Intro
Discover butterfly defense mechanisms, including camouflage, mimicry, and toxicity, that protect them from predators, showcasing their unique survival strategies and adaptations.
The natural world is full of fascinating creatures, and among the most intriguing are butterflies. With their vibrant colors, delicate wings, and graceful flight, it's easy to see why they capture our imagination. However, beyond their aesthetic appeal, butterflies have evolved a range of defense mechanisms that enable them to survive and thrive in a world filled with predators. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of butterfly defense mechanisms, exploring the various strategies they use to protect themselves from harm.
Butterflies face numerous threats in their daily lives, from birds and bats to spiders and other insects. To counter these dangers, they have developed a range of defense mechanisms that are both fascinating and effective. From camouflage and mimicry to toxicity and flight, butterflies have evolved a variety of strategies to avoid predators and protect themselves from harm. By understanding these defense mechanisms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate and complex world of butterflies, as well as the remarkable adaptability of these incredible creatures.
The study of butterfly defense mechanisms is not only fascinating but also important for our understanding of the natural world. By examining the ways in which butterflies protect themselves, we can gain insights into the evolution of defense strategies and the complex interactions between predators and prey. Furthermore, the study of butterfly defense mechanisms can also inform our approaches to conservation and wildlife management, helping us to develop more effective strategies for protecting these incredible creatures and the ecosystems they inhabit. With their delicate beauty and fascinating defense mechanisms, butterflies are a true marvel of nature, and their study offers a wealth of opportunities for discovery and exploration.
Introduction to Butterfly Defense Mechanisms

Camouflage and Concealment
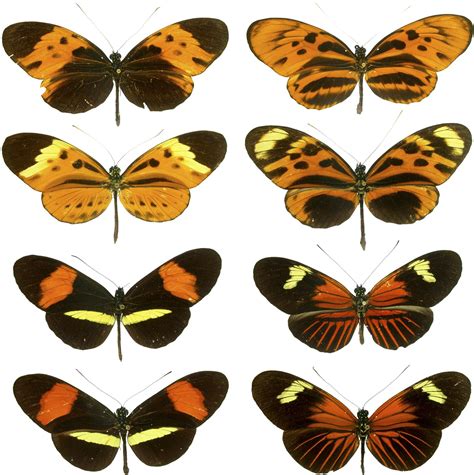
One of the most effective defense mechanisms used by butterflies is camouflage. By blending in with their surroundings, butterflies can avoid detection by predators, reducing the risk of attack. This can be achieved through a range of strategies, including the use of color patterns and shapes that mimic the appearance of leaves, twigs, or other natural features. For example, the viceroy butterfly has a distinctive pattern of brown and orange markings that allow it to blend in with the leaves and branches of trees.Mimicry and Deception

Toxicity and Warning Colors
Some butterflies have evolved to be toxic, accumulating chemicals from the plants they feed on that make them unpalatable to predators. These toxic butterflies often have bright warning colors that advertise their toxicity to potential predators, deterring them from attacking. For example, the pipevine swallowtail butterfly has a distinctive pattern of blue and red markings that warn predators of its toxicity.Flight and Evasion

Behavioral Adaptations
Butterflies have also evolved a range of behavioral adaptations that help them avoid predators. For example, some butterflies will fly at night, when predators are less active, while others will hide in protected areas, such as under leaves or in tree cavities. These behavioral adaptations can be highly effective, allowing butterflies to avoid predators and protect themselves from harm.Evolution of Defense Mechanisms

Co-Evolutionary Relationships
The evolution of defense mechanisms in butterflies is also influenced by co-evolutionary relationships with predators. For example, the development of toxicity in butterflies has led to the evolution of tolerance in some predators, which can then feed on the toxic butterflies without harm. This co-evolutionary relationship has driven the development of even more complex defense mechanisms, as butterflies and predators engage in an ongoing arms race.Conservation Implications

Threats to Butterfly Populations
Butterfly populations are facing numerous threats, from habitat destruction and climate change to pollution and over-collection. These threats can have a significant impact on butterfly defense mechanisms, reducing their effectiveness and making butterflies more vulnerable to predators. For example, the destruction of habitats can reduce the availability of food plants, making it harder for butterflies to accumulate toxins and defend themselves against predators.Gallery of Butterfly Defense Mechanisms
Butterfly Defense Mechanisms Image Gallery








As we conclude our exploration of butterfly defense mechanisms, we are reminded of the incredible diversity and complexity of the natural world. From camouflage and mimicry to toxicity and flight, butterflies have evolved a range of fascinating strategies to protect themselves from predators. By understanding these defense mechanisms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate and interconnected world of butterflies, as well as the importance of conservation and wildlife management. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article, and to join us in our ongoing exploration of the fascinating world of butterflies. Whether you are a seasoned entomologist or simply a nature enthusiast, we hope that this article has inspired you to learn more about these incredible creatures and the amazing defense mechanisms they use to survive and thrive.
