Intro
Ensure safe blood transfusion practices with our 5-step ATi template guide. Learn how to identify patients, verify orders, administer blood products safely, monitor for reactions, and document transfusions accurately. Master blood transfusion safety protocols and reduce risks with our comprehensive template, covering patient assessment, transfusion reactions, and more.
Blood transfusions are a life-saving medical intervention that can help patients recover from various conditions, such as surgery, injury, or disease. However, like any medical procedure, blood transfusions carry risks and complications. Ensuring safe blood transfusion practices is crucial to prevent adverse reactions, transmission of infectious diseases, and other adverse events. In this article, we will outline the 5 essential steps for safe blood transfusion using the ATi template.
Step 1: Patient Identification and Consent

The first step in ensuring safe blood transfusion is to correctly identify the patient and obtain informed consent. This involves verifying the patient's identity using at least two identifiers, such as their name and date of birth, and ensuring that they understand the risks and benefits of the blood transfusion. The healthcare provider should explain the procedure, potential complications, and alternatives to blood transfusion, if any.
Key Considerations
- Verify patient identity using at least two identifiers
- Obtain informed consent from the patient or their authorized representative
- Explain the risks and benefits of blood transfusion
- Document the consent process in the patient's medical record
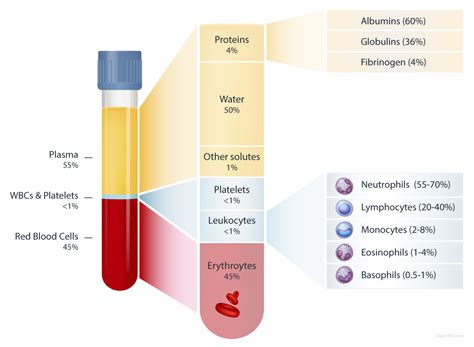
Step 2: Blood Component Selection and Verification
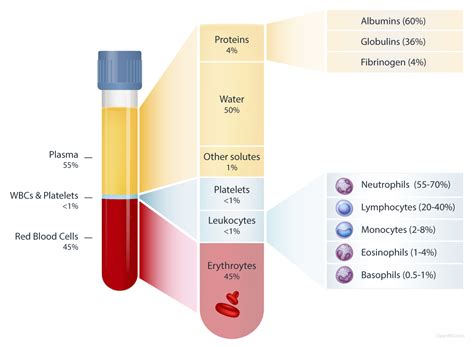
The second step is to select and verify the correct blood component for the patient. This involves reviewing the patient's medical history, laboratory results, and current medications to determine the most suitable blood component. The healthcare provider should also verify the blood component's expiration date, storage conditions, and any special requirements, such as irradiation or leukoreduction.
Key Considerations
- Review patient's medical history, laboratory results, and current medications
- Select the most suitable blood component for the patient
- Verify blood component's expiration date, storage conditions, and special requirements
Step 3: Pre-Transfusion Checks

The third step is to perform pre-transfusion checks to ensure that the blood component is compatible with the patient's blood type and that there are no contraindications to transfusion. This involves checking the patient's vital signs, reviewing their medical history, and performing laboratory tests, such as cross-matching and compatibility testing.
Key Considerations
- Check patient's vital signs and medical history
- Perform laboratory tests, such as cross-matching and compatibility testing
- Verify blood component's compatibility with patient's blood type
Step 4: Transfusion Administration
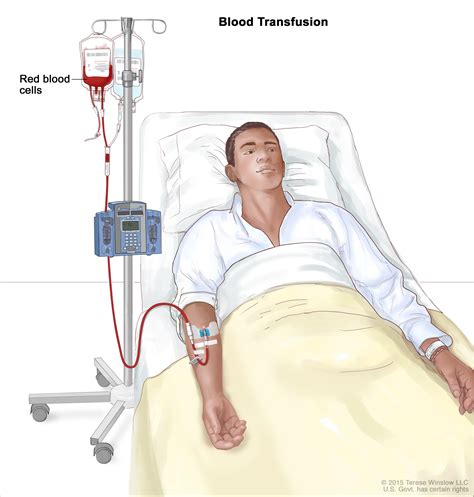
The fourth step is to administer the blood transfusion safely and efficiently. This involves using aseptic technique, verifying the blood component's identity, and monitoring the patient's vital signs and reaction to the transfusion. The healthcare provider should also be prepared to manage any adverse reactions or complications that may arise during or after the transfusion.
Key Considerations
- Use aseptic technique to administer the blood transfusion
- Verify blood component's identity before administration
- Monitor patient's vital signs and reaction to transfusion
- Be prepared to manage adverse reactions or complications
Step 5: Post-Transfusion Monitoring and Documentation
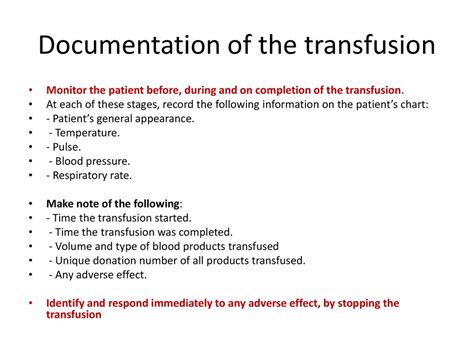
The final step is to monitor the patient's response to the blood transfusion and document the transfusion process in their medical record. This involves monitoring the patient's vital signs, laboratory results, and any adverse reactions or complications, and documenting the transfusion process, including the blood component used, administration time, and any notable events.
Key Considerations
- Monitor patient's response to blood transfusion
- Document transfusion process in patient's medical record
- Record blood component used, administration time, and any notable events
Blood Transfusion Image Gallery


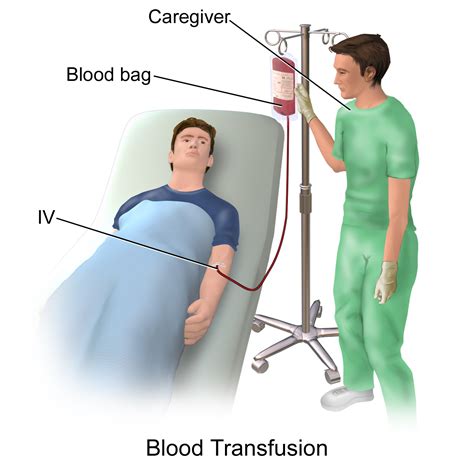
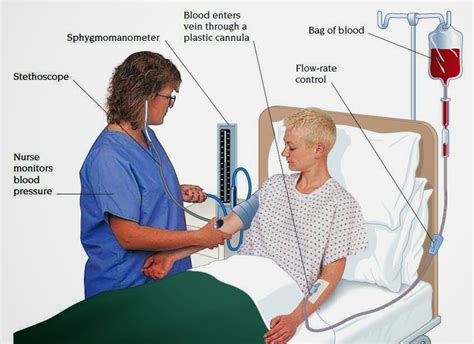
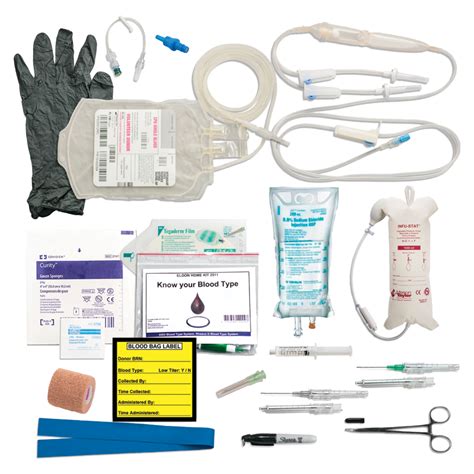
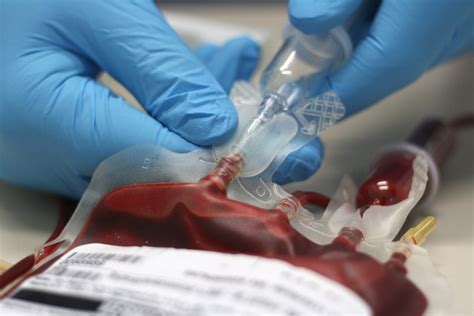
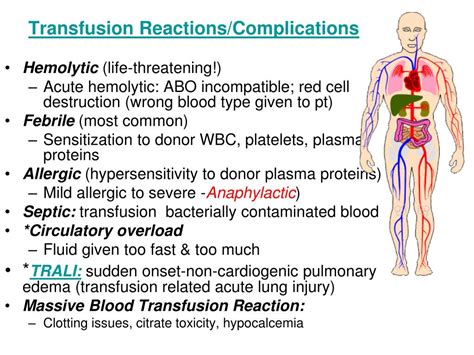

In conclusion, following the 5 essential steps for safe blood transfusion using the ATi template can help ensure that patients receive high-quality care and minimize the risk of adverse reactions and complications. By prioritizing patient identification and consent, blood component selection and verification, pre-transfusion checks, transfusion administration, and post-transfusion monitoring and documentation, healthcare providers can provide safe and effective blood transfusions. We encourage readers to share their experiences and insights on blood transfusion safety in the comments section below.
