What are the enlistment requirements for the Army and Air Force? A: Both branches have similar enlistment requirements, including age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness.
Q: What are the training and education programs like for the Army and Air Force? A: Both branches offer comprehensive training and education programs, including basic training, technical training, and officer training.
Q: What are the career opportunities like for the Army and Air Force? A: Both branches offer a wide range of career opportunities, including infantry and armor, pilots and navigators, and medical and healthcare.
Q: Which branch has better benefits? A: Both branches offer similar benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, and retirement plans. However, the Air Force is known for having better housing and food options.
