Intro
Discover the complexities of Atrial Fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder, and its impact on overall health. Learn about AFib symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, including medication, cardioversion, and catheter ablation. Understand how to manage this arrhythmia and reduce stroke risk with lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
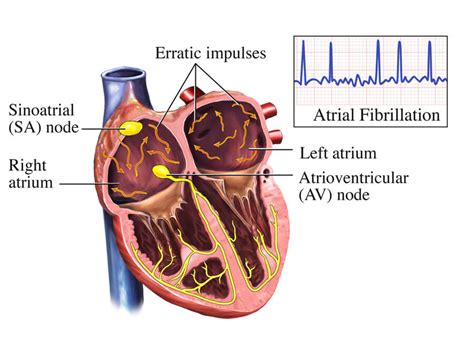
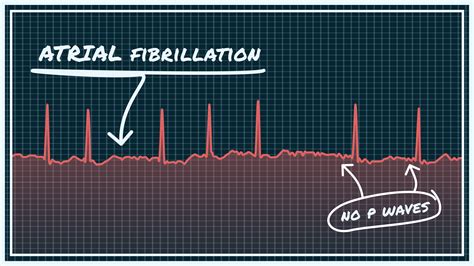
Atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib, is a common type of irregular heartbeat that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the upper chambers of the heart, called the atria, beat too quickly and irregularly, leading to a quivering or fibrillating motion. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other complications.
In simple terms, atrial fibrillation is like a "skip" in the heart's rhythm. Normally, the heart beats in a steady, predictable pattern, but with AFib, the atria beat too fast and irregularly, causing the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart) to contract in an irregular and often rapid manner. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness.
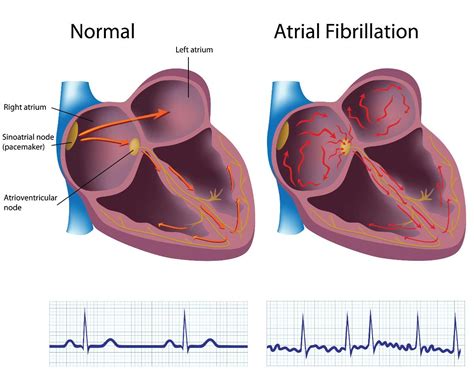
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Atrial Fibrillation
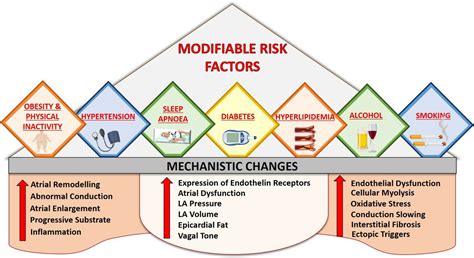
Atrial fibrillation can be caused by a range of factors, including:
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can cause the atria to stretch and thicken, leading to irregular heartbeats.
- Heart valve problems: Conditions such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis can increase the risk of AFib.
- Heart failure: Heart failure can cause the atria to become enlarged and weak, leading to irregular heartbeats.
- Coronary artery disease: Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries can lead to AFib.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control the heart, leading to irregular heartbeats.
- Sleep apnea: Pauses in breathing during sleep can increase the risk of AFib.
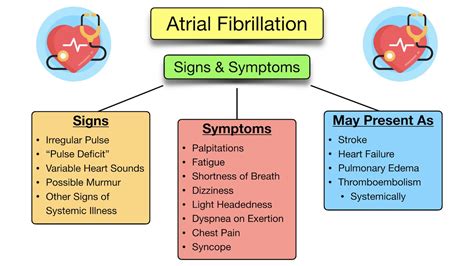
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
The symptoms of atrial fibrillation can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Palpitations: A feeling of irregular or skipped heartbeats.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded even when sitting still.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak, even after resting.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy, especially when standing up.
- Chest pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest, arm, neck, jaw, or back.
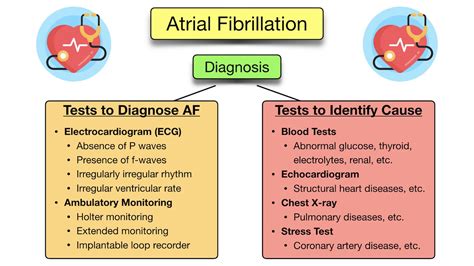
Diagnosing Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation can be diagnosed using a range of tests, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A test that measures the heart's electrical activity.
- Holter monitor: A portable device that records the heart's activity over 24 hours.
- Echocardiogram: A test that uses sound waves to create images of the heart.
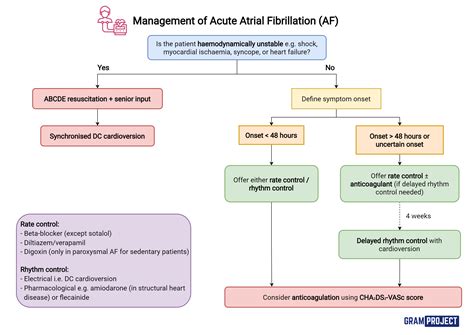
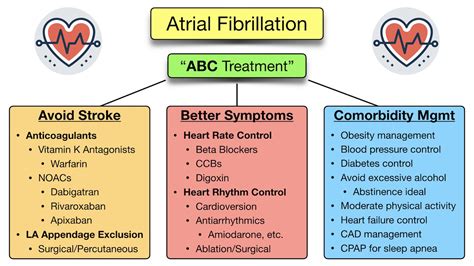
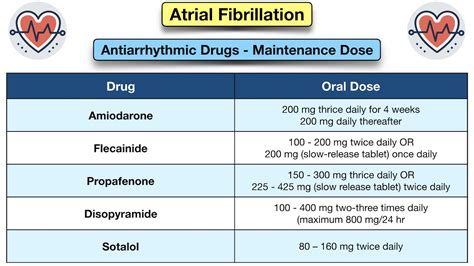
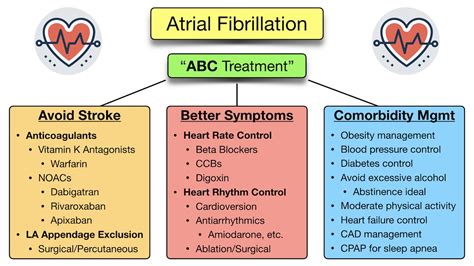
Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation
Treatment for atrial fibrillation usually involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Medications may include:
- Blood thinners: To reduce the risk of stroke.
- Beta blockers: To slow the heart rate.
- Anti-arrhythmics: To regulate the heart rhythm.
Lifestyle changes may include:
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of AFib.
- Reducing stress: Stress can trigger AFib episodes.
- Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce the risk of AFib.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of AFib.
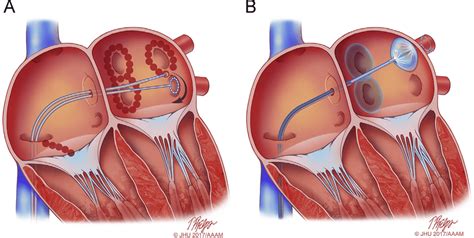
In some cases, surgery or catheter ablation may be necessary to treat AFib. These procedures aim to restore a normal heart rhythm by destroying or scarring the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
Living with Atrial Fibrillation
Living with atrial fibrillation requires making lifestyle changes and working with a healthcare provider to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Here are some tips for living with AFib:
- Monitor your symptoms: Keep track of when your symptoms occur and what triggers them.
- Take your medications as directed: Medications can help regulate your heart rhythm and reduce symptoms.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help reduce the risk of dehydration, which can trigger AFib episodes.
- Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor your condition and prevent complications.
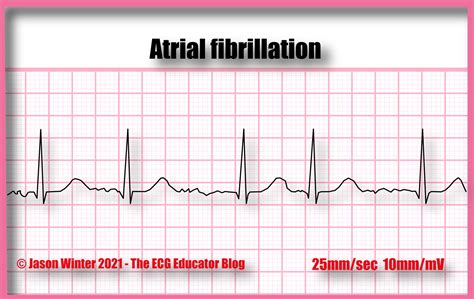
Gallery of Atrial Fibrillation Images
Atrial Fibrillation Image Gallery
We hope this article has helped you understand atrial fibrillation and its effects on the body. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. Share this article with others who may be living with AFib, and let's work together to raise awareness and promote heart health.
Please comment below with your thoughts, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about atrial fibrillation.
