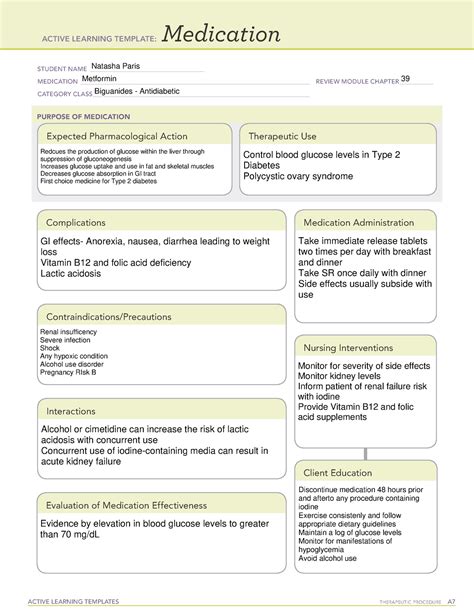
Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of medications known as biguanides, which work by decreasing glucose production in the liver, increasing insulin sensitivity, and enhancing glucose uptake by muscles. As a medication, metformin has been extensively studied and used for decades. Here are five key facts about metformin that you should know:
1. Mechanism of Action
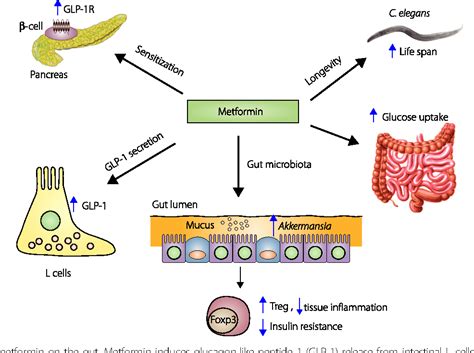
Metformin's primary mechanism of action is the inhibition of hepatic glucose production. It suppresses the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase, which is responsible for the release of glucose from stored glycogen in the liver. Additionally, metformin increases the sensitivity of muscle cells to insulin, allowing glucose to enter the cells more effectively. This results in a reduction of blood glucose levels and an improvement in insulin sensitivity.
How Metformin Works
- Decreases glucose production in the liver
- Increases insulin sensitivity in muscles
- Enhances glucose uptake by muscles
Benefits of Metformin
- Effective in lowering blood glucose levels
- May help with weight loss
- Can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease
2. Side Effects and Contraindications
While metformin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including:
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Muscle pain
In rare cases, metformin can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Lactic acidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of lactic acid in the blood
- Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar
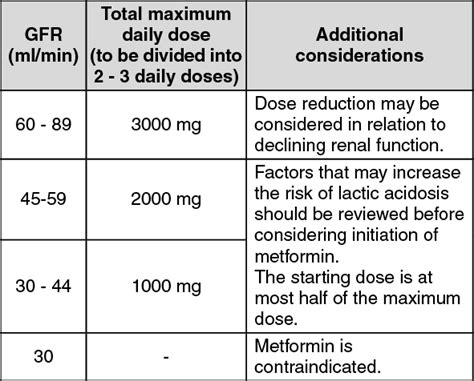
Metformin is contraindicated in individuals with:
- Kidney disease or impairment
- Liver disease or impairment
- Heart failure
- Respiratory disease

3. Dosage and Administration
The dosage of metformin varies depending on the individual's needs and medical history. Typically, the starting dose is 500-850 mg per day, taken orally with meals. The maximum daily dose is 2550 mg. Metformin is available in various formulations, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets.
Metformin Dosage Forms
- Immediate-release tablets: 500-850 mg per day
- Extended-release tablets: 500-2000 mg per day
4. Interactions and Contraindications
Metformin can interact with other medications, including:
- ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Nifedipine
- Cimetidine
- Furosemide
It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products you are taking before starting metformin.

5. Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial when taking metformin. Your healthcare provider will:
- Check your blood glucose levels regularly
- Monitor your kidney function and liver enzymes
- Adjust your dosage as needed
- Monitor for signs of lactic acidosis or hypoglycemia
Monitoring Parameters
- Blood glucose levels
- Kidney function
- Liver enzymes
- Signs of lactic acidosis or hypoglycemia
Metformin Image Gallery




If you have any questions or concerns about metformin, don't hesitate to ask your healthcare provider. Share this article with friends and family who may be taking metformin, and encourage them to discuss their treatment plan with their healthcare provider. By working together, we can ensure the safe and effective use of metformin and other medications.
