Discover the 7 cellular organelles, including mitochondria, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum, and learn about their functions, structures, and importance in cellular biology and organism development.
The human body is made up of approximately 37.2 trillion cells, each of which is a complex and highly organized structure. Within these cells, there are various organelles that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis and ensure the proper functioning of the cell. Understanding the different types of cellular organelles and their functions is crucial for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern life. In this article, we will delve into the world of cellular organelles, exploring their importance, structure, and functions.
The study of cellular organelles is a fascinating field that has led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of cellular biology. By examining the different types of organelles and their interactions, scientists have gained valuable insights into the mechanisms that govern cellular behavior. From the mitochondria, which generate energy for the cell, to the lysosomes, which break down and recycle cellular waste, each organelle plays a vital role in maintaining cellular health. As we explore the world of cellular organelles, we will discover the intricate relationships between these structures and how they work together to sustain life.
The importance of cellular organelles cannot be overstated. Without these structures, cells would be unable to function properly, leading to a range of cellular and organismal disorders. By studying the different types of organelles and their functions, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that govern cellular behavior and develop new treatments for a range of diseases. In this article, we will explore the seven cellular organelles, including the mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and cytoskeleton, and examine their structure, function, and importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Introduction to Cellular Organelles
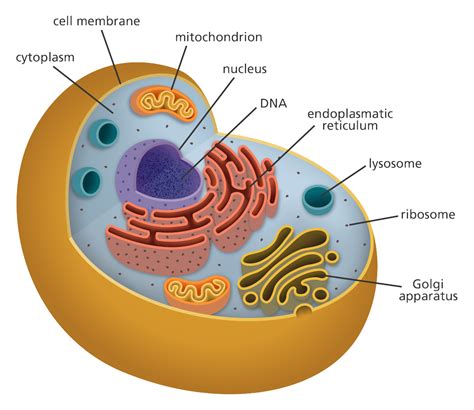
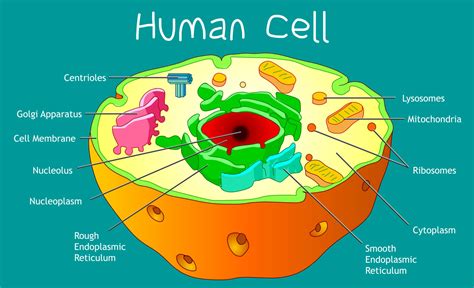
Cellular organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions necessary for cellular survival. These organelles are typically membrane-bound and are found in eukaryotic cells, which include plants, animals, and fungi. Each organelle has a unique structure and function, and they work together to maintain cellular homeostasis. The seven cellular organelles are: mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and cytoskeleton.
Structure and Function of Cellular Organelles
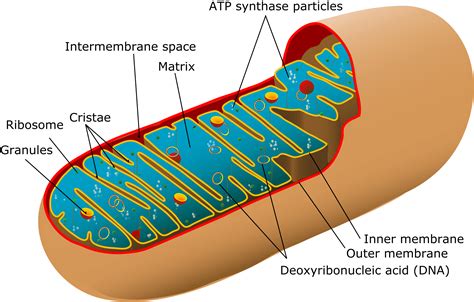
The structure and function of cellular organelles are closely related. Each organelle has a unique shape and organization that allows it to perform its specific function. For example, the mitochondria have a folded inner membrane that increases their surface area, allowing them to generate more energy for the cell. The nucleus, on the other hand, has a double membrane that protects the genetic material and regulates the flow of genetic information.Mitochondria: The Powerhouses of the Cell
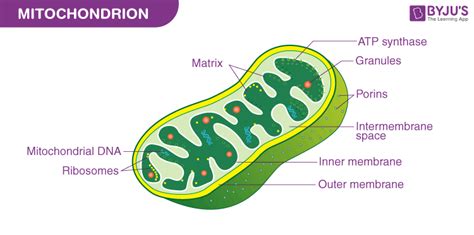
The mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell because they generate most of the energy that the cell needs to function. They are found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and are responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy currency of the cell. The mitochondria have a unique structure, with a folded inner membrane that increases their surface area and allows them to generate more energy.
Function of Mitochondria
The mitochondria perform several important functions, including: * Generating energy for the cell through cellular respiration * Regulating the concentration of calcium ions in the cell * Participating in the regulation of cellular metabolism * Initiating apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in response to cellular stressNucleus: The Control Center of the Cell
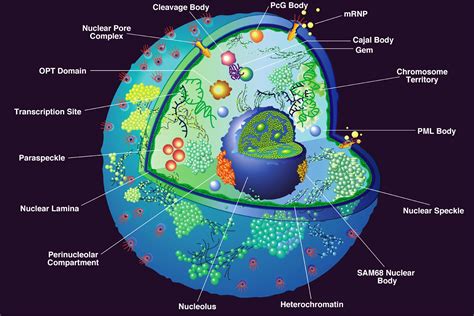
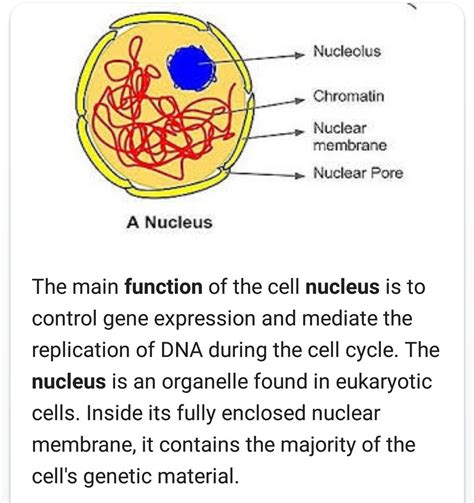
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains most of the cell's genetic material. It is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and is responsible for regulating the flow of genetic information. The nucleus has a double membrane that protects the genetic material and regulates the flow of molecules in and out of the nucleus.
Function of Nucleus
The nucleus performs several important functions, including: * Storing and transmitting genetic information * Regulating the expression of genes * Controlling the cell cycle and cell division * Responding to cellular stress and initiating apoptosisEndoplasmic Reticulum: The Cellular Transport System
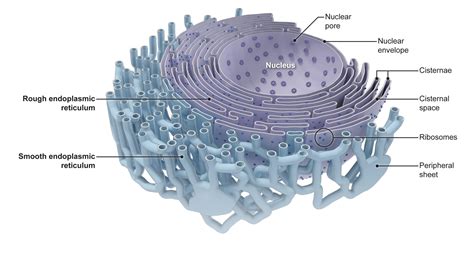
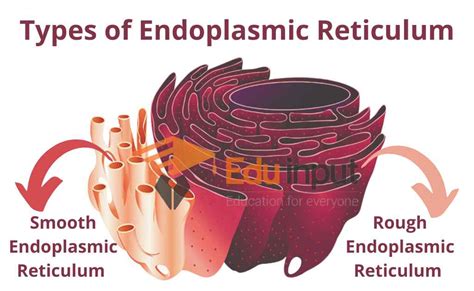
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and flattened sacs that is found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is responsible for transporting molecules throughout the cell and is involved in several important cellular processes, including protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
Function of Endoplasmic Reticulum
The ER performs several important functions, including: * Transporting molecules throughout the cell * Synthesizing proteins and lipids * Regulating the concentration of calcium ions in the cell * Participating in the regulation of cellular metabolismRibosomes: The Protein Synthesis Machines
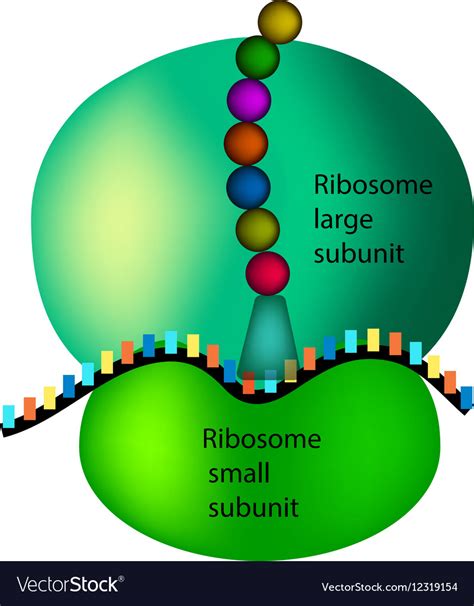
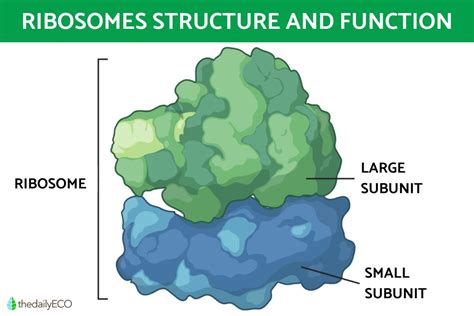
Ribosomes are small organelles that are found throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. They are responsible for synthesizing proteins, which are the building blocks of all living organisms. Ribosomes read the sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA) and assemble amino acids into proteins.
Function of Ribosomes
The ribosomes perform several important functions, including: * Synthesizing proteins * Regulating the expression of genes * Participating in the regulation of cellular metabolism * Responding to cellular stress and initiating apoptosisLysosomes: The Cellular Recycling Centers
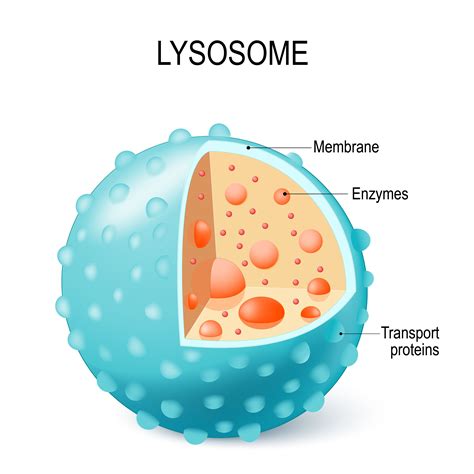
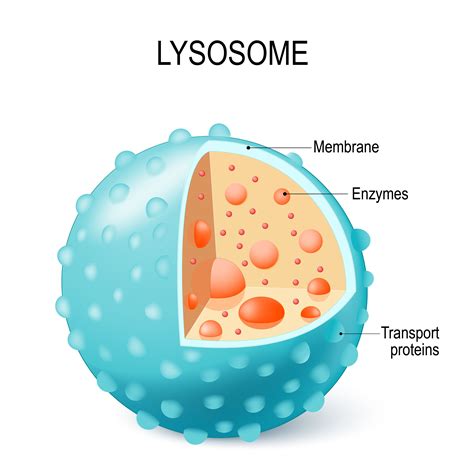
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that are found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. They are responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances that enter the cell. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates into their constituent parts.
Function of Lysosomes
The lysosomes perform several important functions, including: * Breaking down and recycling cellular waste * Regulating the concentration of ions and molecules in the cell * Participating in the regulation of cellular metabolism * Responding to cellular stress and initiating apoptosisGolgi Apparatus: The Cellular Processing Center
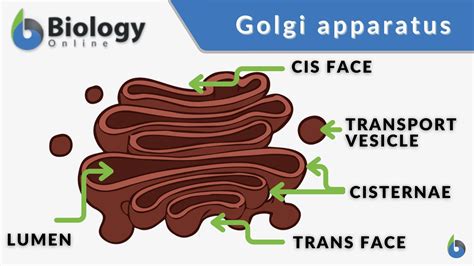
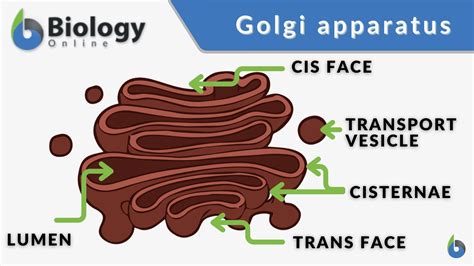
The Golgi apparatus is a complex organelle that is found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is responsible for processing and modifying proteins and lipids that are synthesized by the ER. The Golgi apparatus consists of a series of flattened sacs and tubules that are stacked on top of each other.
Function of Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus performs several important functions, including: * Processing and modifying proteins and lipids * Regulating the expression of genes * Participating in the regulation of cellular metabolism * Responding to cellular stress and initiating apoptosisCytoskeleton: The Cellular Support System
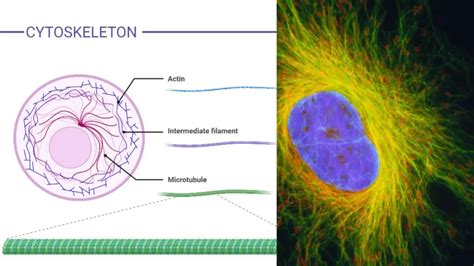
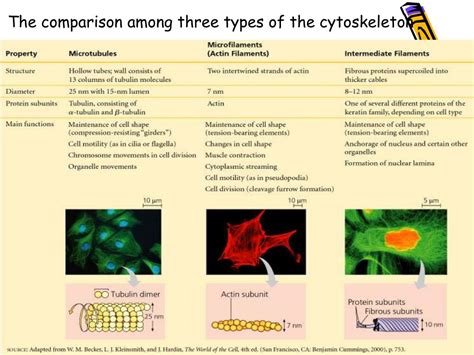
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that is found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It provides structural support and shape to the cell and is involved in several important cellular processes, including cell division and movement.
Function of Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton performs several important functions, including: * Providing structural support and shape to the cell * Regulating the movement of molecules and organelles within the cell * Participating in the regulation of cellular metabolism * Responding to cellular stress and initiating apoptosisCellular Organelles Image Gallery
In conclusion, the seven cellular organelles are essential components of eukaryotic cells, each with unique structures and functions that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis. Understanding the importance of these organelles and their interactions is crucial for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern life. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the cellular organelles and their functions, and has inspired you to learn more about the fascinating world of cellular biology. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to share them with us. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about cellular organelles and their importance in maintaining cellular health.
