Intro
Unlock the complexities of Tuberculosis and ATI System Disorder with our comprehensive template. Understand the relationship between TB and Autonomic Nervous System dysfunction, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve patient outcomes with our expertly crafted template.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis that primarily affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. It is a significant public health concern worldwide, with an estimated 10 million new cases and 1.5 million deaths annually. One of the lesser-known complications of TB is its impact on the autonomic nervous system (ANS), specifically the autonomic nervous system disorder (ATI). In this article, we will explore the relationship between TB and ATI, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
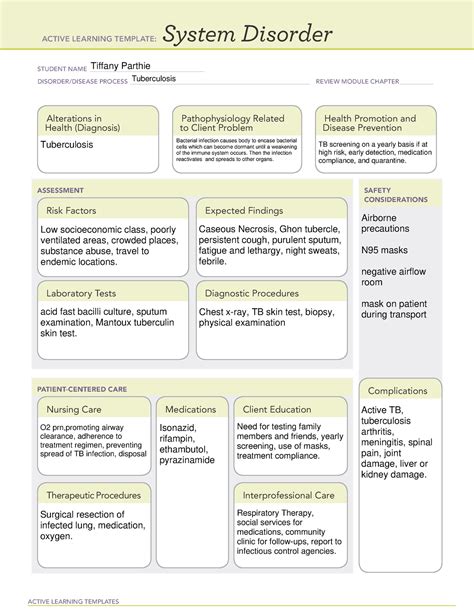
Understanding Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The ANS is a complex system that regulates various involuntary functions of the body, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiratory rate. It is divided into two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The SNS is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, while the PNS promotes relaxation and restoration.
What is Autonomic Nervous System Disorder (ATI)?
ATI, also known as autonomic dysfunction, is a condition where the ANS is impaired, leading to abnormal regulation of the body's involuntary functions. This can result in a range of symptoms, including dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, headache, and digestive problems.
The Relationship Between TB and ATI
TB can affect the ANS in several ways, leading to ATI. The bacteria that cause TB can infect the nerves that control the ANS, leading to inflammation and damage. This can disrupt the normal functioning of the ANS, resulting in a range of symptoms.
Causes of ATI in TB Patients
Several factors can contribute to the development of ATI in TB patients, including:
- Direct infection of the nerves by TB bacteria
- Inflammation and scarring caused by TB
- Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
- Other underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS
Symptoms of ATI in TB Patients
The symptoms of ATI in TB patients can vary depending on the extent of the infection and the specific nerves affected. Common symptoms include:
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Headache and migraines
- Digestive problems, such as nausea and diarrhea
- Rapid heart rate and palpitations
- High blood pressure

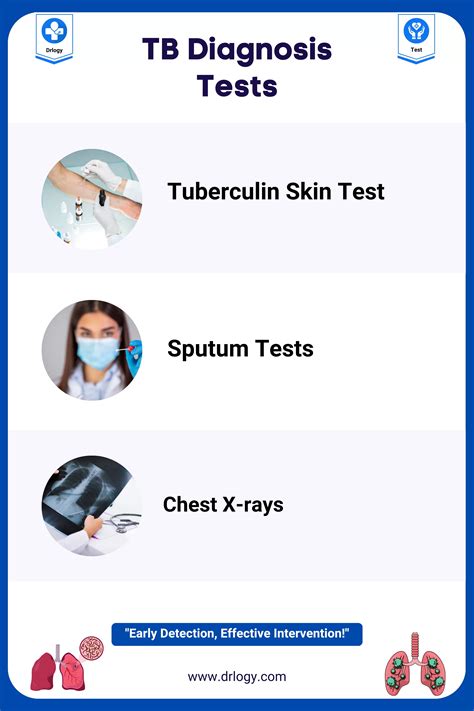
Diagnosis of ATI in TB Patients
Diagnosing ATI in TB patients can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. A comprehensive diagnosis involves:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and imaging studies
- Autonomic function tests, such as heart rate variability and blood pressure monitoring
Treatment of ATI in TB Patients
Treatment of ATI in TB patients typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications. Medications may include:
- Anti-TB medications to treat the underlying infection
- Medications to manage symptoms, such as dizziness and digestive problems
- Medications to regulate the ANS, such as beta blockers and anti-cholinergics
Lifestyle modifications may include:
- Getting plenty of rest and avoiding stress
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Staying hydrated and avoiding dehydration
- Avoiding triggers that can exacerbate symptoms
Conclusion
TB is a significant public health concern that can have serious complications, including ATI. Understanding the relationship between TB and ATI is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the symptoms and causes of ATI in TB patients, healthcare professionals can provide effective treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Gallery of Tuberculosis and Autonomic Nervous System Disorder
Tuberculosis and Autonomic Nervous System Disorder Image Gallery







FAQ
Q: What is the most common cause of TB? A: The most common cause of TB is the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Q: What are the symptoms of ATI in TB patients? A: The symptoms of ATI in TB patients can include dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, headache, and digestive problems.
Q: How is ATI in TB patients diagnosed? A: Diagnosing ATI in TB patients involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and autonomic function tests.
Q: What is the treatment for ATI in TB patients? A: Treatment of ATI in TB patients typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications.

