Intro
Discover 7 expert-backed strategies for managing Autonomic Dysreflexia, a debilitating condition affecting spinal cord injury patients. Learn how to recognize symptoms, prevent episodes, and alleviate AD-related hypertension, bradycardia, and sweating. Improve your quality of life with these evidence-based techniques and take control of your Autonomic Dysreflexia management today.
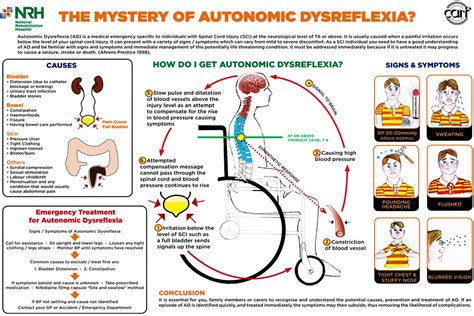
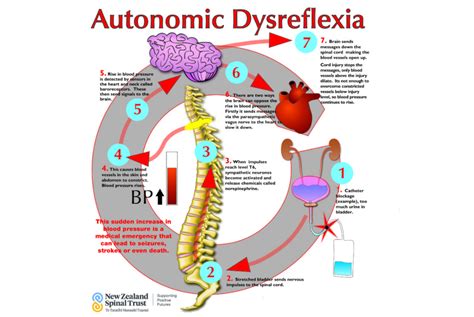
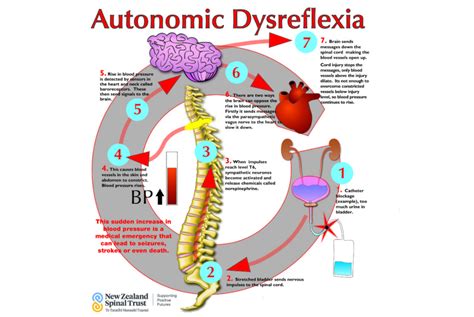
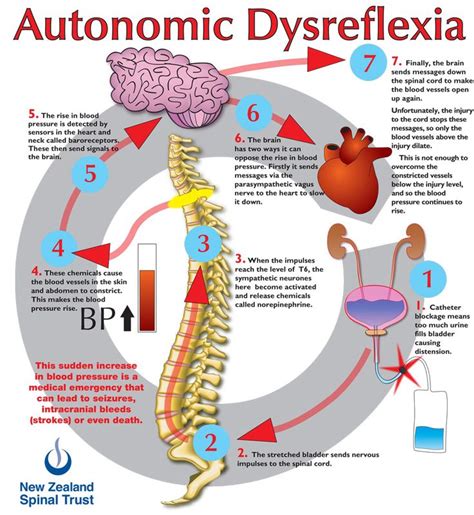
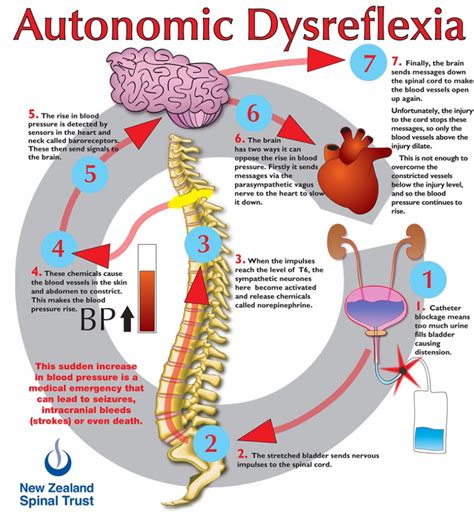
Living with Autonomic Dysreflexia (AD) can be a daunting experience, especially when it comes to managing the symptoms and preventing episodes. Autonomic Dysreflexia is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition that affects individuals with spinal cord injuries or disorders, causing an overactive response of the autonomic nervous system. If left unmanaged, AD can lead to severe complications, including stroke, heart attack, and even death. However, with the right knowledge and strategies, individuals with AD can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
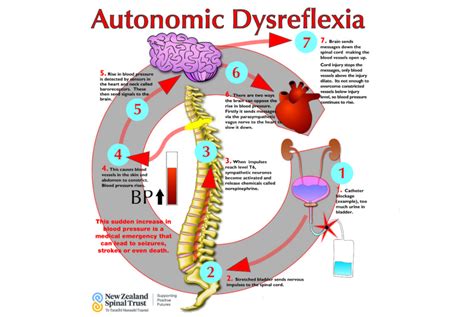
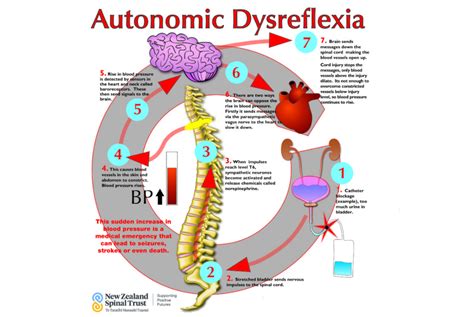
Understanding Autonomic Dysreflexia
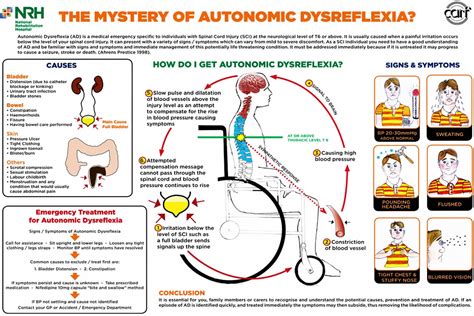
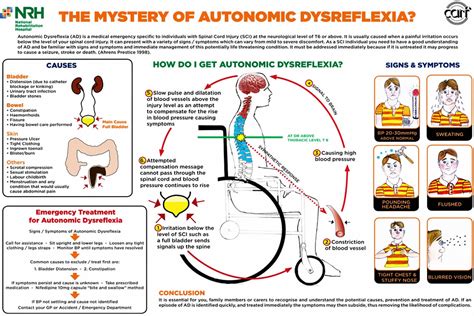
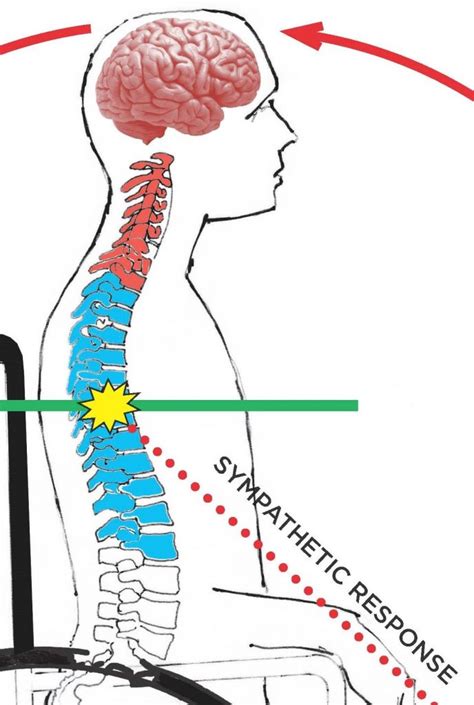
Before we dive into the management strategies, it's essential to understand the basics of Autonomic Dysreflexia. AD occurs when the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion, becomes overactive in response to a stimulus. This overactivity can cause a range of symptoms, including high blood pressure, sweating, headache, and nausea.
Causes and Triggers of Autonomic Dysreflexia
To manage AD effectively, it's crucial to identify the causes and triggers of episodes. Common causes and triggers of AD include:
- Urinary tract infections or bladder distension
- Constipation or bowel impaction
- Skin irritation or pressure sores
- Infections or illnesses
- Tight clothing or constrictive devices
7 Ways to Manage Autonomic Dysreflexia
While there is no cure for Autonomic Dysreflexia, there are several strategies that can help manage the symptoms and prevent episodes. Here are seven ways to manage AD:
1. Maintain Good Bladder and Bowel Habits
Establishing a regular bladder and bowel routine can help prevent AD episodes. This includes:
- Regular bladder emptying and catheterization
- Bowel training and regular bowel movements
- Avoiding constipation by increasing fiber and fluid intake

2. Monitor Blood Pressure
Regular blood pressure monitoring can help identify AD episodes early, allowing for prompt treatment. Individuals with AD should:
- Monitor blood pressure regularly, especially during times of stress or illness
- Keep a blood pressure log to track changes and patterns
- Seek medical attention if blood pressure readings are elevated
3. Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate AD symptoms and trigger episodes. Stress management techniques, such as:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation and relaxation
- Yoga and other relaxation therapies
can help reduce stress and anxiety.

4. Prevent Skin Irritation
Skin irritation and pressure sores can trigger AD episodes. To prevent skin irritation:
- Use gentle skin care products and avoid harsh chemicals
- Avoid tight clothing and constrictive devices
- Use pressure-relieving devices, such as cushions and mattresses
5. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can exacerbate AD symptoms and trigger episodes. Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help:
- Thin out mucus and prevent respiratory complications
- Prevent constipation and bowel impaction
- Regulate body temperature

6. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise can help improve overall health and reduce AD symptoms. However, it's essential to:
- Avoid overexertion and strenuous activities
- Warm up and cool down slowly
- Monitor blood pressure and heart rate during exercise
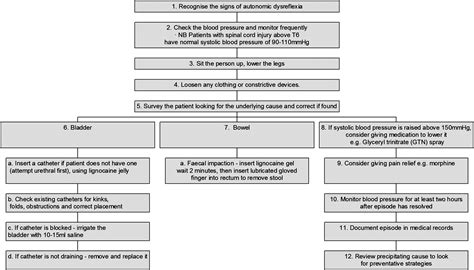
7. Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any symptoms of AD, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can:
- Diagnose and treat underlying causes of AD
- Provide medication and other treatments to manage symptoms
- Develop a personalized management plan to prevent future episodes

Conclusion
Managing Autonomic Dysreflexia requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, stress management, and medical attention. By understanding the causes and triggers of AD and implementing these seven management strategies, individuals with AD can reduce their symptoms, prevent episodes, and improve their overall quality of life.
Autonomic Dysreflexia Management Gallery
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information on managing Autonomic Dysreflexia. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
