Intro
Discover the comprehensive Aspirin Therapy Medication Template Guide, a detailed resource for healthcare professionals and patients. Learn about aspirin therapy benefits, dosage guidelines, and management strategies for cardiovascular health, pain relief, and anti-inflammatory treatment. Get expert insights on medication adherence, side effects, and contraindications.
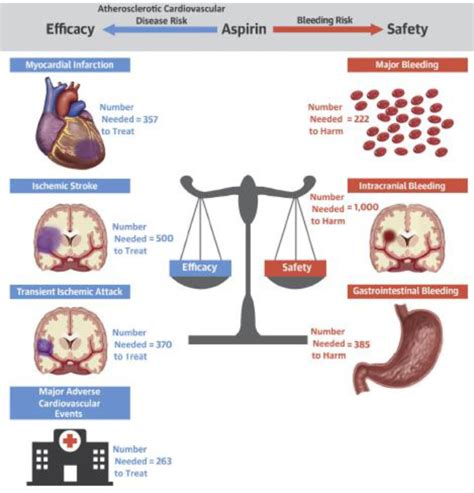
Aspirin has been a cornerstone of medical treatment for over a century, with its use dating back to ancient civilizations. Today, it remains one of the most widely used medications globally, with millions of people relying on it for pain relief, anti-inflammatory effects, and cardiovascular protection. Aspirin therapy, in particular, has become a crucial aspect of patient care, with many healthcare providers recommending it for various medical conditions. However, navigating the complexities of aspirin therapy can be daunting, especially for patients and caregivers. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of aspirin therapy, including its benefits, risks, and practical considerations.
What is Aspirin Therapy?
Aspirin therapy refers to the long-term use of aspirin for the prevention and treatment of various medical conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer. Aspirin works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that cause pain, inflammation, and fever. By taking aspirin regularly, individuals can reduce their risk of developing certain health problems and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Benefits of Aspirin Therapy
Aspirin therapy has numerous benefits, including:
- Cardiovascular protection: Aspirin helps prevent blood clots from forming, reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
- Pain relief: Aspirin is an effective analgesic, providing relief from headaches, arthritis, and other types of pain.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Aspirin reduces inflammation, which can help alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
- Cancer prevention: Some studies suggest that long-term aspirin use may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colorectal cancer.
Risks and Side Effects of Aspirin Therapy

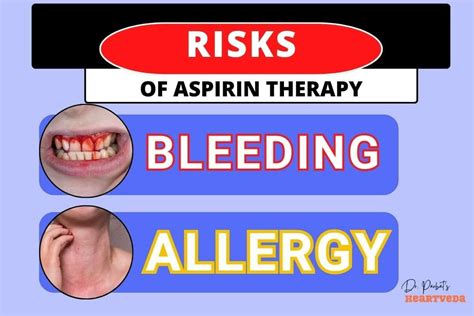
While aspirin therapy can be beneficial, it is not without risks and side effects. Some of the most common concerns include:
- Bleeding complications: Aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding, particularly when taken in high doses or combined with other medications.
- Gastrointestinal problems: Aspirin can cause stomach upset, nausea, and ulcers, especially when taken for extended periods.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to aspirin, which can cause symptoms like hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
- Interactions with other medications: Aspirin can interact with other medications, such as blood thinners, diabetes medications, and certain antidepressants.
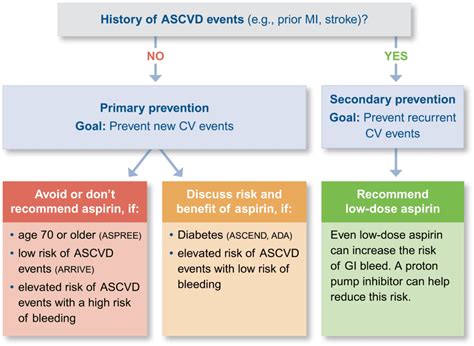
Who Should Take Aspirin Therapy?
Aspirin therapy is typically recommended for individuals who are at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease or other conditions that may benefit from aspirin's effects. These include:
- Individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease: Those who have had a heart attack, stroke, or other cardiovascular event may benefit from aspirin therapy to prevent future events.
- Individuals with high blood pressure: Aspirin can help reduce blood pressure and prevent cardiovascular disease in individuals with hypertension.
- Individuals with high cholesterol: Aspirin may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with high cholesterol.
- Individuals with a family history of cardiovascular disease: Those with a strong family history of cardiovascular disease may benefit from aspirin therapy as a preventive measure.
How to Take Aspirin Therapy Safely

To take aspirin therapy safely, follow these guidelines:
- Consult your doctor: Before starting aspirin therapy, consult with your doctor to discuss the benefits and risks and determine the best dosage for your individual needs.
- Take the correct dosage: Take the recommended dosage of aspirin, usually 81-100 mg per day, and avoid taking more than directed.
- Monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels: Regularly monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels to ensure that aspirin therapy is effective and adjust your dosage as needed.
- Be aware of potential interactions: Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal products you are taking to avoid potential interactions with aspirin.
Aspirin Therapy and Special Populations
Aspirin therapy may not be suitable for everyone, particularly:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding and other complications during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Children and adolescents: Aspirin can be toxic to children and adolescents, and its use should be carefully monitored and guided by a doctor.
- Individuals with bleeding disorders: Aspirin can exacerbate bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, and its use should be carefully monitored and guided by a doctor.
Conclusion and Future Directions

Aspirin therapy remains a crucial aspect of patient care, offering numerous benefits for cardiovascular protection, pain relief, and anti-inflammatory effects. However, it is essential to weigh the benefits against the risks and side effects, particularly for special populations. By understanding the ins and outs of aspirin therapy, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their unique needs.
Final Thoughts
Aspirin therapy can be a valuable tool in maintaining good health, but it is crucial to approach its use with caution and careful consideration. By following the guidelines outlined in this article and consulting with your doctor, you can ensure that aspirin therapy is safe and effective for you.
Gallery of Aspirin Therapy Images
Aspirin Therapy Image Gallery




We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with a deeper understanding of aspirin therapy and its role in maintaining good health. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or leave a comment below.
