Intro
Receiving a felony conviction can significantly impact an individual's life, affecting their employment opportunities, housing, and access to government assistance programs. For those struggling to make ends meet, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as food stamps, can be a vital resource. However, the relationship between felony convictions and SNAP eligibility is complex, varying from state to state.
In the United States, approximately 70 million people rely on SNAP to purchase groceries, and many of these individuals have felony convictions. The good news is that, in most cases, having a felony does not automatically disqualify someone from receiving food stamps. However, certain types of felonies and state-specific laws may affect eligibility.
To understand the intricacies of SNAP eligibility with a felony, it's essential to explore the federal laws and regulations governing the program. This article will delve into the specifics of SNAP eligibility, the application process, and the implications of having a felony conviction.
Understanding SNAP Eligibility
SNAP is a federally funded program, administered by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), which provides assistance to low-income individuals and families to purchase food. The program's primary goal is to alleviate hunger and malnutrition, ensuring that those in need have access to nutritious food.
To be eligible for SNAP, applicants must meet specific requirements, including:
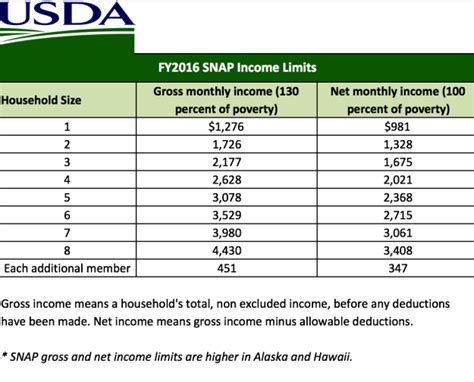
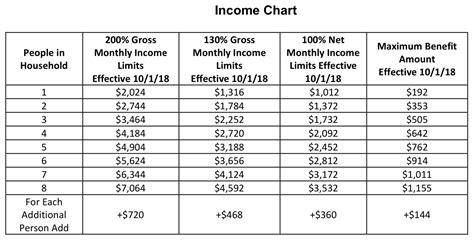
- Income: Households must have a gross income at or below 130% of the federal poverty level.
- Resources: Households must have countable resources, such as cash, savings, and other assets, below a certain threshold.
- Citizenship: Applicants must be U.S. citizens, nationals, or qualified aliens.
- Residency: Applicants must reside in the state where they are applying for SNAP.
While having a felony conviction does not automatically disqualify someone from receiving SNAP benefits, certain types of felonies may impact eligibility. These include:
- Felony drug convictions: Individuals with felony drug convictions may be ineligible for SNAP benefits for a specific period, typically one to two years, depending on the state.
- Felony convictions involving violent crimes: In some states, individuals with felony convictions involving violent crimes, such as murder or assault, may be ineligible for SNAP benefits.
State-Specific Laws and Regulations
SNAP eligibility laws and regulations vary from state to state, and some states have more stringent requirements than others. For example:
- Some states, like California and New York, have implemented laws that prohibit the denial of SNAP benefits based solely on a felony conviction.
- Other states, like Florida and Texas, have laws that restrict SNAP eligibility for individuals with felony convictions, particularly those involving violent crimes or drug offenses.
It's essential to note that even if a state has restrictive laws, there may be exceptions or alternative programs available for individuals with felony convictions.
The Application Process
Applying for SNAP benefits can be a straightforward process, but it may require additional documentation for individuals with felony convictions. Here's an overview of the application process:
- Determine eligibility: Before applying, individuals can check their eligibility using the SNAP eligibility tool on the USDA website.
- Gather required documents: Applicants will need to provide proof of identity, income, resources, and residency.
- Submit the application: Applications can be submitted online, by phone, or in person at a local SNAP office.
- Interview: Applicants may be required to participate in an interview with a SNAP representative to discuss their application and provide additional information.
- Verification: SNAP representatives will verify the information provided in the application and make a determination regarding eligibility.

Tips for Applying with a Felony Conviction
When applying for SNAP benefits with a felony conviction, it's essential to be prepared and provide accurate information. Here are some tips:
- Disclose the felony conviction: Applicants must disclose their felony conviction on the application.
- Provide documentation: Applicants may need to provide documentation, such as court records or proof of rehabilitation.
- Be prepared to discuss the conviction: Applicants may be asked to discuss their felony conviction during the interview process.
- Seek assistance: Applicants can seek assistance from a SNAP representative or a social services agency to help navigate the application process.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Receiving a felony conviction can be a challenging and life-altering experience, but it does not necessarily mean that an individual is ineligible for SNAP benefits. By understanding the eligibility requirements, state-specific laws, and application process, individuals with felony convictions can take the first step towards accessing the nutrition assistance they need.
If you or someone you know is struggling to access SNAP benefits due to a felony conviction, it's essential to:
- Research state-specific laws and regulations.
- Reach out to a SNAP representative or social services agency for assistance.
- Provide accurate and detailed information during the application process.
By taking these steps, individuals with felony convictions can overcome the barriers to accessing SNAP benefits and start building a more stable and secure future.
Food Stamps With A Felony Image Gallery









We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the complex relationship between food stamps and felony convictions. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences, please feel free to comment below.
