Intro
Discover the crucial base of a house foundation, exploring its components, types, and importance in ensuring a stable and secure home. Learn about footings, walls, and slab foundations, and understand how a strong foundation affects the overall structure and durability of your house, preventing costly repairs and ensuring a safe living space.
A house foundation is the structural base of a building that transfers loads from the walls and floors to the ground, providing stability and support. It is a critical component of a house, as it ensures the safety and durability of the entire structure. In this article, we will explore the different types of house foundations, their characteristics, and the factors that influence their design.
Types of House Foundations

There are several types of house foundations, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of house foundations are:
- Slab Foundation: A slab foundation is a continuous slab of concrete that is poured directly on the ground. It is the most common type of foundation in warm climates, as it is easy to construct and can be built on a variety of soils.
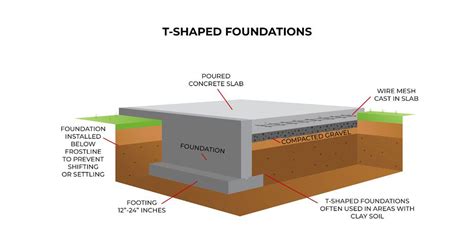
- T-Shaped Foundation: A T-shaped foundation is a combination of a slab foundation and a footer. It is used in areas with freezing temperatures, as it provides additional support against frost heave.
- Full Basement Foundation: A full basement foundation is a full-height basement that is built below grade. It is the most expensive type of foundation, but it provides additional living space and storage.
- Crawl Space Foundation: A crawl space foundation is a raised foundation that provides a small space between the ground and the floor joists. It is used in areas with high water tables or poor drainage.
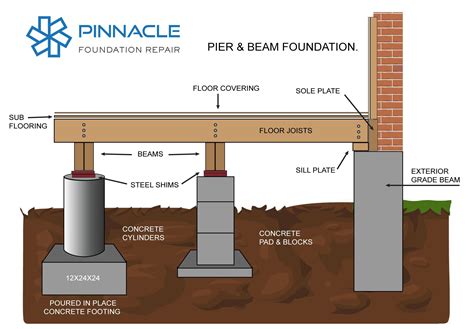
- Pier-and-Beam Foundation: A pier-and-beam foundation is a foundation that consists of a series of piers and beams that support the house. It is used in areas with unstable soils or high water tables.
Factors that Influence Foundation Design
The design of a house foundation is influenced by several factors, including:
- Soil Conditions: The type and stability of the soil affect the design of the foundation. Soils that are prone to settlement or erosion require deeper foundations.
- Climate: Climate affects the design of the foundation, as areas with freezing temperatures require additional support against frost heave.
- Water Table: The water table affects the design of the foundation, as areas with high water tables require additional support against water damage.
- Load-Bearing Capacity: The load-bearing capacity of the soil affects the design of the foundation, as soils that can support heavy loads require shallower foundations.
Components of a House Foundation
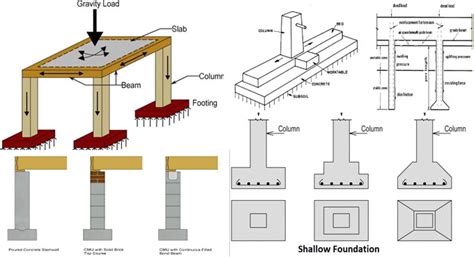
A house foundation consists of several components, including:
- Footings: Footings are the horizontal beams that transfer loads from the walls and floors to the ground.
- Walls: Foundation walls are the vertical walls that support the house and transfer loads to the footings.
- Slab: The slab is the horizontal surface that provides a base for the house.
- Piers: Piers are the vertical columns that support the house and transfer loads to the footings.
- Beams: Beams are the horizontal beams that support the house and transfer loads to the piers.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Foundation
A well-designed foundation provides several benefits, including:
- Stability: A well-designed foundation ensures the stability of the house, providing a safe and secure living space.
- Durability: A well-designed foundation ensures the durability of the house, providing a long-lasting structure that can withstand various environmental conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: A well-designed foundation can improve energy efficiency, as it can reduce heat loss and gain.
- Increased Property Value: A well-designed foundation can increase property value, as it provides a safe and secure living space.
Common Foundation Problems
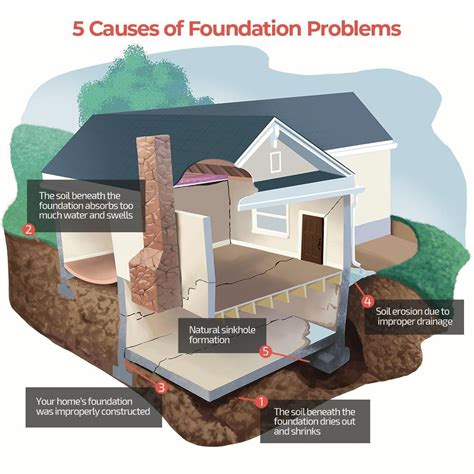
Common foundation problems include:
- Settlement: Settlement occurs when the foundation settles into the ground, causing cracks and uneven floors.
- Cracks: Cracks occur when the foundation walls or slab crack, allowing water to enter the house.
- Water Damage: Water damage occurs when water enters the house through cracks or poor drainage.
- Frost Heave: Frost heave occurs when the soil freezes and expands, causing the foundation to shift and crack.
Prevention and Repair of Foundation Problems
Prevention and repair of foundation problems can be achieved through:
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as inspecting the foundation for cracks and uneven floors, can prevent foundation problems.
- Drainage: Proper drainage, such as installing a French drain, can prevent water damage.
- Foundation Repair: Foundation repair, such as injecting epoxy into cracks, can repair foundation problems.
House Foundation Image Gallery







In conclusion, a house foundation is a critical component of a building that requires careful design and construction. By understanding the different types of foundations, factors that influence design, and common problems, homeowners can ensure the stability and durability of their house. Regular maintenance and repair can prevent foundation problems, and proper drainage can prevent water damage. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions about house foundations in the comments section below.
