Intro
Discover the comprehensive guide to Bupropion medication, including its uses, side effects, and nursing considerations. Learn about this antidepressant and smoking cessation aid, its mechanisms of action, and potential interactions. Get informed on safe administration, patient education, and monitoring requirements for optimal patient care.
Bupropion is a medication that has been widely used to treat depression, seasonal affective disorder, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It is also used as a smoking cessation aid under the brand name Zyban. As a healthcare professional, it is essential to understand the medication guide and nursing considerations to ensure safe and effective use of bupropion.
What is Bupropion?
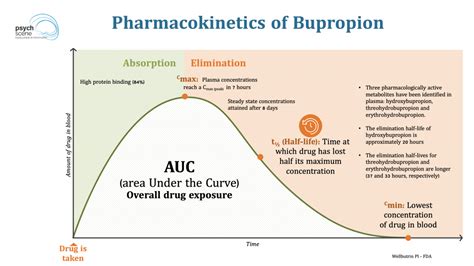
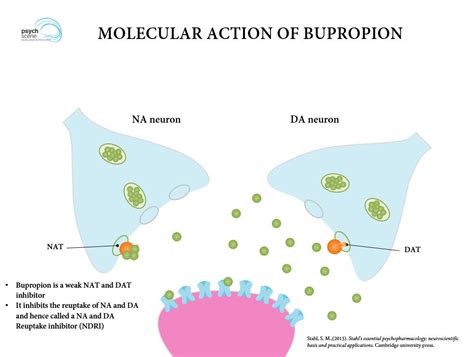
Bupropion is an antidepressant medication that belongs to the class of norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRI). It works by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as norepinephrine and dopamine, in the brain. This helps to improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression, and increase motivation.
Mechanism of Action
Bupropion's mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve the inhibition of the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine. This leads to an increase in the levels of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, which can help to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
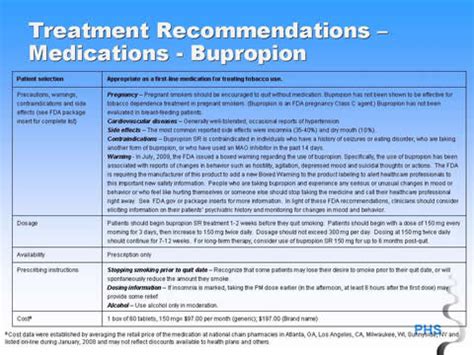
Indications and Dosage
Bupropion is indicated for the treatment of:
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Smoking cessation
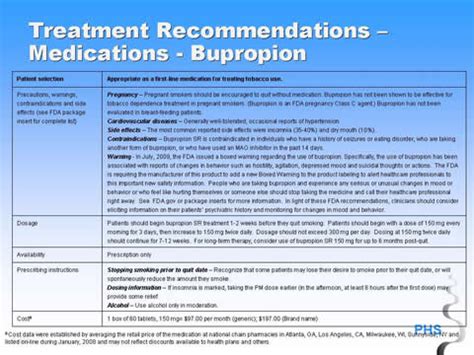
The dosage of bupropion varies depending on the indication and the patient's response to treatment. The typical dosage range is 150-450 mg per day, divided into 2-3 doses.
Contraindications and Precautions
Bupropion is contraindicated in patients with:
- Seizure disorders
- Eating disorders (e.g., bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) use
- Severe renal impairment
Precautions should be taken when using bupropion in patients with:
- History of head trauma or brain injury
- Hepatic impairment
- Renal impairment
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
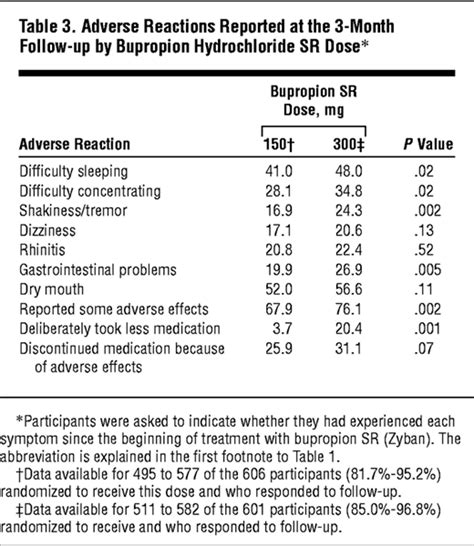
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions

Common side effects of bupropion include:
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Insomnia and vivid dreams
- Dry mouth and constipation
Less common but serious side effects include:
- Seizures
- Allergic reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema)
- Hepatic toxicity
- Psychosis and hallucinations
Nursing Considerations
Nursing considerations for patients taking bupropion include:
- Monitoring for side effects and adverse reactions
- Assessing for suicidal ideation and behavior
- Providing education on medication use and potential side effects
- Encouraging patients to report any concerns or changes in their mental status
- Collaborating with the healthcare team to adjust dosage or discontinue medication as needed
Interactions and Contraindications
Bupropion interacts with several medications, including:
- MAOIs (e.g., phenelzine, tranylcypromine)
- Thioridazine
- Lithium
- Warfarin
- Theophylline
Contraindications include:
- Use of MAOIs within the past 14 days
- Use of thioridazine within the past 14 days
- History of seizure disorders
- Eating disorders (e.g., bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa)
Withdrawal and Discontinuation
Bupropion can cause withdrawal symptoms when discontinued abruptly. Gradual tapering of the dose is recommended to minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms.
Patient Education
Patient education is essential to ensure safe and effective use of bupropion. Patients should be informed about:
- Potential side effects and adverse reactions
- Importance of adhering to the dosage schedule
- Risks of withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing medication
- Importance of reporting any concerns or changes in their mental status
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial to ensure the safe and effective use of bupropion. Patients should be monitored for:
- Side effects and adverse reactions
- Suicidal ideation and behavior
- Changes in mental status
- Adherence to medication regimen
Bupropion Image Gallery


As a healthcare professional, it is essential to stay up-to-date on the latest information about bupropion to ensure safe and effective use of this medication. By understanding the medication guide and nursing considerations, you can provide high-quality care to your patients and help them achieve optimal outcomes.
