Discover the secrets of the B-37 Bomber, a game-changing aircraft of World War II. Learn about its top speed, range, and payload capacity, as well as its innovative design features, combat history, and impact on military aviation. Get the inside scoop on this legendary bomber and its role in shaping airpower.
The B-17 Bomber, also known as the Flying Fortress, is one of the most iconic and revered aircraft in history. From its conception to its service in World War II and beyond, the B-17 has left an indelible mark on the world of aviation and warfare. Here are 7 things about the B-17 Bomber that you need to know:

The B-17 Bomber was first conceived in the 1930s as a response to the growing threat of global conflict. The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was looking for a bomber that could fly high and fast, carry a heavy payload, and defend itself against enemy fighters. Boeing, the manufacturer, delivered on all fronts, and the B-17 was born.
Design and Development
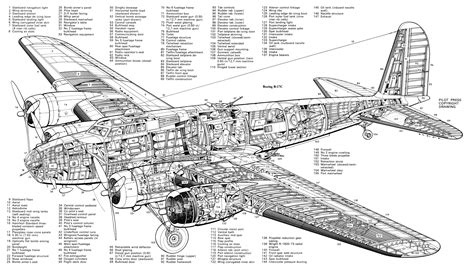
The B-17 was designed to be a high-altitude bomber, capable of flying above 30,000 feet and carrying a payload of up to 4,000 pounds. It was powered by four Wright R-1820 radial engines, each producing 1,200 horsepower. The aircraft's defenses consisted of 12.50-caliber machine guns, including two in the tail turret, two in the nose turret, and eight in the waist and top turret positions.
Key Features
- High-altitude capability
- Heavy payload capacity
- Multiple defensive gun positions
- Four radial engines
Service History

The B-17 saw extensive service in World War II, flying thousands of sorties over Europe and the Pacific. It played a crucial role in the Allied victory, helping to destroy enemy infrastructure, supply lines, and military installations. The aircraft's ruggedness and reliability earned it a reputation as one of the most reliable bombers of the war.
Notable Missions
- The Doolittle Raid (1942)
- The Schweinfurt-Regensburg Mission (1943)
- The Berlin Raids (1944-1945)
Legacy

The B-17's impact on aviation and warfare extends far beyond its service in World War II. It helped to establish the Boeing company as a leading manufacturer of military aircraft, and its design influenced the development of subsequent bombers, including the B-29 and B-52. Today, the B-17 remains an iconic symbol of American airpower, with many preserved examples on display in museums and airparks around the world.
Preserved Examples
- The National Museum of the United States Air Force (Ohio)
- The National World War II Museum (Louisiana)
- The Imperial War Museum (UK)
Specifications
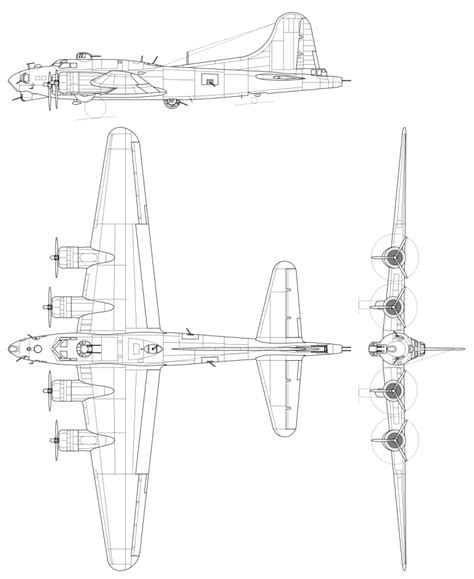
- Length: 74 feet 4 inches (22.6 meters)
- Wingspan: 103 feet 9 inches (31.6 meters)
- Height: 19 feet 1 inch (5.8 meters)
- Maximum speed: 260 mph (418 km/h)
- Range: 3,000 miles (4,800 km)
- Service ceiling: 35,600 feet (10,863 meters)
Crew and Armament
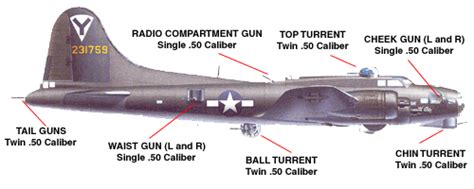
- Crew: 10 (pilot, co-pilot, navigator, bombardier, radioman, and six gunners)
- Armament: 12.50-caliber machine guns
- Bombs: Up to 4,000 pounds (1,814 kg)
Conclusion
The B-17 Bomber is an American icon, a symbol of strength, resilience, and sacrifice. Its impact on aviation and warfare continues to be felt today, with many of its design innovations still influencing modern aircraft. Whether you're a historian, an aviation enthusiast, or simply someone who appreciates the bravery and sacrifice of those who flew the B-17, this aircraft is sure to captivate and inspire.
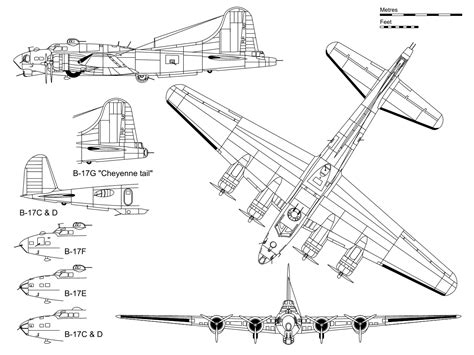
B-17 Bomber Image Gallery








Feel free to share your thoughts, ask questions, or provide feedback about this article in the comments below.
