Intro
Unlock the secrets of Metoprolol with our ATi medication template guide. Learn about this beta-blockers uses, dosages, side effects, and interactions. Understand how Metoprolol works, its indications, and contraindications. Perfect for nursing students and healthcare professionals, this comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of Metoprolols pharmacology and therapeutic applications.
Understanding Metoprolol Medication: Benefits, Side Effects, and More
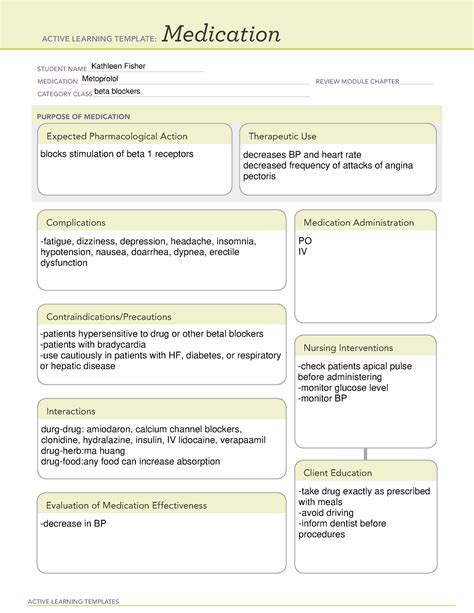
As one of the most commonly prescribed medications for heart-related conditions, Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that has been widely used for decades. It's essential to understand the benefits, side effects, and proper usage of this medication to maximize its effectiveness and minimize potential risks. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of Metoprolol, exploring its uses, dosage, interactions, and more.
What is Metoprolol Used For?
Metoprolol is primarily used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Angina pectoris (chest pain)
- Heart failure
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction)
- Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat)
By reducing the heart rate and blood pressure, Metoprolol helps alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent complications associated with these conditions.
How Does Metoprolol Work?
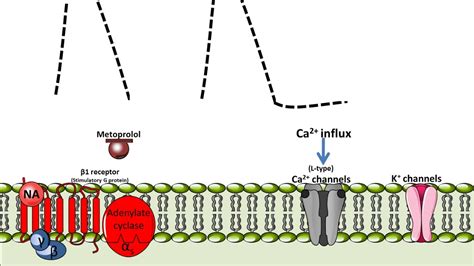
Metoprolol belongs to the beta-blocker class of medications, which work by blocking the effects of epinephrine (adrenaline) on the heart. This leads to a decrease in heart rate, contractility, and cardiac output, resulting in lower blood pressure and reduced oxygen demand.
By slowing the heart rate, Metoprolol also increases the time for the heart to fill with blood, allowing for more efficient pumping and improved cardiac function.
Metoprolol Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of Metoprolol vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual patient's needs.
- For hypertension, the typical starting dose is 100-200 mg per day, taken in divided doses.
- For angina, the starting dose is usually 100-200 mg per day, taken in divided doses.
- For heart failure, the starting dose is typically 25-50 mg per day, taken in divided doses.
It's essential to take Metoprolol exactly as prescribed by your doctor, with or without food, and at the same time each day.
Metoprolol Side Effects and Interactions
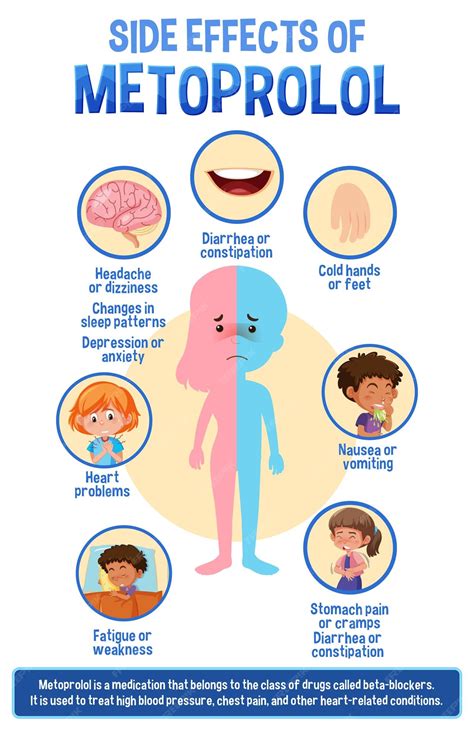
Like any medication, Metoprolol can cause side effects, some of which may be serious. Common side effects include:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Shortness of breath
More severe side effects may include:
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Worsening heart failure
- Allergic reactions
Metoprolol can interact with other medications, including:
- Other beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Anti-arrhythmic medications
- Clonidine
- MAOIs
It's crucial to inform your doctor about all medications you're taking, including supplements and herbal products, to minimize potential interactions.
Metoprolol and Exercise
Regular exercise is essential for overall health, but it's essential to exercise safely while taking Metoprolol. Here are some tips:
- Consult your doctor before starting a new exercise program.
- Avoid strenuous exercise, especially if you're new to physical activity.
- Warm up and cool down slowly to prevent sudden changes in heart rate and blood pressure.
- Monitor your heart rate and blood pressure regularly.
Metoprolol and Weight Gain

Some patients may experience weight gain while taking Metoprolol, particularly those with heart failure. This is often due to increased fluid retention and decreased metabolism.
To minimize weight gain, focus on a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
Metoprolol and Anxiety
Beta-blockers like Metoprolol can exacerbate anxiety symptoms in some individuals. If you experience anxiety, talk to your doctor about:
- Adjusting your dosage
- Adding an anti-anxiety medication
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing
Metoprolol and Pregnancy

Metoprolol can be used during pregnancy, but it's essential to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. Beta-blockers may affect fetal development, particularly if taken during the first trimester.
If you become pregnant while taking Metoprolol, inform your doctor immediately.
Metoprolol and Breastfeeding
Metoprolol is excreted in breast milk, but the amounts are typically small. However, it's essential to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before breastfeeding while taking Metoprolol.
Metoprolol Overdose and Withdrawal

Taking too much Metoprolol can lead to overdose symptoms, including:
- Slow heart rate
- Low blood pressure
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Coma
If you suspect an overdose, seek medical attention immediately.
Stopping Metoprolol abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as:
- Increased heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Chest pain
- Anxiety
Gradually tapering off the medication under medical supervision can minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Metoprolol Medication Image Gallery
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into Metoprolol medication. Remember to consult your doctor or healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Share your thoughts and experiences with Metoprolol in the comments section below.
