Collecting a sterile urine specimen is a crucial step in diagnosing various medical conditions, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney diseases, and other disorders affecting the urinary system. A sterile urine specimen is essential for accurate laboratory results, as contamination can lead to false positives or false negatives. In this article, we will outline the 5 steps to collecting a sterile urine specimen using the ATI (Assessment Technologies Institute) template.

Step 1: Prepare the Patient and Equipment
Before collecting a sterile urine specimen, it is essential to prepare the patient and gather the necessary equipment. Ensure the patient understands the importance of providing a sterile specimen and is willing to cooperate. Gather the following equipment:
- Sterile urine collection container
- Antiseptic wipes or soap and water for cleaning the genital area
- Gloves (optional)
- Label and marker for specimen identification
Step 2: Clean and Prepare the Genital Area
Thoroughly clean and prepare the genital area to minimize the risk of contamination. Use antiseptic wipes or soap and water to clean the urethral opening and surrounding area. For females, clean the labia and vaginal opening. For males, clean the tip of the penis and surrounding area.

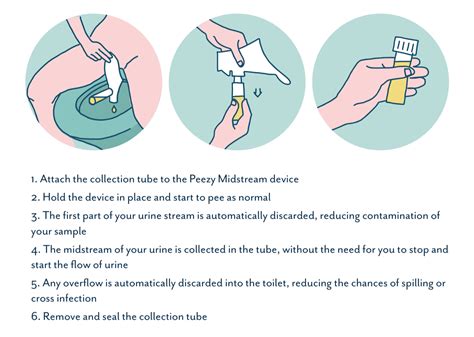
Step 3: Collect the Urine Specimen
Collect the urine specimen using the midstream collection method. Instruct the patient to:
- Start urinating into the toilet
- Then, without stopping the urine flow, place the sterile collection container under the urine stream
- Collect 10-15 mL of urine
- Remove the container from the urine stream without touching the inside of the container
Step 4: Label and Handle the Specimen
Properly label and handle the urine specimen to maintain its integrity. Label the specimen container with the patient's identification, date, and time of collection. Handle the specimen carefully to avoid contamination and ensure timely transportation to the laboratory.

Step 5: Transport and Store the Specimen
Transport the urine specimen to the laboratory promptly and store it according to laboratory guidelines. Typically, urine specimens are stored in a refrigerator at 2-8°C (36-46°F) until analysis.

Urine Specimen Collection Tips and Variations
- For pediatric patients, use a sterile urine collection bag or a catheter to collect the specimen.
- For patients with urinary catheters, collect the specimen from the catheter tubing.
- For patients with urinary diversions (e.g., ostomy), collect the specimen from the diversion site.
Urine Specimen Collection Gallery




By following these 5 steps to collecting a sterile urine specimen using the ATI template, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate laboratory results and effective patient care. Remember to handle the specimen carefully and transport it promptly to the laboratory to maintain its integrity.
