Intro
Unlock the connection between Ati System Disorder and Cystic Fibrosis. Discover 5 key ways these conditions intersect, including respiratory implications, nutritional deficiencies, and gastrointestinal complications. Learn how understanding these relationships can improve treatment outcomes and enhance patient care for those with Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder.
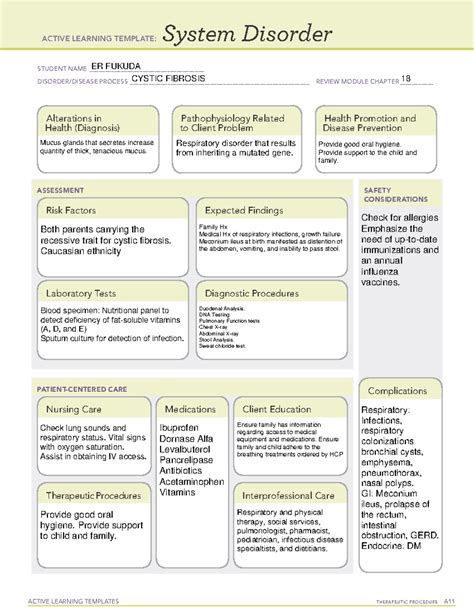
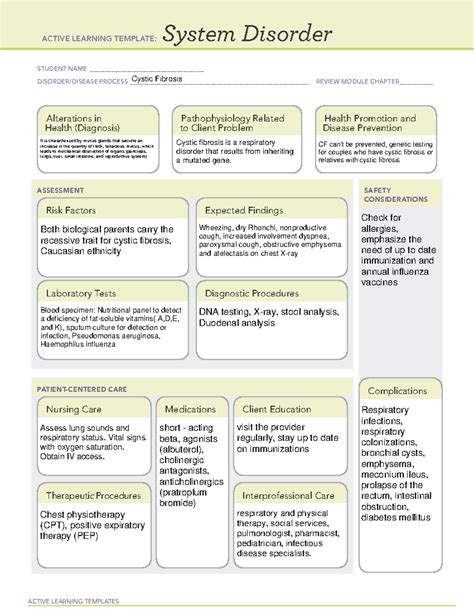
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems, causing severe damage and reducing life expectancy. While researching the complexities of CF, scientists have discovered a surprising connection between Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder (ASD). In this article, we will explore the relationship between these two seemingly unrelated conditions and examine the commonalities that exist between them.
Historically, Cystic Fibrosis was thought to be solely a respiratory disease, but recent studies have shown that it has a significant impact on the body's entire system, including the digestive system, pancreas, and even the brain. Ati System Disorder, on the other hand, is a lesser-known condition that affects the Ati system, which is responsible for maintaining balance and harmony in the body. Despite their differences, research has revealed a surprising overlap between the two conditions.
1. Shared Genetic Mutations
Studies have shown that certain genetic mutations associated with Cystic Fibrosis may also contribute to the development of Ati System Disorder. For example, mutations in the CFTR gene, which is responsible for regulating chloride channels in the body, have been linked to both CF and ASD. This suggests that there may be a common underlying genetic mechanism that contributes to the development of both conditions.
CFTR Gene Mutations
The CFTR gene is responsible for encoding a protein that regulates chloride channels in the body. Mutations in this gene can lead to the development of Cystic Fibrosis, as well as other conditions, including Ati System Disorder. Research has shown that CFTR gene mutations can affect the function of the Ati system, leading to an imbalance in the body's energy and potentially contributing to the development of ASD.
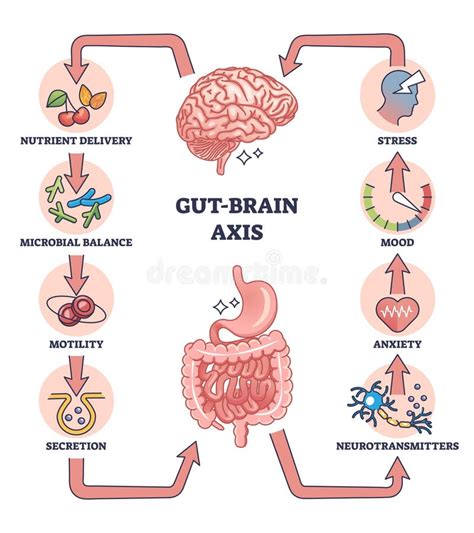
2. Gut-Brain Axis Connection
Both Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder have been linked to alterations in the gut-brain axis, which is the bidirectional communication network between the gut microbiome and the central nervous system. Research has shown that changes in the gut microbiome can affect the development and function of the brain, leading to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and even ASD. Similarly, CF has been linked to changes in the gut microbiome, which can affect the body's ability to digest and absorb nutrients.
Gut Microbiome Alterations
Alterations in the gut microbiome have been linked to both CF and ASD. In CF, the gut microbiome is often characterized by an overgrowth of certain bacteria, which can lead to inflammation and damage to the gut lining. Similarly, in ASD, the gut microbiome is often altered, with changes in the balance of certain bacteria. This suggests that the gut microbiome may play a critical role in the development and function of the Ati system, and that alterations in the gut microbiome may contribute to the development of ASD.
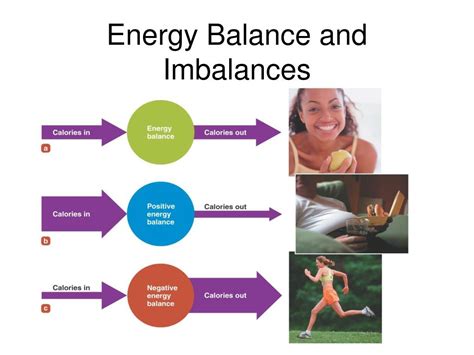
3. Energy Imbalance
Both Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder are characterized by an energy imbalance in the body. In CF, the body's energy is often depleted due to the constant battle against infection and inflammation. Similarly, in ASD, the body's energy is often imbalanced, leading to fatigue, lethargy, and other symptoms. This energy imbalance can affect the body's ability to function properly, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
ATP Production
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the primary energy source for the body's cells. In CF, ATP production is often impaired, leading to a decrease in energy levels. Similarly, in ASD, ATP production is often altered, leading to an energy imbalance. Research has shown that ATP production is critical for the proper functioning of the Ati system, and that alterations in ATP production may contribute to the development of ASD.
4. Inflammation Connection

Both Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder are characterized by chronic inflammation, which can lead to tissue damage and a range of symptoms. In CF, inflammation is often caused by the presence of bacteria in the lungs, which can lead to a cycle of infection and inflammation. Similarly, in ASD, inflammation is often present, and can lead to tissue damage and a range of symptoms.
Cytokine Imbalance
Cytokines are signaling molecules that play a critical role in the body's immune response. In CF, cytokine imbalance is often present, leading to an overactive immune response and chronic inflammation. Similarly, in ASD, cytokine imbalance is often present, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Research has shown that cytokine imbalance may contribute to the development of ASD, and that targeting cytokine imbalance may be a potential therapeutic strategy.
5. Treatment Overlap
Despite their differences, Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder share some common treatment strategies. For example, both conditions often require nutritional support, as well as management of inflammation and infection. Additionally, both conditions may benefit from stress management and relaxation techniques, such as meditation and yoga.
Nutritional Support
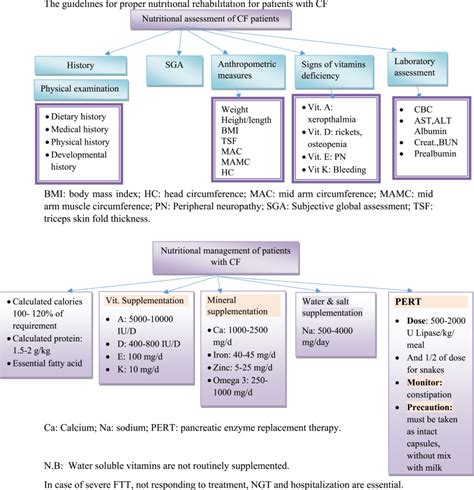
Nutritional support is critical for both CF and ASD, as both conditions can lead to malnutrition and weight loss. Research has shown that nutritional support can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life in both conditions.
Gallery of Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder
Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder Image Gallery




In conclusion, the relationship between Cystic Fibrosis and Ati System Disorder is complex and multifaceted. While the two conditions may seem unrelated at first glance, research has revealed a surprising overlap between them. By understanding the shared genetic mutations, gut-brain axis connection, energy imbalance, inflammation connection, and treatment overlap between CF and ASD, we may be able to develop new therapeutic strategies for managing these conditions. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with CF and ASD in the comments below.
