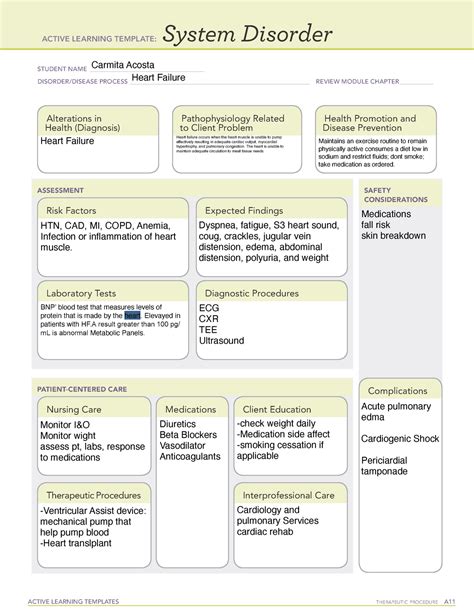
Heart failure is a complex and debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment of heart failure. The American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) have developed guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the diagnosis of heart failure using the ACC/AHA diagnostic template.
Understanding Heart Failure
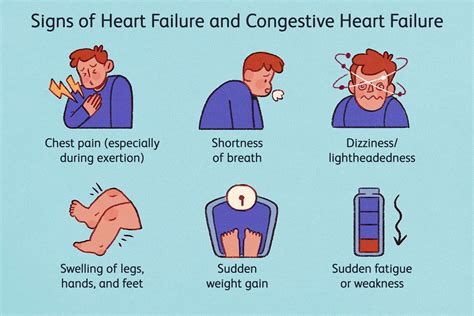
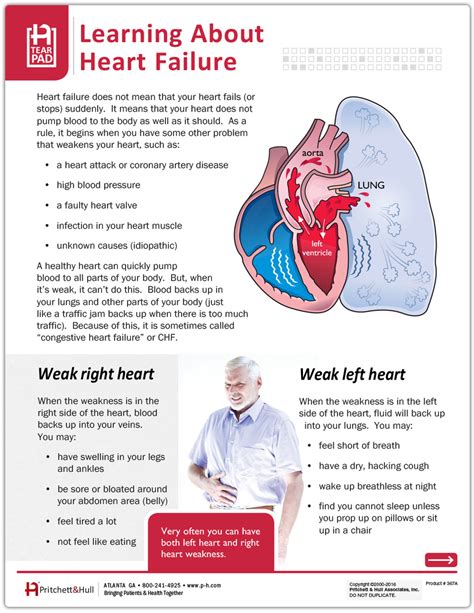
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome characterized by symptoms of volume overload, fatigue, and shortness of breath, resulting from impaired ventricular function. It is a progressive condition that can lead to significant morbidity and mortality if left untreated.
Types of Heart Failure
There are two main types of heart failure:
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF): This type of heart failure is characterized by a reduced ejection fraction (EF) of less than 40%.
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): This type of heart failure is characterized by a normal or near-normal EF, but with evidence of diastolic dysfunction.
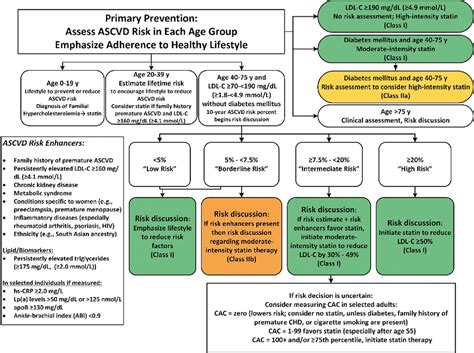
Diagnostic Criteria for Heart Failure
The ACC/AHA diagnostic template for heart failure includes the following criteria:

- Symptoms: The patient must have symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling.
- Physical Examination: The patient must have physical examination findings consistent with heart failure, such as jugular venous distension, pulmonary rales, or peripheral edema.
- Laboratory Tests: The patient must have laboratory tests that support the diagnosis of heart failure, such as elevated B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels or cardiac troponin.
- Imaging Studies: The patient must have imaging studies that support the diagnosis of heart failure, such as echocardiography or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
BNP Levels and Heart Failure
BNP levels are a valuable diagnostic tool for heart failure. Elevated BNP levels are associated with an increased risk of heart failure and mortality.
- BNP levels < 100 pg/mL: Low risk for heart failure
- BNP levels 100-500 pg/mL: Intermediate risk for heart failure
- BNP levels > 500 pg/mL: High risk for heart failure
Echocardiography in Heart Failure
Echocardiography is a critical diagnostic tool for heart failure. It can provide information on:
- Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF): LVEF is a measure of the left ventricle's ability to pump blood.
- Left ventricular size: Left ventricular size can provide information on the severity of heart failure.
- Valvular function: Valvular function can provide information on the presence of valvular heart disease.
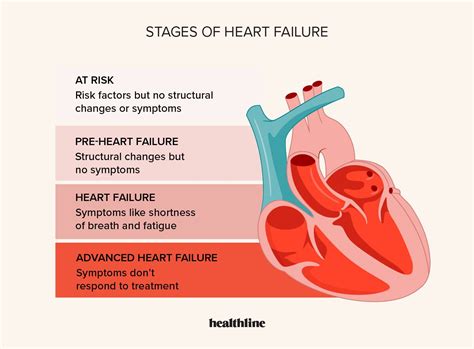
Stages of Heart Failure
The ACC/AHA has defined four stages of heart failure:
- Stage A: High risk for heart failure, but no symptoms or structural heart disease
- Stage B: Structural heart disease, but no symptoms
- Stage C: Symptomatic heart failure
- Stage D: Refractory heart failure
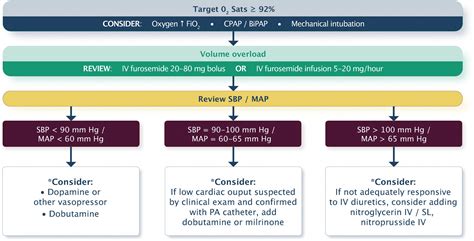
Treatment of Heart Failure
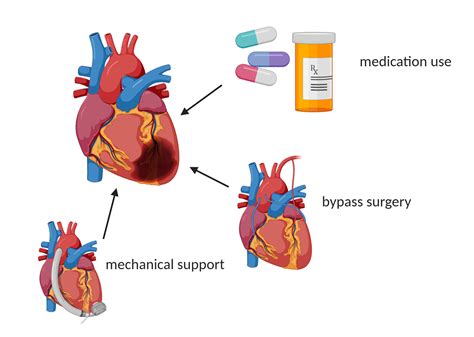
Treatment of heart failure depends on the stage and severity of the disease. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and exercise, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Medications: Medications, such as beta blockers and ACE inhibitors, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Device therapy: Device therapy, such as implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
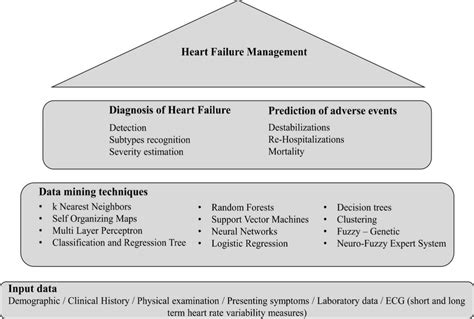
Heart Failure Management
Heart failure management involves a team approach, including:
- Primary care physicians: Primary care physicians play a critical role in managing heart failure.
- Cardiologists: Cardiologists play a critical role in managing heart failure.
- Other healthcare professionals: Other healthcare professionals, such as nurses and pharmacists, play a critical role in managing heart failure.
Conclusion
Heart failure is a complex and debilitating condition that requires accurate diagnosis and effective management. The ACC/AHA diagnostic template provides a comprehensive guide to the diagnosis of heart failure. By using this template, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care for patients with heart failure.
Heart Failure Image Gallery




We hope this article has provided valuable information on the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Share your thoughts and experiences with heart failure in the comments below.
