Intro
Discover 5 key Atrophic Vulvovaginitis symptoms, including vaginal dryness, itching, and burning, to recognize signs of this hormonal condition affecting women, characterized by thinning vaginal tissues and decreased estrogen levels.
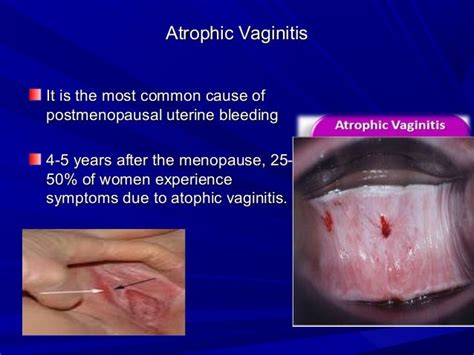
Atrophic vulvovaginitis, also known as vaginal atrophy, is a condition characterized by the thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls due to a decrease in estrogen levels. This condition is common among postmenopausal women, but it can also affect women who are breastfeeding, taking certain medications, or experiencing early menopause. The symptoms of atrophic vulvovaginitis can significantly impact a woman's quality of life, making it essential to understand and address them.
The decline in estrogen levels leads to a reduction in the production of natural lubricants, causing the vaginal tissue to become thinner, drier, and less elastic. This can result in a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain, affecting not only a woman's sexual health but also her daily activities. Recognizing the symptoms of atrophic vulvovaginitis is crucial for seeking appropriate medical attention and finding relief from its effects.
Atrophic vulvovaginitis can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms may vary from woman to woman. Common symptoms include vaginal dryness, itching, and burning, which can be exacerbated by sexual intercourse, leading to painful sex. Additionally, women may experience an increase in urinary tract infections due to the thinning of the vaginal walls, which can no longer provide the natural barrier against bacteria. Understanding these symptoms and their implications on a woman's health is vital for managing the condition effectively.
Understanding Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
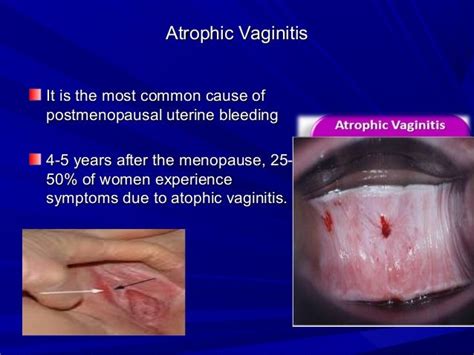
Atrophic vulvovaginitis is primarily caused by the decrease in estrogen levels, which can occur due to various factors such as menopause, breastfeeding, or certain medical treatments. The condition can also be influenced by lifestyle factors, including smoking and a lack of regular sexual activity, which can further reduce blood flow to the vaginal area. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with atrophic vulvovaginitis is essential for preventing its onset and managing its symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
The diagnosis of atrophic vulvovaginitis typically involves a pelvic exam, during which a healthcare provider will look for signs of vaginal atrophy, such as thinning and pale vaginal walls. A medical history will also be taken to identify any underlying conditions or medications that could be contributing to the symptoms. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions that could be causing the symptoms.Symptoms of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
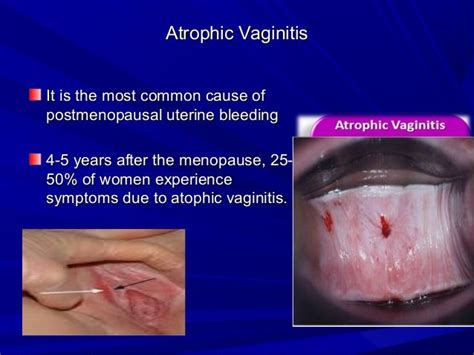
The symptoms of atrophic vulvovaginitis can vary in severity and impact different aspects of a woman's life. Common symptoms include:
- Vaginal dryness and itching
- Painful sex
- Burning sensation in the vagina
- Increased risk of urinary tract infections
- Light bleeding after sex These symptoms can significantly affect a woman's sexual health, relationships, and overall well-being, making it crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options
Treatment for atrophic vulvovaginitis aims to alleviate symptoms, improve vaginal health, and enhance quality of life. Available treatment options include: - Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to restore estrogen levels - Local estrogen therapy, which involves applying estrogen directly to the vaginal area - Vaginal moisturizers and lubricants to reduce dryness and discomfort - Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and engaging in regular sexual activity to improve blood flow to the vaginaManaging Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
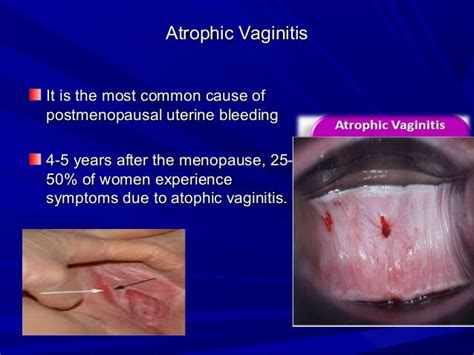
Managing atrophic vulvovaginitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and open communication with healthcare providers. Women can take several steps to manage their symptoms and improve their vaginal health, such as using vaginal moisturizers regularly, avoiding harsh soaps and douching, and staying hydrated to help maintain natural lubrication.
Prevention Strategies
While atrophic vulvovaginitis is a common condition, especially among postmenopausal women, there are strategies that can help prevent its onset or reduce its severity. These include: - Maintaining a healthy weight - Engaging in regular physical activity - Not smoking - Practicing good genital hygiene - Considering hormone replacement therapy for menopausal symptomsLifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in managing atrophic vulvovaginitis. Women can benefit from making dietary changes, such as increasing their intake of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Additionally, staying sexually active, either through intercourse or masturbation, can help maintain blood flow to the vagina, reducing the risk of atrophy.
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes can support the management of atrophic vulvovaginitis by promoting overall health and reducing symptoms. Key dietary recommendations include: - Increasing intake of fruits and vegetables - Consuming foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and flaxseeds - Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated - Limiting caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate drynessSeeking Medical Attention

Seeking medical attention is the first step towards managing atrophic vulvovaginitis. Healthcare providers can offer guidance on the best treatment options and provide support throughout the management process. Women should not hesitate to discuss their symptoms openly, as this will help in receiving appropriate care and improving their quality of life.
Importance of Open Communication
Open communication with healthcare providers is vital for the effective management of atrophic vulvovaginitis. Women should feel comfortable discussing their symptoms, sexual health, and any concerns they may have. This open dialogue will help healthcare providers understand the severity of the condition and tailor treatment plans accordingly.Atrophic Vulvovaginitis Image Gallery







In conclusion, atrophic vulvovaginitis is a condition that affects many women, particularly during and after menopause. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition and improving quality of life. By seeking medical attention, making lifestyle modifications, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, women can find relief from the symptoms of atrophic vulvovaginitis and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and seek support from healthcare professionals to better understand and manage atrophic vulvovaginitis.
