Intro
Discover the 5 essential facts about Lisinopril medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions. Learn how this ACE inhibitor works to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart failure, strokes, and kidney disease. Understand the benefits and risks of Lisinopril therapy and how to take it safely and effectively.
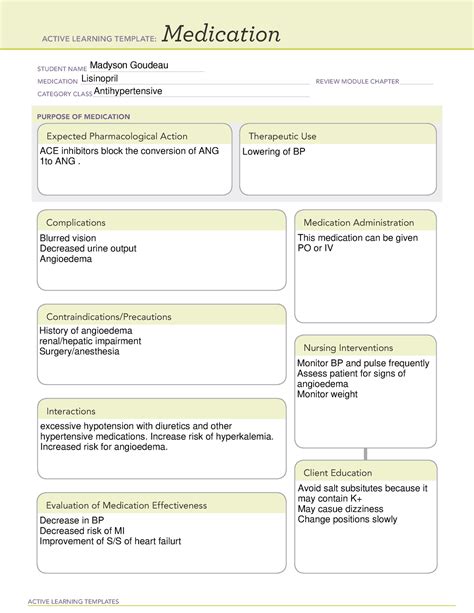
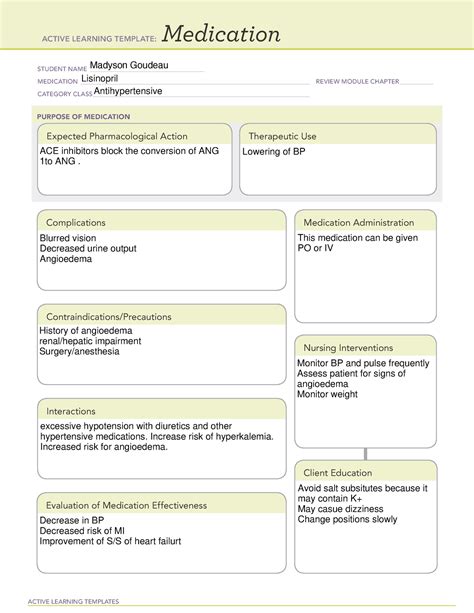
Lisinopril is a medication widely used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. It belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. These medications work by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. By doing so, lisinopril helps to relax blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily and reducing blood pressure.
The effects of lisinopril can be life-changing for individuals dealing with hypertension or heart failure. However, as with any medication, it's crucial to understand the essential facts about lisinopril to ensure safe and effective use. This article will delve into five critical aspects of lisinopril medication that every user should know.
What is Lisinopril Used For?
Lisinopril is primarily used to treat two main conditions: high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. High blood pressure is a condition where the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. This can lead to cardiovascular diseases, kidney damage, and stroke. Lisinopril helps to lower blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels, thereby reducing the risk of these complications.
In the case of heart failure, lisinopril works by improving the heart's pumping efficiency. Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Lisinopril helps to alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles.
How Does Lisinopril Work?
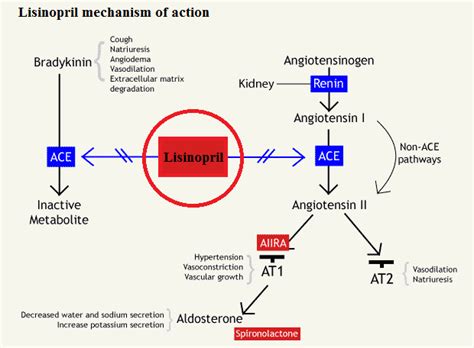
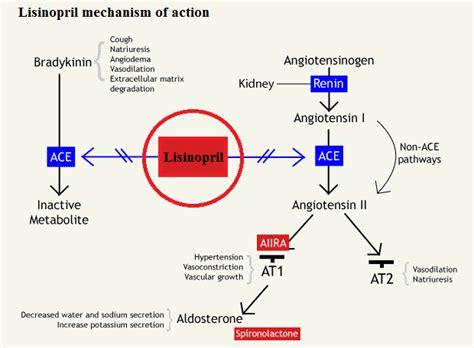
Lisinopril works by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). ACE is responsible for converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. By blocking this conversion, lisinopril reduces the levels of angiotensin II in the blood. This leads to vasodilation, or the widening of blood vessels, which in turn lowers blood pressure.
Additionally, lisinopril increases the levels of bradykinin, a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate. This further contributes to the reduction in blood pressure.
Lisinopril Side Effects
While lisinopril is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects. Common side effects include:
- Cough (dry, persistent)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
In rare cases, lisinopril can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat)
- High levels of potassium in the blood
- Decreased kidney function
- Allergic reactions
It's essential to report any side effects to your doctor, especially if they are severe or persistent.
Lisinopril Interactions
Lisinopril can interact with other medications, including:
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Potassium-sparing diuretics
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Lithium
- Gold injections
These interactions can lead to increased levels of potassium in the blood, decreased kidney function, or other complications. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.

Lisinopril Dosage
The dosage of lisinopril varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual's response to the medication. For high blood pressure, the typical starting dose is 5-10 mg per day. For heart failure, the starting dose is usually 2.5-5 mg per day.
It's essential to follow your doctor's instructions regarding dosage and titration. Do not adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
Lisinopril Warnings
Lisinopril is not suitable for everyone. Certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid taking lisinopril, including:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with kidney disease or kidney failure
- Those with a history of angioedema
- People with diabetes or kidney disease taking aliskiren
Your doctor will assess your medical history and current health status to determine if lisinopril is safe for you to take.
Conclusion
Lisinopril is a valuable medication for treating high blood pressure and heart failure. However, it's crucial to understand the essential facts about lisinopril to ensure safe and effective use. By knowing the indications, mechanism of action, side effects, interactions, dosage, and warnings, you can work with your doctor to manage your condition and improve your quality of life.
We encourage you to share your experiences with lisinopril in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please consult with your doctor or pharmacist.
Lisinopril Medication Template Image Gallery