Intro
Learn about preventing Microsporidia infections, a parasitic disease, through effective control measures, diagnosis, and treatment options, reducing risk of microsporidiosis and promoting public health safety.
Microsporidia infections are a significant concern for individuals with compromised immune systems, particularly those with HIV/AIDS. These infections can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can be challenging to diagnose and treat. Understanding the importance of preventing Microsporidia infections is crucial for maintaining good health, especially for vulnerable populations.
The impact of Microsporidia infections can be substantial, leading to malabsorption, diarrhea, and weight loss, among other symptoms. In severe cases, these infections can be life-threatening, emphasizing the need for effective prevention strategies. By taking proactive steps to prevent Microsporidia infections, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these illnesses and maintain their overall health and well-being.
Preventing Microsporidia infections requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates good hygiene practices, safe food and water handling, and awareness of the risks associated with these infections. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from the harmful effects of Microsporidia infections. It is essential to recognize the importance of prevention and take immediate action to minimize the risk of infection.
Introduction to Microsporidia
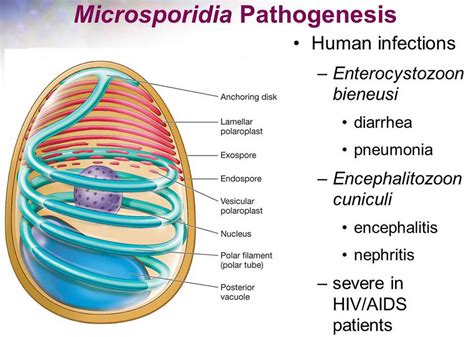
Microsporidia are a group of parasitic fungi that can infect a wide range of hosts, including humans. These organisms are typically found in water and soil and can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or contact with infected animals. Microsporidia infections can affect various organs and tissues, including the intestines, liver, and eyes, leading to a range of symptoms and health complications.
Transmission and Risk Factors
The transmission of Microsporidia infections can occur through various routes, including: * Contaminated food and water * Contact with infected animals or their feces * Person-to-person contact, particularly in cases of poor hygiene * Contaminated medical equipment or supplies Understanding the risk factors associated with Microsporidia infections is essential for preventing these illnesses. Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are at higher risk of developing Microsporidia infections.Prevention Strategies
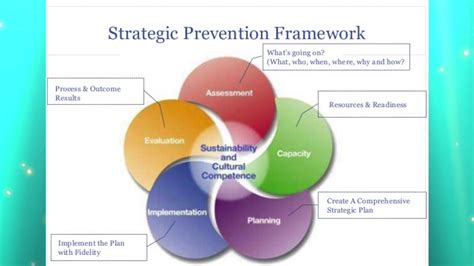
Preventing Microsporidia infections requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates good hygiene practices, safe food and water handling, and awareness of the risks associated with these infections. Some effective prevention strategies include:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and thoroughly
- Avoiding contaminated food and water
- Using safe and effective water treatment methods, such as filtration or boiling
- Avoiding contact with infected animals or their feces
- Using personal protective equipment, such as gloves and masks, when handling potentially contaminated materials
Safe Food and Water Handling
Safe food and water handling are critical components of preventing Microsporidia infections. Some tips for safe food and water handling include: * Washing fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption * Avoiding raw or undercooked meat, poultry, and seafood * Using safe and effective water treatment methods, such as filtration or boiling * Avoiding contaminated food and water, particularly in areas with poor sanitationDiagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosing Microsporidia infections can be challenging, as the symptoms are often non-specific and can resemble those of other illnesses. A definitive diagnosis typically requires laboratory testing, such as microscopy or PCR. Treatment for Microsporidia infections usually involves antiparasitic medications, such as albendazole or fumagillin, and supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Supportive Care and Management
Supportive care and management are essential components of treating Microsporidia infections. Some strategies for supportive care and management include: * Providing nutritional support to manage malabsorption and weight loss * Managing symptoms, such as diarrhea and abdominal pain * Preventing complications, such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances * Monitoring for potential side effects of treatment, such as allergic reactions or liver damagePublic Health Implications

Microsporidia infections have significant public health implications, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and limited access to healthcare. These infections can lead to substantial morbidity and mortality, particularly in vulnerable populations, such as those with HIV/AIDS. Public health efforts to prevent Microsporidia infections should focus on promoting good hygiene practices, safe food and water handling, and awareness of the risks associated with these infections.
Global Health Initiatives
Global health initiatives are essential for preventing and controlling Microsporidia infections. Some strategies for global health initiatives include: * Developing and implementing effective prevention and control programs * Providing access to safe and effective water treatment methods * Promoting good hygiene practices and safe food handling * Supporting research and development of new diagnostic and treatment toolsFuture Directions

Future directions for preventing and controlling Microsporidia infections should focus on developing and implementing effective prevention and control programs, providing access to safe and effective water treatment methods, and promoting good hygiene practices and safe food handling. Additionally, supporting research and development of new diagnostic and treatment tools is essential for improving our understanding and management of these infections.
Research and Development
Research and development are critical components of improving our understanding and management of Microsporidia infections. Some areas of research and development include: * Developing new diagnostic tools, such as rapid tests and molecular assays * Investigating new treatment options, such as antiparasitic medications and immunotherapy * Understanding the epidemiology and transmission of Microsporidia infections * Developing effective prevention and control programsMicrosporidia Infections Image Gallery
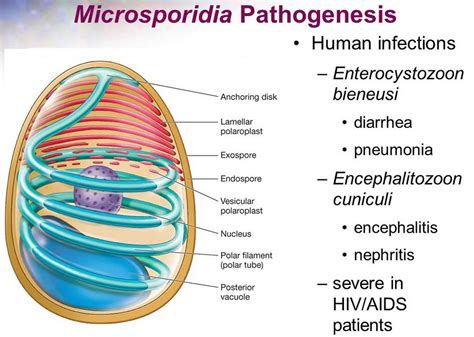
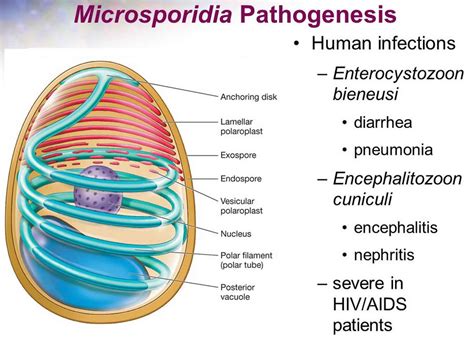
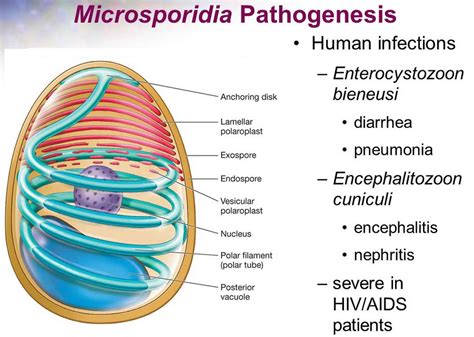
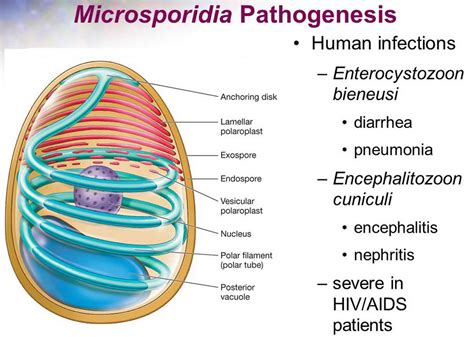
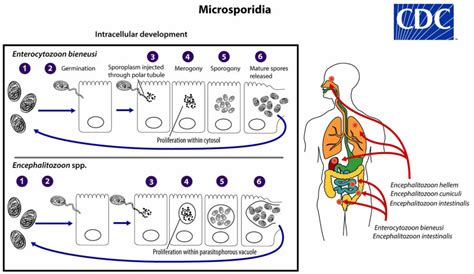

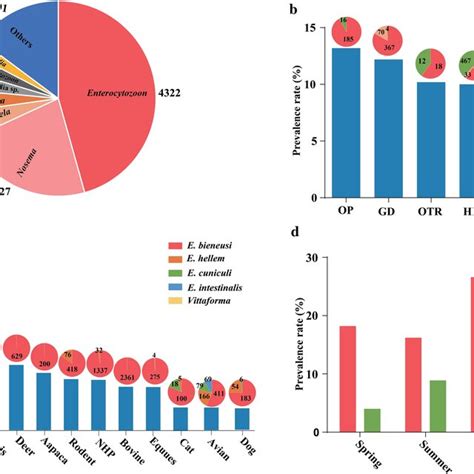
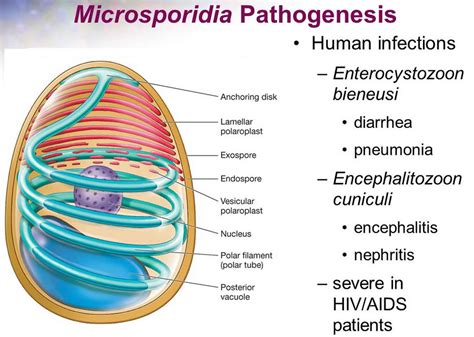
In conclusion, preventing Microsporidia infections requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates good hygiene practices, safe food and water handling, and awareness of the risks associated with these infections. By taking proactive steps to prevent Microsporidia infections, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these illnesses and maintain their overall health and well-being. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences on preventing Microsporidia infections and to take action in promoting public health awareness and initiatives. Please comment below and share this article with others to help prevent the spread of Microsporidia infections.
