Intro
Explore the key differences between the Constitution and Articles of Confederation, understanding federalism, sovereignty, and governance, to grasp the evolution of the US government system.
The United States of America has a rich history, and one of the most significant periods in its development was the transition from the Articles of Confederation to the United States Constitution. This transition marked a crucial shift in the country's governance, structure, and overall direction. Understanding the differences between the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution is essential to grasping the fundamental principles of American democracy. In this article, we will delve into the history, key features, and implications of both the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution, exploring why the latter replaced the former and how it has shaped the United States into the powerful nation it is today.
The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, were the first attempt at a unified government for the newly independent states. This document was designed to provide a framework for cooperation among the states, with a focus on preserving state sovereignty and preventing the concentration of power. However, the Articles of Confederation had several significant flaws, including the lack of a strong central government, no executive or judicial branches, and the requirement for unanimous consent among states for major decisions. These weaknesses led to inefficiencies, conflicts, and an inability to effectively address national issues, prompting the need for a more robust and effective system of government.
Introduction to the Constitution

Key Features of the Constitution
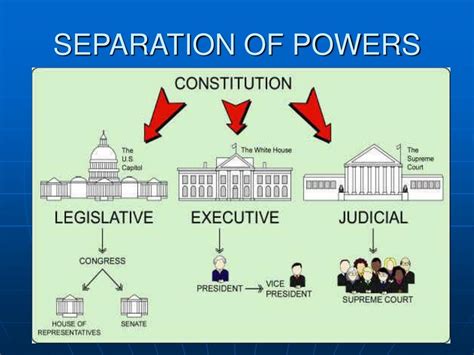
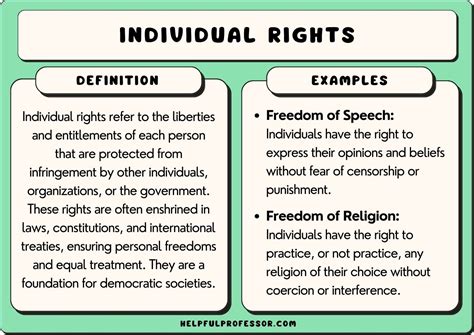
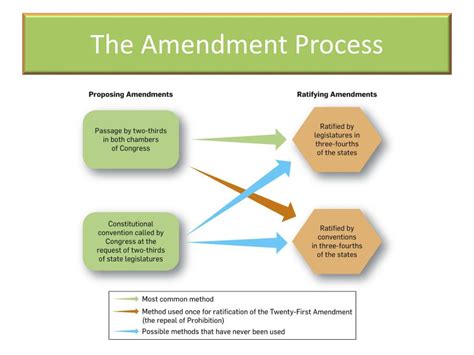
The Constitution is renowned for its innovative approach to governance, incorporating several key features that distinguish it from the Articles of Confederation. These include: - **Federalism:** The division of power between the federal government and the states, allowing for a balance between national unity and regional autonomy. - **Separation of Powers:** The establishment of three branches of government (the legislative, executive, and judicial), each with distinct responsibilities and the ability to check the actions of the others. - **Individual Rights:** The protection of individual liberties and rights, as outlined in the Bill of Rights and subsequent amendments, ensuring that citizens are safeguarded against abuses of power. - **Amendment Process:** A mechanism for altering the Constitution, allowing it to adapt to the changing needs and values of the American society.Comparing the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution
Implications of the Constitution
The adoption of the Constitution has had profound implications for the United States, shaping its political, social, and economic development. Some of the key implications include: - **Strengthened Federal Government:** The Constitution enabled the creation of a strong central government, capable of addressing national issues, regulating commerce, and providing for the common defense. - **Protection of Individual Rights:** The Constitution and its amendments have safeguarded individual liberties, ensuring that citizens are protected against governmental abuses and have the freedom to pursue their goals and aspirations. - **Economic Growth:** The stability and predictability provided by the Constitution have fostered economic growth, as investors, businesses, and individuals have confidence in the rule of law and the protection of property rights. - **Global Influence:** The United States, under the guidance of the Constitution, has become a global leader, influencing international relations, promoting democracy, and setting standards for human rights and governance.The Ratification Process and Its Challenges

Lessons Learned and Legacy
The transition from the Articles of Confederation to the Constitution offers valuable lessons for governance, democracy, and the importance of adaptability. The Constitution's enduring legacy is a testament to the foresight and wisdom of its creators, who designed a system that could evolve with the needs of the nation. Today, the Constitution remains a cornerstone of American democracy, inspiring similar documents around the world and serving as a model for democratic governance.Gallery of Constitutional Images
Constitutional Gallery






Final Thoughts and Future Directions

We invite readers to share their thoughts on the importance of the Constitution and its role in shaping American democracy. How do you think the Constitution has influenced the development of the United States? What challenges do you see for its interpretation and application in the future? Join the conversation by commenting below, sharing this article with others, and exploring the rich history and significance of the United States Constitution.
