Intro
Discover key Aspirin 81mg nursing considerations, including dosage, side effects, and patient education, to ensure safe administration and minimize risks, particularly for cardiovascular and antiplatelet therapy management.
Aspirin, commonly known as acetylsalicylic acid, is a widely used medication for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antiplatelet properties. The 81mg dose of aspirin is particularly notable for its role in preventing cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, in patients at high risk. Nursing considerations for aspirin 81mg are crucial for ensuring safe and effective use, minimizing adverse effects, and maximizing therapeutic benefits.
The importance of aspirin 81mg in clinical practice cannot be overstated. It is a cornerstone in the management of patients with cardiovascular disease, offering a simple yet potent strategy to reduce the risk of future cardiovascular events. However, like all medications, aspirin comes with its own set of considerations, from dosing and administration to potential side effects and interactions. Nurses play a pivotal role in educating patients, monitoring their response to therapy, and managing any complications that may arise.
Aspirin's mechanism of action involves the inhibition of cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2), which in turn reduces the production of thromboxane A2, a potent stimulator of platelet aggregation. This antiplatelet effect is primarily responsible for aspirin's ability to prevent arterial thrombosis. The 81mg dose is considered low-dose aspirin, which is specifically chosen for its antiplatelet effect while minimizing gastrointestinal side effects associated with higher doses.
Benefits of Aspirin 81mg

Working Mechanism of Aspirin
Aspirin's working mechanism is based on its ability to irreversibly inhibit the COX enzymes, thereby affecting the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes. This irreversible inhibition lasts for the lifespan of the platelet, which is approximately 7-10 days. The antiplatelet effect of aspirin is dose-dependent, but even low doses can achieve significant platelet inhibition.Nursing Considerations
Steps for Administration
Administration of aspirin 81mg involves: - Ensuring the patient can swallow the tablet or using an enteric-coated form if necessary. - Administering the medication with food to reduce gastrointestinal upset. - Monitoring for signs of bleeding or other adverse effects. - Regularly reviewing the patient's medication list for potential interactions.Potential Side Effects

Management of Side Effects
Management of side effects involves: - Dose adjustment or switching to an enteric-coated formulation for gastrointestinal upset. - Monitoring for signs of bleeding and adjusting the treatment plan as necessary. - Immediate medical attention if severe side effects occur.Practical Examples and Statistical Data

Key Information for Patients
Key information for patients includes: - The importance of adherence to the prescribed regimen. - Recognition of potential side effects and when to seek medical help. - The need for regular follow-up appointments. - Lifestyle modifications to further reduce cardiovascular risk, such as diet, exercise, and smoking cessation.SEO Optimization and Readability

Encouraging Engagement
Readers are encouraged to share their experiences with aspirin 81mg, ask questions, and seek further information on cardiovascular health. Engaging with the content can help foster a community of individuals interested in heart health and the prevention of cardiovascular disease.Aspirin 81mg Image Gallery




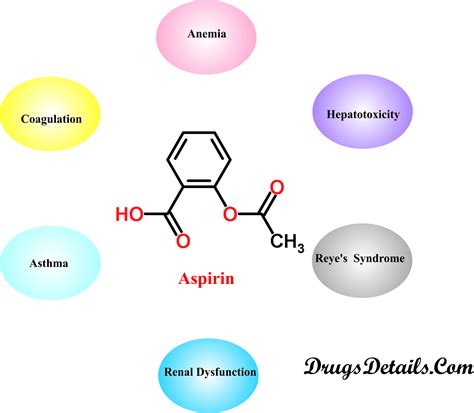


In summary, aspirin 81mg is a vital medication in the prevention of cardiovascular events, with its antiplatelet effect being the primary mechanism of action. Nursing considerations are essential for safe and effective use, including patient education, monitoring for side effects, and managing potential interactions. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and nursing considerations of aspirin 81mg, healthcare professionals can better support patients in reducing their risk of cardiovascular disease. We invite readers to engage with this topic further, sharing insights and questions to promote a deeper understanding of aspirin's role in heart health.
