Intro
Master the ATI Diagnostic Template for CHF with our expert guide. Discover 5 effective ways to apply this template in clinical practice, enhancing your assessment and diagnostic skills for congestive heart failure patients. Learn how to streamline your workflow, improve patient outcomes, and ensure accurate diagnoses with our actionable tips and insights.
The American Teachers of Nursing (ATI) Diagnostic Template is a valuable tool for nursing students and professionals to develop critical thinking skills and create individualized care plans for patients. One common condition that nursing students often practice with is congestive heart failure (CHF). In this article, we will explore five ways to apply the ATI Diagnostic Template for CHF, along with examples and explanations to help you better understand the process.
Understanding CHF and the ATI Diagnostic Template
CHF is a chronic progressive condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. The ATI Diagnostic Template is a framework used to organize and prioritize patient data, identify nursing diagnoses, and develop a plan of care. The template consists of seven columns: Patient Profile, Presenting Problem, Functional Patterns, Nursing Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention, and Evaluation.
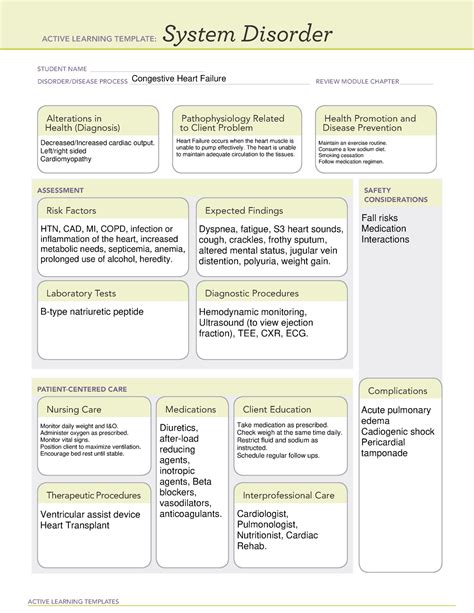
Way 1: Identifying Patient Profile and Presenting Problem
When applying the ATI Diagnostic Template for CHF, the first step is to identify the patient's profile and presenting problem. This involves gathering demographic information, medical history, and current symptoms. For example:
- Patient Profile: 65-year-old male with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia.
- Presenting Problem: Shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs.
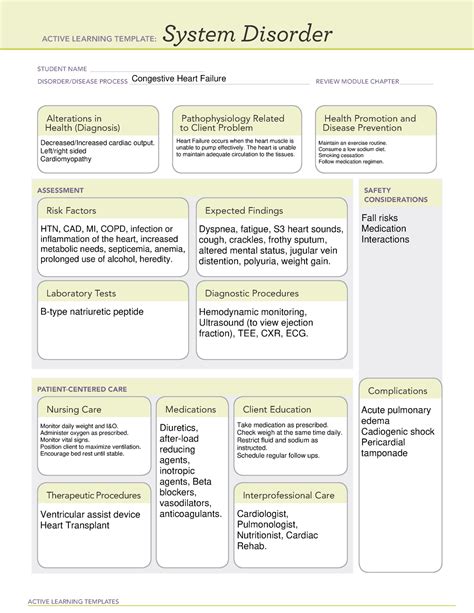
Way 2: Analyzing Functional Patterns
The next step is to analyze the patient's functional patterns, including nutritional, elimination, activity, and sleep patterns. For CHF patients, common functional patterns include:
- Nutritional: Decreased appetite, sodium-restricted diet.
- Elimination: Decreased urine output, nocturia.
- Activity: Decreased energy levels, fatigue.
- Sleep: Disturbed sleep patterns, orthopnea.
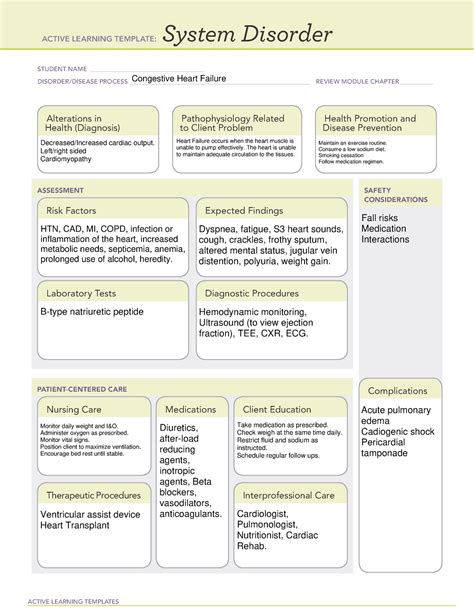
Way 3: Identifying Nursing Diagnoses
Using the data gathered from the patient's profile, presenting problem, and functional patterns, the next step is to identify nursing diagnoses. For CHF patients, common nursing diagnoses include:
- Excess Fluid Volume
- Activity Intolerance
- Fatigue
- Decreased Cardiac Output
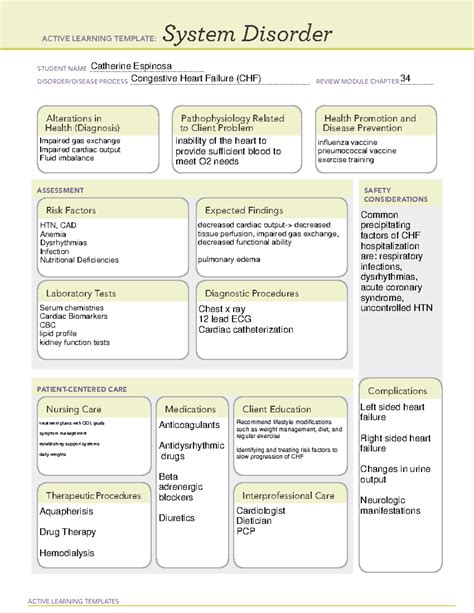
Way 4: Planning and Interventions
Once nursing diagnoses are identified, the next step is to develop a plan of care and interventions. This may include:
- Medication management: ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, diuretics.
- Lifestyle modifications: Sodium-restricted diet, regular exercise, stress reduction.
- Monitoring: Daily weights, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
Way 5: Evaluation and Revision
The final step is to evaluate the effectiveness of the plan of care and revise as necessary. This may involve:
- Monitoring patient outcomes: Weight, blood pressure, oxygen saturation.
- Revising the plan of care: Adjusting medications, increasing exercise intensity.
- Discharge planning: Educating patient and family on self-care and follow-up appointments.
Gallery of CHF ATI Diagnostic Template Images
CHF ATI Diagnostic Template Image Gallery
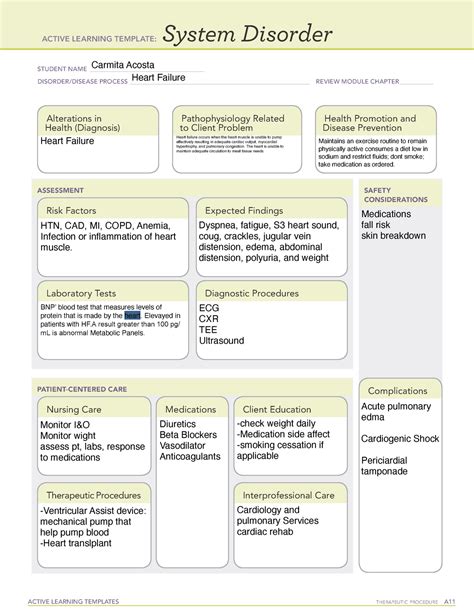
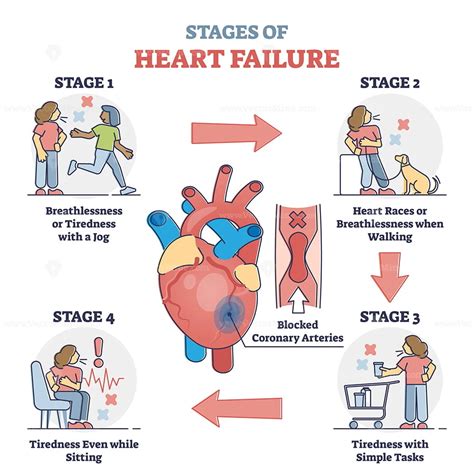


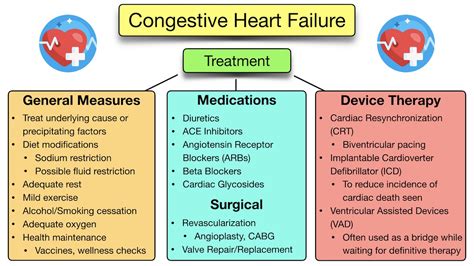

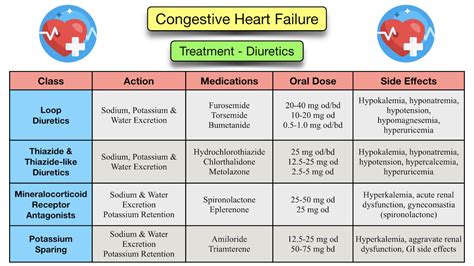


We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of how to apply the ATI Diagnostic Template for CHF. By following these five ways, you can develop a thorough plan of care that addresses the unique needs of your patients. Remember to always evaluate and revise your plan as necessary to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Share your thoughts and experiences with us in the comments below! Have you used the ATI Diagnostic Template for CHF patients? What were some challenges you faced, and how did you overcome them?
