Intro
Explore the diverse world of agriculture beyond farming. Discover 7 unexpected careers in agriculture, from agritourism to agricultural engineering, and learn about the innovative roles that are shaping the future of food production and sustainability. Find out which career paths in agriculture can lead to a fulfilling and lucrative profession.
Agriculture is often perceived as a traditional and narrow field, with careers limited to farming, ranching, or working in a related industry. However, the truth is that agriculture is a diverse and dynamic field, encompassing a wide range of careers that require various skills and expertise. From technology and innovation to environmental sustainability and international trade, the agriculture industry offers numerous career opportunities that may surprise you.
In this article, we will explore seven careers in agriculture that you may not have known existed. These careers highlight the diversity and complexity of the agriculture industry, and demonstrate the many ways in which professionals can contribute to the production, processing, and distribution of food and other agricultural products.

Agricultural Biotechnologist
Agricultural biotechnologists use biotechnology to develop new products, technologies, and processes that improve crop yields, disease resistance, and nutritional content. They work with farmers, researchers, and industry professionals to develop and implement biotechnology solutions that benefit the agriculture industry. Agricultural biotechnologists may work in laboratories, greenhouses, or in the field, and may specialize in areas such as genetic engineering, gene editing, or plant breeding.
Education and Skills Required
Agricultural biotechnologists typically require a bachelor's degree in agricultural biotechnology, biology, chemistry, or a related field. They may also require a master's or doctoral degree for advanced positions or to work in research and development. Key skills for agricultural biotechnologists include knowledge of biotechnology techniques, genetics, and plant biology, as well as analytical and problem-solving skills.

Drone Pilot for Agriculture
Drone pilots for agriculture use unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to collect data and images of crops, livestock, and farmland. They may work with farmers, researchers, or agricultural companies to monitor crop health, detect pests and diseases, and optimize irrigation and fertilizer application. Drone pilots for agriculture may also use specialized software to analyze data and create maps and reports.
Education and Skills Required
Drone pilots for agriculture typically require a bachelor's degree in a related field such as agriculture, engineering, or computer science. They may also require a certification or license to operate a UAV. Key skills for drone pilots for agriculture include knowledge of UAV operation and safety, data analysis and interpretation, and communication and problem-solving skills.

Sustainability Specialist
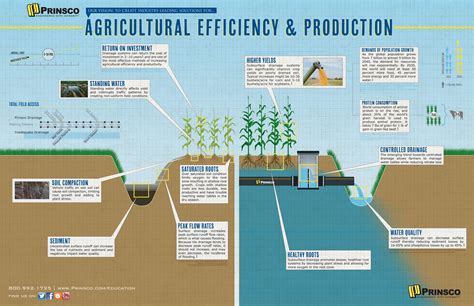
Sustainability specialists work with farmers, agricultural companies, and government agencies to develop and implement sustainable agricultural practices. They may focus on areas such as soil conservation, water management, and biodiversity, and may develop and implement programs to reduce the environmental impact of agricultural production.
Education and Skills Required
Sustainability specialists typically require a bachelor's degree in a related field such as environmental science, ecology, or agriculture. They may also require a master's or doctoral degree for advanced positions or to work in research and development. Key skills for sustainability specialists include knowledge of sustainable agricultural practices, environmental policy and regulations, and communication and project management skills.

Agricultural Economist
Agricultural economists analyze data and trends in agricultural markets, industries, and policies. They may work with government agencies, agricultural companies, or non-profit organizations to develop and implement policies and programs that benefit the agriculture industry. Agricultural economists may focus on areas such as market analysis, trade policy, and risk management.
Education and Skills Required
Agricultural economists typically require a bachelor's degree in agricultural economics or a related field. They may also require a master's or doctoral degree for advanced positions or to work in research and development. Key skills for agricultural economists include knowledge of economic theory and analysis, statistical software, and communication and problem-solving skills.

Soil Scientist
Soil scientists study the properties and behavior of soils, and develop and implement strategies to improve soil health and fertility. They may work with farmers, researchers, or agricultural companies to develop and implement soil conservation and management practices, and may focus on areas such as soil chemistry, physics, and biology.
Education and Skills Required
Soil scientists typically require a bachelor's degree in soil science or a related field. They may also require a master's or doctoral degree for advanced positions or to work in research and development. Key skills for soil scientists include knowledge of soil science and chemistry, analytical and problem-solving skills, and communication and project management skills.

Agricultural Engineer
Agricultural engineers design and develop equipment, systems, and processes to improve agricultural production and efficiency. They may work with farmers, researchers, or agricultural companies to develop and implement solutions to agricultural challenges, and may focus on areas such as irrigation systems, precision agriculture, and bioenergy.
Education and Skills Required
Agricultural engineers typically require a bachelor's degree in agricultural engineering or a related field. They may also require a master's or doctoral degree for advanced positions or to work in research and development. Key skills for agricultural engineers include knowledge of engineering principles and practices, analytical and problem-solving skills, and communication and project management skills.

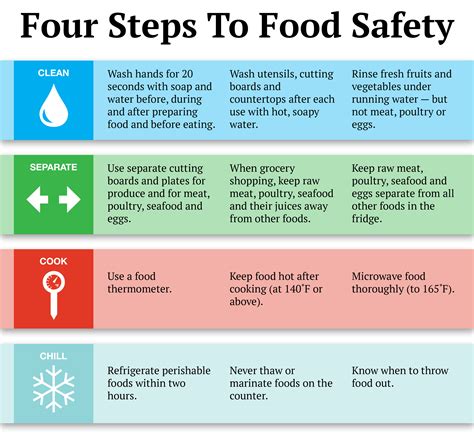
Food Safety Specialist
Food safety specialists work with farmers, agricultural companies, and government agencies to develop and implement practices and policies that ensure the safety of food products. They may focus on areas such as food handling and processing, sanitation and hygiene, and regulatory compliance.
Education and Skills Required
Food safety specialists typically require a bachelor's degree in food science or a related field. They may also require a certification or license to work in food safety. Key skills for food safety specialists include knowledge of food safety principles and practices, analytical and problem-solving skills, and communication and project management skills.

Agriculture Careers Image Gallery








In conclusion, the agriculture industry offers a wide range of career opportunities that go beyond traditional farming and ranching. From biotechnology and engineering to sustainability and food safety, professionals can contribute to the production, processing, and distribution of food and other agricultural products in many different ways. Whether you are interested in science, technology, or policy, there is a career in agriculture that may be right for you.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the agriculture industry. What careers in agriculture do you find most interesting or rewarding? How can professionals contribute to the sustainability and efficiency of agricultural production? Share your comments and insights below, and let's continue the conversation about the many careers available in agriculture.
