Intro
Streamline patient care with a comprehensive Ati Diagnostic Procedure Template. Master the 6-step process to accurately diagnose and treat medical conditions. Learn to identify symptoms, conduct thorough assessments, and develop effective care plans, while improving patient outcomes and streamlining workflows with our expert guide.
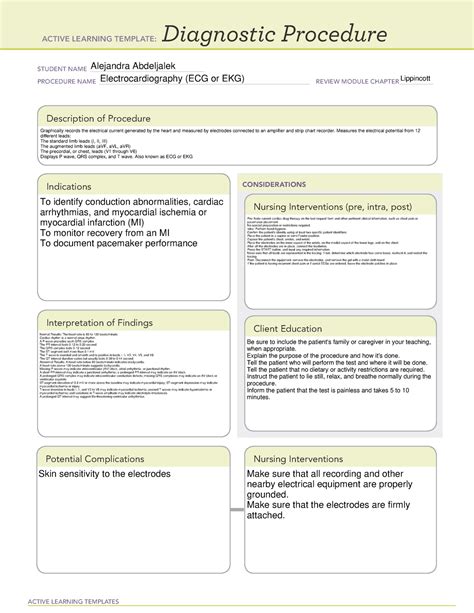
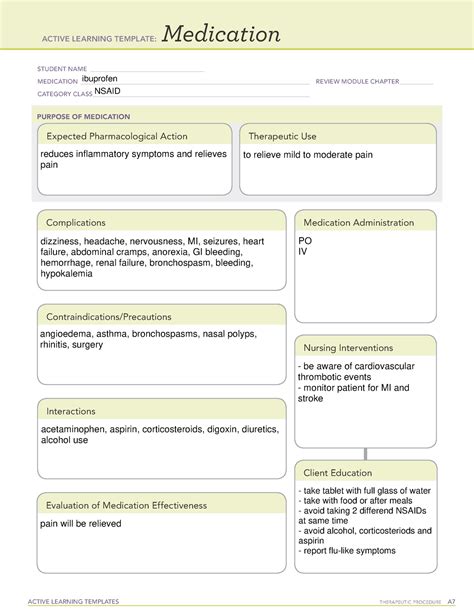
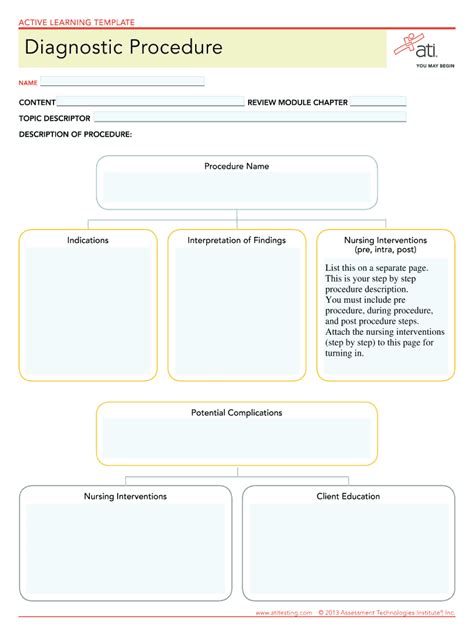
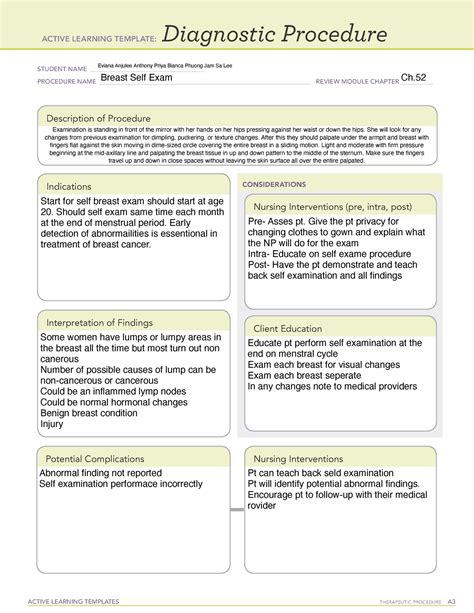
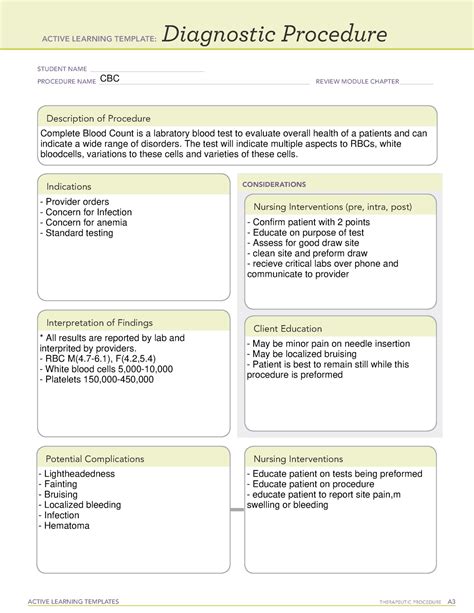
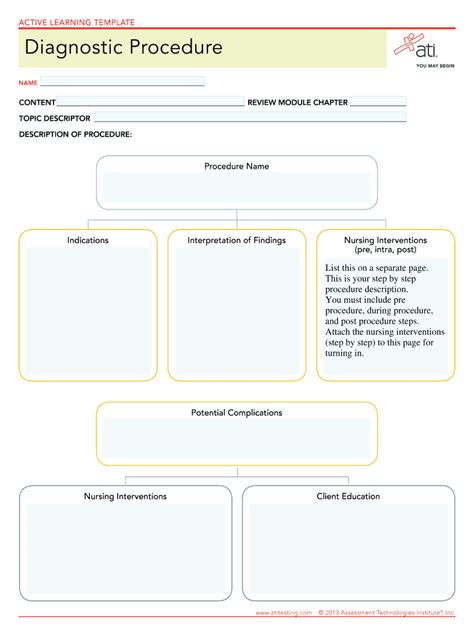
Effective diagnostic procedures are crucial in the medical field, as they enable healthcare professionals to identify and treat various conditions accurately and efficiently. One widely used tool in nursing education and practice is the ATI (Assessment Technologies Institute) Diagnostic Procedure Template. This template provides a structured framework for nurses to gather and analyze patient data, leading to precise diagnoses and optimal patient care. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use the ATI Diagnostic Procedure Template effectively:

Step 1: Gather Information
Gathering Relevant Patient Data
The first step in using the ATI Diagnostic Procedure Template is to gather all relevant information about the patient's condition. This involves reviewing the patient's medical history, current symptoms, laboratory results, and any other pertinent data. Effective information gathering is crucial for making accurate diagnoses and developing appropriate care plans.
- Medical History: Review the patient's past medical history, including any previous illnesses, surgeries, or allergies.
- Current Symptoms: Document the patient's current symptoms, including their onset, duration, and severity.
- Laboratory Results: Review any relevant laboratory results, such as blood work or imaging studies.
- Physical Assessment: Conduct a thorough physical assessment of the patient, including vital signs and any notable physical findings.
Step 2: Analyze Data
Data Analysis for Diagnosis
Once all relevant data has been gathered, the next step is to analyze this information to identify patterns or clues that can lead to a diagnosis. This involves using critical thinking skills to evaluate the data, considering the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results.
- Identify Patterns: Look for patterns or correlations between the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results.
- Consider Differential Diagnoses: Develop a list of potential diagnoses based on the analysis of the patient's data.
- Evaluate the Evidence: Assess the strength of the evidence supporting each potential diagnosis.

Step 3: Develop a Diagnosis
Formulating a Diagnosis
After analyzing the patient's data and considering potential diagnoses, the next step is to formulate a diagnosis. This involves selecting the most likely diagnosis based on the evidence and justifying this choice.
- Select the Most Likely Diagnosis: Choose the diagnosis that best fits the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results.
- Justify the Diagnosis: Explain why this diagnosis is the most likely, citing the evidence that supports it.
Step 4: Plan Interventions
Developing a Plan of Care
With a diagnosis in hand, the next step is to develop a plan of care that addresses the patient's specific needs. This involves identifying the patient's goals, selecting appropriate interventions, and outlining a plan for implementation.
- Identify Patient Goals: Determine what the patient hopes to achieve through treatment.
- Select Interventions: Choose interventions that are likely to help the patient achieve their goals.
- Outline the Plan: Develop a clear plan outlining the interventions, including who will implement them, how they will be implemented, and when they will be evaluated.

Step 5: Implement the Plan
Implementing the Plan of Care
The next step is to implement the plan of care. This involves putting the plan into action, which may involve administering medications, performing procedures, or providing patient education.
- Administer Medications: Give medications as prescribed, ensuring that the patient understands their purpose and potential side effects.
- Perform Procedures: Carry out any necessary procedures, such as wound care or injections.
- Provide Patient Education: Educate the patient on their condition, treatment, and any necessary self-care activities.
Step 6: Evaluate the Plan
Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Plan
The final step is to evaluate the effectiveness of the plan of care. This involves assessing the patient's progress, identifying any issues or concerns, and making adjustments to the plan as needed.
- Assess Progress: Evaluate the patient's progress toward their goals.
- Identify Issues: Identify any issues or concerns that may have arisen during implementation.
- Make Adjustments: Make adjustments to the plan as needed to ensure that the patient's needs are being met.
By following these six steps, healthcare professionals can use the ATI Diagnostic Procedure Template to deliver high-quality patient care that is tailored to the individual's specific needs. Remember, effective diagnostic procedures are critical in the medical field, and using a structured framework like the ATI template can help ensure that diagnoses are accurate and care plans are optimal.
Call to Action
We invite you to share your experiences with the ATI Diagnostic Procedure Template in the comments below. How has this tool helped you in your practice? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? Your insights can help others refine their use of this valuable resource.
Diagnostic Procedure Template Image Gallery